Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
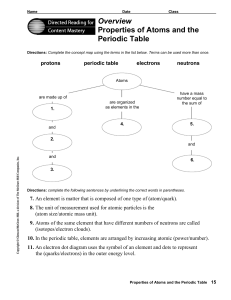
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
PPT Ch4
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
Unit #3 - Wikispaces
... 9) Rutherford's Atomic Theorya) Ernest Rutherford (1871 - 1937 = 66 yrs. old). English physicist. b) Rutherford's experiment concluded that most of the atom must consist of space without the nucleus. The nucleus must occupy a very, very, small portion of the volume of an atom. This nucleus contains ...
... 9) Rutherford's Atomic Theorya) Ernest Rutherford (1871 - 1937 = 66 yrs. old). English physicist. b) Rutherford's experiment concluded that most of the atom must consist of space without the nucleus. The nucleus must occupy a very, very, small portion of the volume of an atom. This nucleus contains ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions History
... Angstrom (A) - a convenient non-SI unit of length used to express atomic dimensions. • 1 Angstrom = 1 x 10-10 meters -10 m • most atoms have diameters between ...
... Angstrom (A) - a convenient non-SI unit of length used to express atomic dimensions. • 1 Angstrom = 1 x 10-10 meters -10 m • most atoms have diameters between ...
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
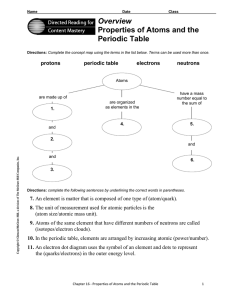
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
Inside an Atom - Mrs. Ericka Williams
... They are identified by the number or protons because this number never changes without changing the identity of the element Are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons; for example, the three isotopes of carbon differ in the number of neutrons in each nucleus such as Carbon ...
... They are identified by the number or protons because this number never changes without changing the identity of the element Are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons; for example, the three isotopes of carbon differ in the number of neutrons in each nucleus such as Carbon ...
Atoms - Sterlingwikisci
... • The orbitals are three-dimensional probability “shapes” in which electrons from that set may be found. • The number of orbitals increases as electrons are farther away from nucleus (they have more room there…) • The orbitals are assigned letters: s= “sharp”, p= “principal”, d= “diffuse”, and f= “f ...
... • The orbitals are three-dimensional probability “shapes” in which electrons from that set may be found. • The number of orbitals increases as electrons are farther away from nucleus (they have more room there…) • The orbitals are assigned letters: s= “sharp”, p= “principal”, d= “diffuse”, and f= “f ...
Chapter 3 - mrgoosby
... The inner ring, #1, can only have 2 electrons The second ring can have up to 8 electrons The third ring can have up to 18 electrons The fourth ring can have up to 32 electrons All rings up to ring #7, the last ring, can have up to 32 electrons KEY VOCAB: Energy Level – the rings containing electrons ...
... The inner ring, #1, can only have 2 electrons The second ring can have up to 8 electrons The third ring can have up to 18 electrons The fourth ring can have up to 32 electrons All rings up to ring #7, the last ring, can have up to 32 electrons KEY VOCAB: Energy Level – the rings containing electrons ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... ultimate chemical particles. – An element is composed of identical atoms with fixed, identical properties and masses. – Compounds are formed by the combination of atoms of 2 or more different elements in a fixed whole number ratio. – A chemical reaction involves a combination, separation or rearrang ...
... ultimate chemical particles. – An element is composed of identical atoms with fixed, identical properties and masses. – Compounds are formed by the combination of atoms of 2 or more different elements in a fixed whole number ratio. – A chemical reaction involves a combination, separation or rearrang ...
Goal 1 Study Guide and Practice Problems Fill in the following table
... sample after 60 hours? M = 1.125 g 19. How are radioactive decay, fission, and fusion different? ...
... sample after 60 hours? M = 1.125 g 19. How are radioactive decay, fission, and fusion different? ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
Atomic - zsnedu
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
atoms - Harjono
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
Chapter 5 Atomic Structure & the Periodic Table
... • Lithium = Greek word lithos, meaning stone • Neptunium = after the planet Neptune • Hydrogen (H), Sulfur (S), Carbon (C) • Gold (Au), Lead (Pb), Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu) = symbols come from latin names. ...
... • Lithium = Greek word lithos, meaning stone • Neptunium = after the planet Neptune • Hydrogen (H), Sulfur (S), Carbon (C) • Gold (Au), Lead (Pb), Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu) = symbols come from latin names. ...
Interesting and Helpful Websites Early Models of the Atom
... Law of conservation of matter. Law of constant composition, compounds contain the same elements in the same proportions by mass. – FORM A BASIC UNDERSTANDING… All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different elemen ...
... Law of conservation of matter. Law of constant composition, compounds contain the same elements in the same proportions by mass. – FORM A BASIC UNDERSTANDING… All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different elemen ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.