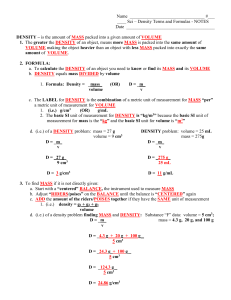
Chapter 1: Introduction
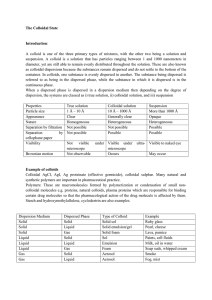
... Closely spaced molecules with large intermolecular forces Retain volume and take shape of container container liquid ...
... Closely spaced molecules with large intermolecular forces Retain volume and take shape of container container liquid ...
Van der Waals equation
The van der Waals equation is a thermodynamic equation describing gases and liquids (fluids) under a given set of pressure (P), volume (V), and temperature (T) conditions (i.e., it is a thermodynamic equation of state). In particular, it theorizes that fluids are composed of particles with non-zero volumes, and subject to a pairwise inter-particle attractive force. It was derived in 1873 by Johannes Diderik van der Waals, who received the Nobel Prize in 1910 for ""his work on the equation of state for gases and liquids,"" who did related work on the attractive force that bears his name. It is available via its traditional derivation (a mechanical equation of state), or via a derivation based in statistical thermodynamics, the latter of which provides the partition function of the system and allows thermodynamic functions to be specified. The resulting equation is a modification to and improvement of the ideal gas law, taking into account the nonzero size of atoms and molecules and the attraction between them. It successfully approximates the behavior of real fluids above their critical temperatures and is qualitatively reasonable for their liquid and low-pressure gaseous states at low temperatures. However, near the transitions between gas and liquid, in the range of P, V, and T where the liquid phase and the gas phase are in equilibrium, the van der Waals equation fails to accurately model observed experimental behaviour, in particular that P is a constant function of V at given temperatures. As such, the van der Waals model is useful only for teaching and qualitative purposes, but is not used for calculations intended to predict real behaviour. Empirical corrections to address these predictive deficiencies have been inserted into the van der Waals model, e.g., by James Clerk Maxwell in his equal area rule, and related but distinct theoretical models, e.g., based on the principle of corresponding states, have been developed to achieve better fits to real fluid behaviour in equations of comparable complexity.