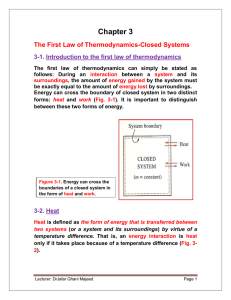
First Law of Thermodynamics
... We will be discussing three states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas). The molecules of a solid are fixed in a rigid structure. The molecules of a liquid are loosely bound and may mix with one another freely. (While a liquid has a definite volume, it still takes the shape of its container. The molec ...
... We will be discussing three states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas). The molecules of a solid are fixed in a rigid structure. The molecules of a liquid are loosely bound and may mix with one another freely. (While a liquid has a definite volume, it still takes the shape of its container. The molec ...
GAS PROCESSES - Elements of Heat Engines
... 200 kPa and at a temperature of15 ’C. If 0 9 kg of additional air is pumped intothe receiver at constant temperature, what will be the pressure in the receiver ? Assume that specific volume of air at N.T.P. (O 'C and 101-325 kPa) is 0-7734 m3 per kg. Applying characteristic equation at N.T.P., p 0v0 ...
... 200 kPa and at a temperature of15 ’C. If 0 9 kg of additional air is pumped intothe receiver at constant temperature, what will be the pressure in the receiver ? Assume that specific volume of air at N.T.P. (O 'C and 101-325 kPa) is 0-7734 m3 per kg. Applying characteristic equation at N.T.P., p 0v0 ...
Sub Module 2.12 Measurement of vacuum
... manometers, Bourdon gages for the measurement of vacuum as long as it is not high vacuum. In the case of the U tube with mercury as the manometer liquid we can practically go all the way down to -760 mm mercury but there is no way of using it to measure vacuum pressures involving less than a fractio ...
... manometers, Bourdon gages for the measurement of vacuum as long as it is not high vacuum. In the case of the U tube with mercury as the manometer liquid we can practically go all the way down to -760 mm mercury but there is no way of using it to measure vacuum pressures involving less than a fractio ...
Engineering Thermodynamics
... pV 2 = constant. Sketch the process on a p–V diagram and determine the work, in kJ. 4. A gas undergoes two processes in series: Process 1–2: constant volume from p1 = 50 lbf/in2 to p2 =10lbf/in2 Process 2–3: compression with pV1..3 = constant from state 2 to p3 = 50 lbf/in2 and V3 = 1 ft3 Sketch the ...
... pV 2 = constant. Sketch the process on a p–V diagram and determine the work, in kJ. 4. A gas undergoes two processes in series: Process 1–2: constant volume from p1 = 50 lbf/in2 to p2 =10lbf/in2 Process 2–3: compression with pV1..3 = constant from state 2 to p3 = 50 lbf/in2 and V3 = 1 ft3 Sketch the ...