Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
... derivatives. The relationship of these compounds to biochemical is also discussed. Students registering for this course must also register for CHEM 2310L which is the laboratory component of the course. ...
... derivatives. The relationship of these compounds to biochemical is also discussed. Students registering for this course must also register for CHEM 2310L which is the laboratory component of the course. ...
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
... derivatives. The relationship of these compounds to biochemical is also discussed. Students registering for this course must also register for CHEM 2310L which is the laboratory component of the course. ...
... derivatives. The relationship of these compounds to biochemical is also discussed. Students registering for this course must also register for CHEM 2310L which is the laboratory component of the course. ...
CHEM 263 (AS 40) Organic Chemistry II Winter 2017 Instructor: Dr
... laboratory grade. In all other cases, a mark of zero will be assigned. To obtain a minimum grade of C- in CHEM 263, a score of 50% or higher must be obtained for the laboratory component and, at least 70% of the experiments, must be completed. Upon completion of this course the student will be able ...
... laboratory grade. In all other cases, a mark of zero will be assigned. To obtain a minimum grade of C- in CHEM 263, a score of 50% or higher must be obtained for the laboratory component and, at least 70% of the experiments, must be completed. Upon completion of this course the student will be able ...
CHEM 212B, Organic Chemistry - City College of San Francisco
... 1. Graded laboratory reports which include data, observations, calculations and interpretation of lab results. 2. Graded computer assignments for molecular modeling and NMR problems which include answering questions and interpretation of the results. 3. Written quizzes covering concepts from lab and ...
... 1. Graded laboratory reports which include data, observations, calculations and interpretation of lab results. 2. Graded computer assignments for molecular modeling and NMR problems which include answering questions and interpretation of the results. 3. Written quizzes covering concepts from lab and ...
Organic Chemistry 2014 finalzzz
... Find the parent chain. Use the appropriate root and suffix. Number the carbon atoms, starting from the end closest to the branch(es) so that the numbers are the lowest possible Identify any branches and their location number on the parent chain (use the suffix –yl for branches) Write the complete IU ...
... Find the parent chain. Use the appropriate root and suffix. Number the carbon atoms, starting from the end closest to the branch(es) so that the numbers are the lowest possible Identify any branches and their location number on the parent chain (use the suffix –yl for branches) Write the complete IU ...
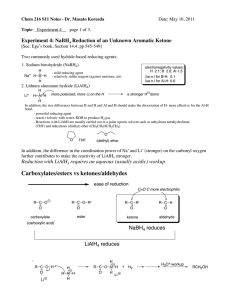
Carboxylates/esters vs ketones/aldehydes
... BH3 becomes B(OC2H5)3 by reacting with ethanol, then, when heated with water, becomes B(OH)3. The mechanism of the NaBH4 reduction in a protic solvent such as ethanol, methanol, and water is known to be quite complex since NaBH4 reacts with the solvent, e.g., NaBH4 + C2H5OH → NaBH3(OC2H5) + H2 Becau ...
... BH3 becomes B(OC2H5)3 by reacting with ethanol, then, when heated with water, becomes B(OH)3. The mechanism of the NaBH4 reduction in a protic solvent such as ethanol, methanol, and water is known to be quite complex since NaBH4 reacts with the solvent, e.g., NaBH4 + C2H5OH → NaBH3(OC2H5) + H2 Becau ...
Physical Organic Chemistry
... halides are less reactive in Nucleophilic substitution reaction due to: high electron density in benzene ring. bond in C-X stronger and shorter Aryl cation unstable therefore no SN1 There is no transition state with same plane of the ring C-Br hence no SN2 ...
... halides are less reactive in Nucleophilic substitution reaction due to: high electron density in benzene ring. bond in C-X stronger and shorter Aryl cation unstable therefore no SN1 There is no transition state with same plane of the ring C-Br hence no SN2 ...
CH 2
... Tetrahedral Nature of Carbon • When carbon forms four bonds to other atoms, the bonds are situated 109.5o apart from each other. • This arrangement is a tetrahedral arrangement. ...
... Tetrahedral Nature of Carbon • When carbon forms four bonds to other atoms, the bonds are situated 109.5o apart from each other. • This arrangement is a tetrahedral arrangement. ...
organic compounds in three dimensions
... Cis- and Trans- Isomers: An important difference between alkanes and alkenes is the degree of flexibility of the carbon-carbon bonds in the molecules. Rotation around single carbon-carbon bonds in alkanes occurs readily at room temperature, but the carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes is strong enou ...
... Cis- and Trans- Isomers: An important difference between alkanes and alkenes is the degree of flexibility of the carbon-carbon bonds in the molecules. Rotation around single carbon-carbon bonds in alkanes occurs readily at room temperature, but the carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes is strong enou ...