Rethinking the central bank`s mandate 4
... stability, with low and stable inflation, by adjusting interest rates. This, in combination with deregulation, financial innovation and globalisation, contributed to high and stable economic growth in several countries in the 1990s and in the early 2000s. This took place without any surge in inflati ...
... stability, with low and stable inflation, by adjusting interest rates. This, in combination with deregulation, financial innovation and globalisation, contributed to high and stable economic growth in several countries in the 1990s and in the early 2000s. This took place without any surge in inflati ...
Economics R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O'Brien, 2e.
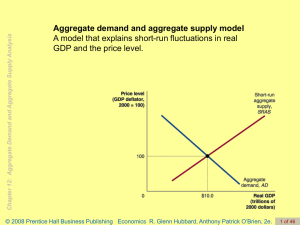
... What Shifts the Aggregate Demand Curve? Changes in Government Policies intended to achieve macroeconomic objectives: high employment, price stability, steady economic growth. •Monetary policy Actions the Federal Reserve takes to manage the money supply and interest rates. •Fiscal policy Changes in f ...
... What Shifts the Aggregate Demand Curve? Changes in Government Policies intended to achieve macroeconomic objectives: high employment, price stability, steady economic growth. •Monetary policy Actions the Federal Reserve takes to manage the money supply and interest rates. •Fiscal policy Changes in f ...
Free Full Text ( Final Version , 817kb )
... deflator, producer price indices (PPI), core price indices (CI) and retail price index (RPI). GDP deflator, calculated by (nominal GDP/real GDP)*100, targets all goods that were produced domestically, which are different from CPI “fixed” basket of goods and services. PPI refers to the ex-factory pri ...
... deflator, producer price indices (PPI), core price indices (CI) and retail price index (RPI). GDP deflator, calculated by (nominal GDP/real GDP)*100, targets all goods that were produced domestically, which are different from CPI “fixed” basket of goods and services. PPI refers to the ex-factory pri ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... of Economic Research
... the money supply to lower inflation. The key question has been whether, in the absence of an active monetary response, labor markets can adjust without costly deviations from full employment (see, for example, Gordon 1975; 1984; Phelps 1978; Blinder 1981; Rasche and Tatom 1981; and Fischer 1985). Ou ...
... the money supply to lower inflation. The key question has been whether, in the absence of an active monetary response, labor markets can adjust without costly deviations from full employment (see, for example, Gordon 1975; 1984; Phelps 1978; Blinder 1981; Rasche and Tatom 1981; and Fischer 1985). Ou ...
ESSAYS ON FINANCIAL REFORMS AND MONETARY POLICY IN MALAWI A Thesis
... appeared to be associated with depreciations of the exchange rate rather than the expected real appreciation. There is also evidence of limited impact of a positive aid shock on depreciation and inflation when RBM targets monetary aggregates compared to when the authorities use the Taylor rule and i ...
... appeared to be associated with depreciations of the exchange rate rather than the expected real appreciation. There is also evidence of limited impact of a positive aid shock on depreciation and inflation when RBM targets monetary aggregates compared to when the authorities use the Taylor rule and i ...
Low for long? Causes and consequences of persistently low interest
... While the downward trend in rates has been pretty remorseless since the late 1990s, it would be unwise simply to assume that the trend will be maintained. Indeed in many countries, nominal interest rates are already close to their lower bound – in some cases, they are already mildly negative – so fu ...
... While the downward trend in rates has been pretty remorseless since the late 1990s, it would be unwise simply to assume that the trend will be maintained. Indeed in many countries, nominal interest rates are already close to their lower bound – in some cases, they are already mildly negative – so fu ...
Chapter 7 Aggregate Demand, Aggregate Supply, and the Self
... 56) The term monetary impotence refers to the A) failure of firms to lower prices even when wages are falling. B) problems that an economy faces when industries are not perfectly competitive and prices do not fluctuate. C) failure of fiscal policy to drive down prices in a depression. D) inability ...
... 56) The term monetary impotence refers to the A) failure of firms to lower prices even when wages are falling. B) problems that an economy faces when industries are not perfectly competitive and prices do not fluctuate. C) failure of fiscal policy to drive down prices in a depression. D) inability ...
Volume 71 No. 3, September 2008 Contents Themed issue: Inflation
... inflation pressure. For some other countries, growth is set to ...
... inflation pressure. For some other countries, growth is set to ...
Mods 17-18-19 Practice
... ____ 10. Changes in aggregate demand can be caused by changes in: A. production technology. B. business costs. C. raw materials costs. D. worker productivity. E. government spending. ____ 11. A rise in labor productivity is most likely to result in: A. an increase in aggregate demand. B. a decrease ...
... ____ 10. Changes in aggregate demand can be caused by changes in: A. production technology. B. business costs. C. raw materials costs. D. worker productivity. E. government spending. ____ 11. A rise in labor productivity is most likely to result in: A. an increase in aggregate demand. B. a decrease ...
Inflation targeting, economic performance, and income distribution: a
... into an excess demand and higher prices on the market for produced goods and services. Mainstream Keynesians, on the other hand, would argue that low interest rates will lead to higher investment, increased economic activity, and higher prices owing to a Phillipscurve-like relation between prices an ...
... into an excess demand and higher prices on the market for produced goods and services. Mainstream Keynesians, on the other hand, would argue that low interest rates will lead to higher investment, increased economic activity, and higher prices owing to a Phillipscurve-like relation between prices an ...
Short description of models available in MMB 2.0
... amount of hours. Clarida et al. (2002) introduce an exogenous time-varying elasticity of labor demand to vary the wage-mark-up over time. The system of equations is collapsed into an IS equation and a Phillips curve, which determine the output gap and inflation, conditional on the path of the nomina ...
... amount of hours. Clarida et al. (2002) introduce an exogenous time-varying elasticity of labor demand to vary the wage-mark-up over time. The system of equations is collapsed into an IS equation and a Phillips curve, which determine the output gap and inflation, conditional on the path of the nomina ...
PROGRESS TOWARDS CONVERGENCE 1996
... of below 3% of GDP, the reference value provided for in the Treaty, while Luxembourg registered a surplus. For 1996, the most recent Commission data indicate that four countries might have deficit ratios of below 3% (Denmark, Ireland, Luxembourg and the Netherlands). All other Member States project ...
... of below 3% of GDP, the reference value provided for in the Treaty, while Luxembourg registered a surplus. For 1996, the most recent Commission data indicate that four countries might have deficit ratios of below 3% (Denmark, Ireland, Luxembourg and the Netherlands). All other Member States project ...
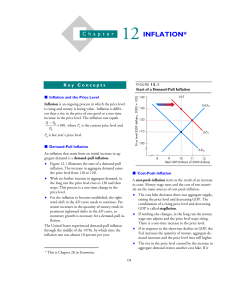
Inflation, Disinflation, and Deflation
... Modern economies use fiat money—pieces of paper that have no intrinsic value but are accepted as a medium of exchange. In the United States and most other wealthy countries, the decision about how many pieces of paper to issue is placed in the hands of a central bank that is somewhat independent of ...
... Modern economies use fiat money—pieces of paper that have no intrinsic value but are accepted as a medium of exchange. In the United States and most other wealthy countries, the decision about how many pieces of paper to issue is placed in the hands of a central bank that is somewhat independent of ...
Principles of Macroeconomics Self-study quiz and Exercises March
... 2) According to the Classical model, an excess supply of labor would drive up wages to a new equilibrium level and therefore unemployment would not persist. 3) According to Keynes, aggregate supply determines the level of economic activities in the economy. 4) According to Keynes, the governmentʹs r ...
... 2) According to the Classical model, an excess supply of labor would drive up wages to a new equilibrium level and therefore unemployment would not persist. 3) According to Keynes, aggregate supply determines the level of economic activities in the economy. 4) According to Keynes, the governmentʹs r ...