Fiscal and Monetary Policies in Transition Economies
... After creating the CB priority must be given to developing a commercial and investment banking system that can be effective in mobilizing savings and allocating investment capital among potential borrowers. – This process is unlikely to be rapid. Some banks can be created by assuming the deposit and ...
... After creating the CB priority must be given to developing a commercial and investment banking system that can be effective in mobilizing savings and allocating investment capital among potential borrowers. – This process is unlikely to be rapid. Some banks can be created by assuming the deposit and ...
8 Economic policy_20..
... ─ Speculative demand: this is demand for money as financial asset for investment opportunities. ...
... ─ Speculative demand: this is demand for money as financial asset for investment opportunities. ...
Obj. 5 Vocabulary
... 6. Interest rate - Percentage rate used to calculate interest 7. Liquidity - How quickly and easily assets can be accessed and converted into cash 8. Pay yourself first - Saving for the future by putting money aside before paying regular monthly bills or using income for discretionary purchases 9. P ...
... 6. Interest rate - Percentage rate used to calculate interest 7. Liquidity - How quickly and easily assets can be accessed and converted into cash 8. Pay yourself first - Saving for the future by putting money aside before paying regular monthly bills or using income for discretionary purchases 9. P ...
ECON 1000-100 Introduction to Economics
... Types of US money supplies and the working of commercial banks in US. The simplified model of money creation, simplified money multiplier and assumptions of the model. Topic 5: Control of Banks in US, history of Federal Reserve System, its functions and different layers of authority. Three weapons t ...
... Types of US money supplies and the working of commercial banks in US. The simplified model of money creation, simplified money multiplier and assumptions of the model. Topic 5: Control of Banks in US, history of Federal Reserve System, its functions and different layers of authority. Three weapons t ...
Keynes Theory and Sample Questions
... Unlike Fisher, Keynes believed that changing the money supply could have real affects on the economy. He thought the government could increase or decrease the money supply to change real GDP to the level they wanted. But he warned that an increase in real GDP would result in increased inflation, an ...
... Unlike Fisher, Keynes believed that changing the money supply could have real affects on the economy. He thought the government could increase or decrease the money supply to change real GDP to the level they wanted. But he warned that an increase in real GDP would result in increased inflation, an ...
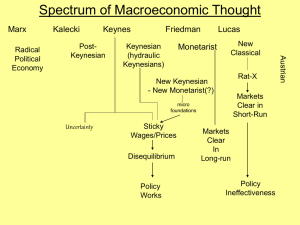
Macro Spectrum
... would enable them to compute perfectly the relative prices they care about, agents make errors…[A]gents temporarily mistake a general increase in all absolute prices as an increase in the relative price of the good they are selling, leading them to increase their supply of that good…Since everyone i ...
... would enable them to compute perfectly the relative prices they care about, agents make errors…[A]gents temporarily mistake a general increase in all absolute prices as an increase in the relative price of the good they are selling, leading them to increase their supply of that good…Since everyone i ...
Fed Focus Phoenix, Arizona April 30, 1998 Robert T. Parry, President, FRBSF
... Now, this difference between the short-run and long-run goals of monetary policy is at the heart of the difference between what the Fed can and cannot do. ...
... Now, this difference between the short-run and long-run goals of monetary policy is at the heart of the difference between what the Fed can and cannot do. ...
MONETARY AND FISCAL POLICIES
... How is the Monetary Policy different from the Fiscal Policy? • The Monetary Policy regulates the supply of money and the cost and availability of credit in the economy. It deals with both the lending and borrowing rates of interest for commercial banks. • The Monetary Policy aims to maintain price ...
... How is the Monetary Policy different from the Fiscal Policy? • The Monetary Policy regulates the supply of money and the cost and availability of credit in the economy. It deals with both the lending and borrowing rates of interest for commercial banks. • The Monetary Policy aims to maintain price ...
MONETARY AND FISCAL POLICIES
... How is the Monetary Policy different from the Fiscal Policy? • The Monetary Policy regulates the supply of money and the cost and availability of credit in the economy. It deals with both the lending and borrowing rates of interest for commercial banks. • The Monetary Policy aims to maintain price ...
... How is the Monetary Policy different from the Fiscal Policy? • The Monetary Policy regulates the supply of money and the cost and availability of credit in the economy. It deals with both the lending and borrowing rates of interest for commercial banks. • The Monetary Policy aims to maintain price ...
ECON 1000-100 Introduction to Economics
... Types of US money supplies and the working of commercial banks in US. The simplified model of money creation, simplified money multiplier and assumptions of the model. Topic 5: Control of Banks in US, history of Federal Reserve System, its functions and different layers of authority. Three weapons t ...
... Types of US money supplies and the working of commercial banks in US. The simplified model of money creation, simplified money multiplier and assumptions of the model. Topic 5: Control of Banks in US, history of Federal Reserve System, its functions and different layers of authority. Three weapons t ...
Fed Focus Pocatello, Idaho For delivery June 2, 1998 9 a.m. MDT
... BOG in Washington: 7 members with staggered 14-year terms; appointed by President with consent of Senate; Chairman preeminent. ...
... BOG in Washington: 7 members with staggered 14-year terms; appointed by President with consent of Senate; Chairman preeminent. ...
Institute of Business Management
... Q#8 Use the IS-LM model to determine the effects of each of the following on the general equilibrium values of the real wage, employment, output, real interest rate, consumption, investment, and price level. a. A reduction in the effective tax rate on capital increases desired investment. b. The ex ...
... Q#8 Use the IS-LM model to determine the effects of each of the following on the general equilibrium values of the real wage, employment, output, real interest rate, consumption, investment, and price level. a. A reduction in the effective tax rate on capital increases desired investment. b. The ex ...
Econ 2012: Macroeconomics
... 8. Using the multiplier calculate the appropriate fiscal policy to reach potential output. 9. Explain the effects of contractionary or expansionary fiscal policy on the government’s budget (i.e. creating a budget surplus or deficit). 10. Explain the difference between discretionary fiscal policy and ...
... 8. Using the multiplier calculate the appropriate fiscal policy to reach potential output. 9. Explain the effects of contractionary or expansionary fiscal policy on the government’s budget (i.e. creating a budget surplus or deficit). 10. Explain the difference between discretionary fiscal policy and ...
ECON 102 Tutorial: Week 19
... Suppose the equation of the demand for money curve is MD = 20,000 8,000i. In part (a) we found the equilibrium rate of interest is 5% if money supply is 19,600. By how much would the central bank have to change the money supply if it wished to increased the equilibrium rate of interest by 1 per ce ...
... Suppose the equation of the demand for money curve is MD = 20,000 8,000i. In part (a) we found the equilibrium rate of interest is 5% if money supply is 19,600. By how much would the central bank have to change the money supply if it wished to increased the equilibrium rate of interest by 1 per ce ...
Economics EOCT Review- Part 2 - "Education is the most powerful
... The buying and selling of government securities is which tool of monetary policy? • Open market operations ...
... The buying and selling of government securities is which tool of monetary policy? • Open market operations ...