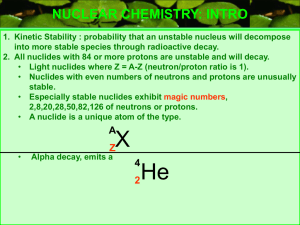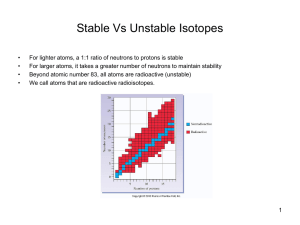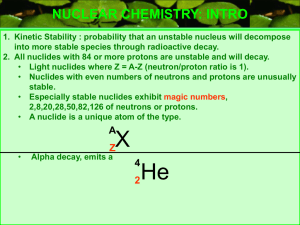
Stable Vs Unstable Isotopes
... For lighter atoms, a 1:1 ratio of neutrons to protons is stable For larger atoms, it takes a greater number of neutrons to maintain stability Beyond atomic number 83, all atoms are radioactive (unstable) We call atoms that are radioactive radioisotopes. ...
... For lighter atoms, a 1:1 ratio of neutrons to protons is stable For larger atoms, it takes a greater number of neutrons to maintain stability Beyond atomic number 83, all atoms are radioactive (unstable) We call atoms that are radioactive radioisotopes. ...
Beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which a proton is transformed into a neutron, or vice versa, inside an atomic nucleus. This process allows the atom to move closer to the optimal ratio of protons and neutrons. As a result of this transformation, the nucleus emits a detectable beta particle, which is an electron or positron.Beta decay is mediated by the weak force. There are two types of beta decay, known as beta minus and beta plus. In beta minus (β−) decay a neutron is lost and a proton appears and the process produces an electron and electron antineutrino, while in beta plus (β+) decay a proton is lost and a neutron appears and the process produces a positron and electron neutrino; β+ decay is thus also known as positron emission.An example of electron emission (β− decay) is the decay of carbon-14 into nitrogen-14:146C → 147N + e− + νeIn this form of decay, the original element becomes a new chemical element in a process known as nuclear transmutation. This new element has an unchanged mass number A, but an atomic number Z that is increased by one. As in all nuclear decays, the decaying element (in this case 146C) is known as the parent nuclide while the resulting element (in this case 147N) is known as the daughter nuclide. The emitted electron or positron is known as a beta particle.An example of positron emission (β+ decay) is the decay of magnesium-23 into sodium-23:2312Mg → 2311Na + e+ + νeIn contrast to β− decay, β+ decay is accompanied by the emission of an electron neutrino and a positron. β+ decay also results in nuclear transmutation, with the resulting element having an atomic number that is decreased by one.Electron capture is sometimes included as a type of beta decay, because the basic nuclear process, mediated by the weak force, is the same. In electron capture, an inner atomic electron is captured by a proton in the nucleus, transforming it into a neutron, and an electron neutrino is released. An example of electron capture is the decay of krypton-81 into bromine-81:8136Kr + e− → 8135Br + νeElectron capture is a competing (simultaneous) decay process for all nuclei that can undergo β+ decay. The converse, however, is not true: electron capture is the only type of decay that is allowed in proton-rich nuclides that do not have sufficient energy to emit a positron and neutrino.