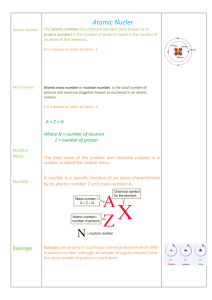
Atomic Terms/People
... Dalton later published his atomic theory. This was used to determine chemical formulas. Dalton made the first table of atomic masses o Later proven inaccurate. Dalton changed his theory based on the Atomic Number: It now states that all atoms of an element contain the same # of protons but they ca ...
... Dalton later published his atomic theory. This was used to determine chemical formulas. Dalton made the first table of atomic masses o Later proven inaccurate. Dalton changed his theory based on the Atomic Number: It now states that all atoms of an element contain the same # of protons but they ca ...
THE ATOM
... • English physicist who in 1897 discovered a particle smaller than the atom ; the electron. • Particle has a negative charge and is much smaller than the atom so must come from the inside of the atom. • Electrons are scattered around the atom like raisins in pudding. (THE PLUM PUDDING MODEL) ...
... • English physicist who in 1897 discovered a particle smaller than the atom ; the electron. • Particle has a negative charge and is much smaller than the atom so must come from the inside of the atom. • Electrons are scattered around the atom like raisins in pudding. (THE PLUM PUDDING MODEL) ...
Chapter 4
... Isotopes and Mass Number Isotopes ■ Elements that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons ■ These atoms keep the same chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons ■ We use the number of neutrons or mass number to tell isotopes apart ■ Mass number or A ...
... Isotopes and Mass Number Isotopes ■ Elements that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons ■ These atoms keep the same chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons ■ We use the number of neutrons or mass number to tell isotopes apart ■ Mass number or A ...
Chemistry--Chapter 5: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... A. Atomic Number--the atomic number is the number of protons; it distinguishes one elements’ atoms from another; small whole numbers on periodic table B. Mass Number--the total number of protons and neutrons (not found on p.t.), the “14” in carbon-14 C. Isotopes--elements of the same atom that have ...
... A. Atomic Number--the atomic number is the number of protons; it distinguishes one elements’ atoms from another; small whole numbers on periodic table B. Mass Number--the total number of protons and neutrons (not found on p.t.), the “14” in carbon-14 C. Isotopes--elements of the same atom that have ...
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, o ...
... particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, o ...
Unit 2
... - alpha particle – two protons and two neutrons bound together and emitted from a nucleus. They are often referred to as helium nuclei particles with a +2 charge. This particle has the lowest penetration of all forms of radiation. - beta particle – an electron emitted from the nucleus during some ki ...
... - alpha particle – two protons and two neutrons bound together and emitted from a nucleus. They are often referred to as helium nuclei particles with a +2 charge. This particle has the lowest penetration of all forms of radiation. - beta particle – an electron emitted from the nucleus during some ki ...
Unit 1 – Atomic Structure
... 2. Atoms are identified by their atomic number 3. Because atoms are neutral, # protons = # electrons 4. Periodic Table is in order of increasing atomic number B. Mass Number 1. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an isotope C. Isotopes 1. Atoms of the same element that have di ...
... 2. Atoms are identified by their atomic number 3. Because atoms are neutral, # protons = # electrons 4. Periodic Table is in order of increasing atomic number B. Mass Number 1. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an isotope C. Isotopes 1. Atoms of the same element that have di ...
Adobe Acrobat file ()
... The nuclear attractive force is stronger than the Coulomb repulsive force at the short ranges within the nucleus ...
... The nuclear attractive force is stronger than the Coulomb repulsive force at the short ranges within the nucleus ...
Atoms Review worksheet
... C. 158 D. 276 ______12. How many protons does an atom with an atomic number of 10 and a mass number of 20.1797 have? A. 10 B. 31 C. 11 D. 30 ______13. Isotopes exist because atoms of the same element can have different numbers of A. protons B. electrons C. neutrons D. None of the above ______14. The ...
... C. 158 D. 276 ______12. How many protons does an atom with an atomic number of 10 and a mass number of 20.1797 have? A. 10 B. 31 C. 11 D. 30 ______13. Isotopes exist because atoms of the same element can have different numbers of A. protons B. electrons C. neutrons D. None of the above ______14. The ...
Atomic Mass
... 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms are not indivisible – they are made of subatomic particles 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. Every atom has at least one isotope; one a ...
... 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms are not indivisible – they are made of subatomic particles 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. Every atom has at least one isotope; one a ...
Nucleon number
... Define relative atomic mass and relative molecular mass based on the C-12 scale. Sketch and explain the function of the following main components of a simple mass spectrum: Analyze mass spectrum of an element. Name cations, anions and salt according to the ...
... Define relative atomic mass and relative molecular mass based on the C-12 scale. Sketch and explain the function of the following main components of a simple mass spectrum: Analyze mass spectrum of an element. Name cations, anions and salt according to the ...
4-2: Structure of the Atom
... electrons in order to get a full valence shell. When an atom either gains one or more electrons or loses one or more electrons, the atom is no longer neutrally charged. When an atom or a group of atoms has either a negative or a positive charge it is called an _________. ...
... electrons in order to get a full valence shell. When an atom either gains one or more electrons or loses one or more electrons, the atom is no longer neutrally charged. When an atom or a group of atoms has either a negative or a positive charge it is called an _________. ...
atoms of different elements differ in size, mass
... Conclusions from the Study of the Electron Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the elec ...
... Conclusions from the Study of the Electron Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the elec ...
The Atom
... hydrogen-1 (hyphen notation), nuclear symbol = Deuterium’s mass number is 2 (1p + 1n), hydrogen-2, nuclear symbol = Tritium’s mass number is 3 (1p +2n), hydrogen-3 , nuclear symbol = ...
... hydrogen-1 (hyphen notation), nuclear symbol = Deuterium’s mass number is 2 (1p + 1n), hydrogen-2, nuclear symbol = Tritium’s mass number is 3 (1p +2n), hydrogen-3 , nuclear symbol = ...
File
... without changing direction very much Because… – The positive charges were spread out evenly - alone they would not be enough to stop the alpha particles ...
... without changing direction very much Because… – The positive charges were spread out evenly - alone they would not be enough to stop the alpha particles ...
Answer on Question #47967 - Chemistry – Other
... e. A model in which the protons, electrons, and neutrons are evenly distributed throughout the volume of the atom 8. The nucleus of an atom is ____________. a. Positively charged and has a high density b. Negatively charged and has a high density c. Positively charged and has a low density d. Negat ...
... e. A model in which the protons, electrons, and neutrons are evenly distributed throughout the volume of the atom 8. The nucleus of an atom is ____________. a. Positively charged and has a high density b. Negatively charged and has a high density c. Positively charged and has a low density d. Negat ...
Nuclear Decay
... decays producing a proton and electron • A beta particle in the form of an electron is released from the nucleus ...
... decays producing a proton and electron • A beta particle in the form of an electron is released from the nucleus ...
The Material World: An Introduction to Chemistry 1. Modern Model of
... The Material World: An Introduction to Chemistry 1. Modern Model of the Atom A. A Closer Look at the Nucleus Since Bohr, the model of the atom has become even more sophisticated. Scientists had to explain why even the thin lines in an emission spectrum could be resolved into more fine lines, and the ...
... The Material World: An Introduction to Chemistry 1. Modern Model of the Atom A. A Closer Look at the Nucleus Since Bohr, the model of the atom has become even more sophisticated. Scientists had to explain why even the thin lines in an emission spectrum could be resolved into more fine lines, and the ...
History of the Atomic Model
... • Atomic mass: is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. • Atomic number: Is the total number of protons ...
... • Atomic mass: is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. • Atomic number: Is the total number of protons ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.