A Theoretical Model of the Water Vapor Diffusion through the
... coordinate r. Then, both are equal to each other only if both are equal at the constant value that is called on ...
... coordinate r. Then, both are equal to each other only if both are equal at the constant value that is called on ...
N241774
... elastomers, and coatings. They are also used as adhesives, moulding compounds and fibres. These products are often traded as one part of a multi-component system or set.” This group also includes mixtures of polyurethane and unreacted polyfunctional diisocyanate (e.g., toluene diisocyanate). Your pr ...
... elastomers, and coatings. They are also used as adhesives, moulding compounds and fibres. These products are often traded as one part of a multi-component system or set.” This group also includes mixtures of polyurethane and unreacted polyfunctional diisocyanate (e.g., toluene diisocyanate). Your pr ...
Export To Word
... This is a fun way to introduce Boyle's Law to students. PredictObserve-Explain models are used to encourage students to think about what will happen to the volume of four different objects (balloon, marshmallow, cotton ball, and penny) when they are placed into a bell jar and the air is removed. The ...
... This is a fun way to introduce Boyle's Law to students. PredictObserve-Explain models are used to encourage students to think about what will happen to the volume of four different objects (balloon, marshmallow, cotton ball, and penny) when they are placed into a bell jar and the air is removed. The ...
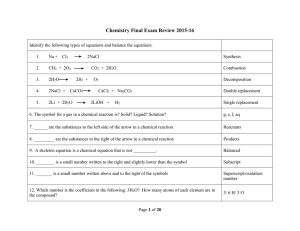
Type Of Chemical Reaction
... 61. A given mass of oxygen occupies 280 ml when the pressure is 400 Pa. If the temperature is kept constant, the volume that the gas will occupy when the pressure changes to 350 Pa is? Page 5 of 20 ...
... 61. A given mass of oxygen occupies 280 ml when the pressure is 400 Pa. If the temperature is kept constant, the volume that the gas will occupy when the pressure changes to 350 Pa is? Page 5 of 20 ...
Chapter 1 Introduction and Definition of Terms
... A mathematical relationship between the state functions. Example: Consider the volume V of a fixed quantity of a pure gas as a property, the value of which is dependent on the values of P and T. The relationship between the dependent variable V and the independent variables P and T can be expressed ...
... A mathematical relationship between the state functions. Example: Consider the volume V of a fixed quantity of a pure gas as a property, the value of which is dependent on the values of P and T. The relationship between the dependent variable V and the independent variables P and T can be expressed ...
2 - PSU MNE
... thermodynamics. We know, for example, that without any external intervention, heat will never flow from a cold body to a hot one,and steam will not spontaneously decompose into H2 and O2. The opposite of these processes, which we know to be correct, cause the entropy of the universe to increase, whi ...
... thermodynamics. We know, for example, that without any external intervention, heat will never flow from a cold body to a hot one,and steam will not spontaneously decompose into H2 and O2. The opposite of these processes, which we know to be correct, cause the entropy of the universe to increase, whi ...
QUATERLY 3 REVIEW CHAPTER 12- Stoichiometry Define the law
... 1. Define the law of conservation of mass 2. Calculate the mass of a product when given the mass / moles of reactant(s) 3. Define Limiting and excess reagent 4. Determine the limiting and excess reagents from given data 5. Define Percent Yield and calculate it from given data 6. a. What mass of iron ...
... 1. Define the law of conservation of mass 2. Calculate the mass of a product when given the mass / moles of reactant(s) 3. Define Limiting and excess reagent 4. Determine the limiting and excess reagents from given data 5. Define Percent Yield and calculate it from given data 6. a. What mass of iron ...
Mixture Solution Notes
... distributed but not chemically bonded. • Normally opaque (not see thru) • Substance that consists of particles dispersed in another substance that are too small to see. • Milk, fog, mud ...
... distributed but not chemically bonded. • Normally opaque (not see thru) • Substance that consists of particles dispersed in another substance that are too small to see. • Milk, fog, mud ...
Lectures 1-6 - TCD Chemistry
... Understand thermodynamics cycles to explain qualitatively ΔH and ΔS of solution for ideal non-ionic and ionic solids. ΔH of hydration of ions. Effect of temperature on solubility and its relationship to ΔH of solution (ΔHsoln ) ...
... Understand thermodynamics cycles to explain qualitatively ΔH and ΔS of solution for ideal non-ionic and ionic solids. ΔH of hydration of ions. Effect of temperature on solubility and its relationship to ΔH of solution (ΔHsoln ) ...
Real Gases
... As mentioned, this process can be inverted and we can solve for B'(T), C'(T), etc. in terms of B(T), C(T), etc. This gives: B'(T) = C'(T) = etc. Finally, real gases also differ from an Ideal gas in that if cooled or compressed, they will typically condense into a liquid. This behavior can be illustr ...
... As mentioned, this process can be inverted and we can solve for B'(T), C'(T), etc. in terms of B(T), C(T), etc. This gives: B'(T) = C'(T) = etc. Finally, real gases also differ from an Ideal gas in that if cooled or compressed, they will typically condense into a liquid. This behavior can be illustr ...
CHAPTER 4: PHASE TRANSITIONS
... example, solid ice, liquid water, and gaseous water vapor are separate phases of the same chemical species ( H 2O ) . Each phase can be distinguished with the density ρ of the constituent. For example, a portion of the Arctic Ocean in vicinity of the North Pole is frozen and consists of ice in a top ...
... example, solid ice, liquid water, and gaseous water vapor are separate phases of the same chemical species ( H 2O ) . Each phase can be distinguished with the density ρ of the constituent. For example, a portion of the Arctic Ocean in vicinity of the North Pole is frozen and consists of ice in a top ...
Chemistry 2008 Multiple Choice
... In another experiment involving the same reaction, a rigid 2.00 L container initially contains 10.0 g of C(s), plus CO(g) and CO2(g), each at a partial pressure of 2.00 atm at 1,160 K. e. Predict whether the partial pressure of CO2(g) will increase, decrease, or remain the same as this system approa ...
... In another experiment involving the same reaction, a rigid 2.00 L container initially contains 10.0 g of C(s), plus CO(g) and CO2(g), each at a partial pressure of 2.00 atm at 1,160 K. e. Predict whether the partial pressure of CO2(g) will increase, decrease, or remain the same as this system approa ...