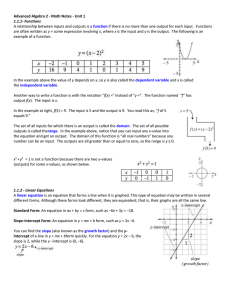
Is sqrt 2 a rational number
... We also know that only perfect square roots are rational numbers. In other words, the square root of 4, 9, 16, 25, etc are rational numbers. The square of a non-perfect square number is not a rational number. (I don’t know where I read this, but I do remember this from my math education.) This is be ...
... We also know that only perfect square roots are rational numbers. In other words, the square root of 4, 9, 16, 25, etc are rational numbers. The square of a non-perfect square number is not a rational number. (I don’t know where I read this, but I do remember this from my math education.) This is be ...
Factorization of Polynomials over Finite Fields
... a = p11 p22 · · · perr , where p1, . . . , pr are (zero or more) distinct prime elements of R. The representation is unique, except for multiplication with units and the order in which the primes occur. ...
... a = p11 p22 · · · perr , where p1, . . . , pr are (zero or more) distinct prime elements of R. The representation is unique, except for multiplication with units and the order in which the primes occur. ...
Full text
... Thus, our assumption implies that (a, b, c) satisfies Fermat's Last Theorem. Conversely, suppose that there exists a positive integer triplet (a, h, c) which satisfies (5) for some n>2, i.e., suppose Fermat's Last Theorem is false. If b - a, then c/a = 2l/n, which is patently impossible; thus, witho ...
... Thus, our assumption implies that (a, b, c) satisfies Fermat's Last Theorem. Conversely, suppose that there exists a positive integer triplet (a, h, c) which satisfies (5) for some n>2, i.e., suppose Fermat's Last Theorem is false. If b - a, then c/a = 2l/n, which is patently impossible; thus, witho ...
Chapter 1 Learning Targets
... 1. _______ use the divisibility rules to determine if a given number can be evenly divided by 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, or 10. (4-1) 2. _______ identify prime and composite numbers. (4-1) 3. _______ determine the prime factorization of a composite number. (4-2) 4. _______ list all the factors of a given num ...
... 1. _______ use the divisibility rules to determine if a given number can be evenly divided by 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, or 10. (4-1) 2. _______ identify prime and composite numbers. (4-1) 3. _______ determine the prime factorization of a composite number. (4-2) 4. _______ list all the factors of a given num ...
Factorization
In mathematics, factorization (also factorisation in some forms of British English) or factoring is the decomposition of an object (for example, a number, a polynomial, or a matrix) into a product of other objects, or factors, which when multiplied together give the original. For example, the number 15 factors into primes as 3 × 5, and the polynomial x2 − 4 factors as (x − 2)(x + 2). In all cases, a product of simpler objects is obtained.The aim of factoring is usually to reduce something to “basic building blocks”, such as numbers to prime numbers, or polynomials to irreducible polynomials. Factoring integers is covered by the fundamental theorem of arithmetic and factoring polynomials by the fundamental theorem of algebra. Viète's formulas relate the coefficients of a polynomial to its roots.The opposite of polynomial factorization is expansion, the multiplying together of polynomial factors to an “expanded” polynomial, written as just a sum of terms.Integer factorization for large integers appears to be a difficult problem. There is no known method to carry it out quickly. Its complexity is the basis of the assumed security of some public key cryptography algorithms, such as RSA.A matrix can also be factorized into a product of matrices of special types, for an application in which that form is convenient. One major example of this uses an orthogonal or unitary matrix, and a triangular matrix. There are different types: QR decomposition, LQ, QL, RQ, RZ.Another example is the factorization of a function as the composition of other functions having certain properties; for example, every function can be viewed as the composition of a surjective function with an injective function. This situation is generalized by factorization systems.