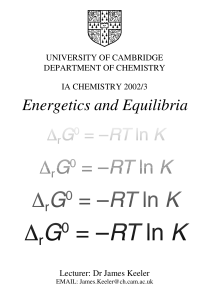Energetics and Equilibria
... Condition for chemical equilibrium..................................................................................7 Relation between K and ∆ rG 0..............................................................................................7 What is ∆r G0?........................................... ...
... Condition for chemical equilibrium..................................................................................7 Relation between K and ∆ rG 0..............................................................................................7 What is ∆r G0?........................................... ...
WRL0638.tmp - Symposium on Chemical Physics
... This postulate has its most profound basis in the microscopic laws of physics. One can use either classical or quantum mechanics. In either case the system as a whole evolves in time and it satisfies the law of conservation of energy. This is true only for conservative systems, but this suffices as ...
... This postulate has its most profound basis in the microscopic laws of physics. One can use either classical or quantum mechanics. In either case the system as a whole evolves in time and it satisfies the law of conservation of energy. This is true only for conservative systems, but this suffices as ...
Inexistence of equilibrium states at absolute negative temperatures
... extensive variables of the n system. Let also Sn (En , Nn , Xn ) be the entropy of the state of n, as given formally by equation (4). Analogously for p, we identify Sp (Ep , Np , Xp ). Consider the situation that the systems are in thermal contact but isolated from any other body. In this case, the ...
... extensive variables of the n system. Let also Sn (En , Nn , Xn ) be the entropy of the state of n, as given formally by equation (4). Analogously for p, we identify Sp (Ep , Np , Xp ). Consider the situation that the systems are in thermal contact but isolated from any other body. In this case, the ...
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
... Consider an ideal gas undergoing several processes such that the change in temperature is DT 5 Tf 2 Ti for all processes. The temperature change can be achieved by taking a variety of paths from one isotherm to another as shown in Figure 21.3. Because DT is the same for each path, the change in inte ...
... Consider an ideal gas undergoing several processes such that the change in temperature is DT 5 Tf 2 Ti for all processes. The temperature change can be achieved by taking a variety of paths from one isotherm to another as shown in Figure 21.3. Because DT is the same for each path, the change in inte ...