In VINI Veritas - Georgia Institute of Technology
... – Latency and jitter comparable between network and IIAS on PL-VINI. – Say something about running on just PlanetLab? Don’t spend much time talking about CPU scheduling… ...
... – Latency and jitter comparable between network and IIAS on PL-VINI. – Say something about running on just PlanetLab? Don’t spend much time talking about CPU scheduling… ...
Link state Routing - 寬頻網路實驗室
... When topology of network changes or failure, the network knowledge base must also change. The knowledge needs to reflect an accurate, consistent view of the new topology. This view is called convergence. When all routers in an inter-network are operating with the same knowledge, the inter-networ ...
... When topology of network changes or failure, the network knowledge base must also change. The knowledge needs to reflect an accurate, consistent view of the new topology. This view is called convergence. When all routers in an inter-network are operating with the same knowledge, the inter-networ ...
Network Layer
... • RIP had widespread use because it was distributed with BSD Unix in “routed”, a router management daemon. • RFC1058 June1988. • Sends packets every 30 seconds or faster. • Runs over UDP. • Metric = hop count • BIG problem = max. hop count =16 RIP limited to running on small networks • Upgraded to ...
... • RIP had widespread use because it was distributed with BSD Unix in “routed”, a router management daemon. • RFC1058 June1988. • Sends packets every 30 seconds or faster. • Runs over UDP. • Metric = hop count • BIG problem = max. hop count =16 RIP limited to running on small networks • Upgraded to ...
Link-state routing protocol A link-state routing protocol is one of the
... The algorithm simply iterates over the collection of link-state advertisements; for each one, it makes links on the map of the network, from the node which sent that message, to all the nodes which that message indicates are neighbors of the sending node. No link is considered to have been correctl ...
... The algorithm simply iterates over the collection of link-state advertisements; for each one, it makes links on the map of the network, from the node which sent that message, to all the nodes which that message indicates are neighbors of the sending node. No link is considered to have been correctl ...
22.3 Figure 22.1 Direct and indirect delivery 22.4 22
... Make the Link State packet. Broadcast the Link State packet to all nodes. After receiving the Link State packets from all other nodes, make the link state database. Compute the shortest paths to reach all other nodes based on the link state database. ...
... Make the Link State packet. Broadcast the Link State packet to all nodes. After receiving the Link State packets from all other nodes, make the link state database. Compute the shortest paths to reach all other nodes based on the link state database. ...
Introduction
... Routing and switching use different information in the process of moving data from source to destination. Each computer and router interface maintains an ARP table for Layer 2 communication. The ARP table is only effective for the broadcast domain (or LAN) that it is connected to. The router a ...
... Routing and switching use different information in the process of moving data from source to destination. Each computer and router interface maintains an ARP table for Layer 2 communication. The ARP table is only effective for the broadcast domain (or LAN) that it is connected to. The router a ...
chapter4_4
... Given: a graph with a nonnegative weight assigned to each edge and a designated source node Compute: the shortest distance from the source node to each other node and a next-hop routing table ...
... Given: a graph with a nonnegative weight assigned to each edge and a designated source node Compute: the shortest distance from the source node to each other node and a next-hop routing table ...
MW2522122216
... Fig 4: Media access Delay in AODV& DSR for mobile nodes (20 nodes) As it is clear from the figure 3 that media access delay of AODV protocol is more than DSR in case of fixed nodes but only in the beginning, but as the time increases delay of DSR goes increases than AODV. In figure 4 media access de ...
... Fig 4: Media access Delay in AODV& DSR for mobile nodes (20 nodes) As it is clear from the figure 3 that media access delay of AODV protocol is more than DSR in case of fixed nodes but only in the beginning, but as the time increases delay of DSR goes increases than AODV. In figure 4 media access de ...
вбг ¤ вбг ¤ ¥ £ ¤ ¥ time, which represents the зй !" $# . Such one
... The problem of QoS routing for mobile Ad hoc networks is studied. Most routing protocols for the mobile Ad hoc networks (MANETs) [1], such as OLSR [2], AODV [3], DSR [4], are designed without explicitly considering QoS of the routes they generate. The number of hops is the most common criterion adop ...
... The problem of QoS routing for mobile Ad hoc networks is studied. Most routing protocols for the mobile Ad hoc networks (MANETs) [1], such as OLSR [2], AODV [3], DSR [4], are designed without explicitly considering QoS of the routes they generate. The number of hops is the most common criterion adop ...
CS 294-7: Introduction to Packet Radio Networks
... – Routing: choosing routes based on link connectivity » Routing schemes: • Flooding methods--inefficient utilization, but simple and may be best strategy for rapidly changing network topologies • Point-to-Point Routing--sequence of links associated with src-dst pair AKA “connection-oriented” routing ...
... – Routing: choosing routes based on link connectivity » Routing schemes: • Flooding methods--inefficient utilization, but simple and may be best strategy for rapidly changing network topologies • Point-to-Point Routing--sequence of links associated with src-dst pair AKA “connection-oriented” routing ...
a security survey of authenticated routing protocol (aran)
... E. Byzantine robustness:It should be able tofunction properly even if some participating nodes inrouting are intentionally obstructing its operation. Byzantinerobustness can be thought as self-stabilizationproperty’s severe version. The routing protocol must not onlyautomatically recuperate from an ...
... E. Byzantine robustness:It should be able tofunction properly even if some participating nodes inrouting are intentionally obstructing its operation. Byzantinerobustness can be thought as self-stabilizationproperty’s severe version. The routing protocol must not onlyautomatically recuperate from an ...
Document
... • Routers with in an area floods the area with routing info – router sends to all it’s neighbors and each neighbor sends to all it’s neighbors and etc.. • At the border of an area, special routers called area border routers are used to (1) summarize info about an area and (2) send info amongst areas ...
... • Routers with in an area floods the area with routing info – router sends to all it’s neighbors and each neighbor sends to all it’s neighbors and etc.. • At the border of an area, special routers called area border routers are used to (1) summarize info about an area and (2) send info amongst areas ...
Introduction to computer communication networks
... the destination is an IP net ID: a packages addressed to any host in the net, send to the associated gateway the destination is a complete IP address: route all packages to the specified host via the associated gateway ...
... the destination is an IP net ID: a packages addressed to any host in the net, send to the associated gateway the destination is a complete IP address: route all packages to the specified host via the associated gateway ...
AODV-BR: Backup Routing in Ad hoc Networks
... All mobile nodes in an ad-hoc network are capable of communicating with each other without the aid of any established infrastructure or centralized controller. ...
... All mobile nodes in an ad-hoc network are capable of communicating with each other without the aid of any established infrastructure or centralized controller. ...
IJ2214401442
... packet has to pass; the sender explicitly lists this route in the packet’s header, identifying each forwarding “hop” by the address of the next node to which to transmit the packet on its way to the destination host. There are two significant stages in working of DSR: Route Discovery and Route Maint ...
... packet has to pass; the sender explicitly lists this route in the packet’s header, identifying each forwarding “hop” by the address of the next node to which to transmit the packet on its way to the destination host. There are two significant stages in working of DSR: Route Discovery and Route Maint ...
... where vehicles are equipped with wireless and form a network without help of any infrastructure. The equipment is placed inside vehicles as well as on the road for providing access to other vehicles in order to form a network and communicate. Intelligent Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks ( InVANET’s) - Vehi ...
Hwk 5 Soln
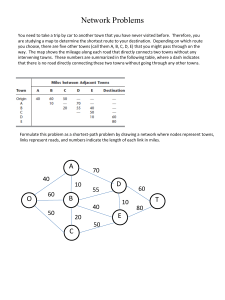
... Network Problems You need to take a trip by car to another town that you have never visited before. Therefore, you are studying a map to determine the shortest route to your destination. Depending on which route you choose, there are five other towns (call them A, B, C, D, E) that you might pass thr ...
... Network Problems You need to take a trip by car to another town that you have never visited before. Therefore, you are studying a map to determine the shortest route to your destination. Depending on which route you choose, there are five other towns (call them A, B, C, D, E) that you might pass thr ...
Routing Protocol
... with more detailed information, with the first of these being the neighbor table. Other two: topology of entire network, routing table Once all of that raw data is shared and each one of the routers has the data in its topology table, then the routing protocol runs the Shortest Path First (SPF) algo ...
... with more detailed information, with the first of these being the neighbor table. Other two: topology of entire network, routing table Once all of that raw data is shared and each one of the routers has the data in its topology table, then the routing protocol runs the Shortest Path First (SPF) algo ...
Network Routing Algorithms
... • Neighboring routers periodically exchange information from their routing tables. • Routers replace routes in their own routing tables anytime that neighbors have found better routes. • Information provided from neighbors – Outgoing line used for destination – Estimate of time or distance • can be ...
... • Neighboring routers periodically exchange information from their routing tables. • Routers replace routes in their own routing tables anytime that neighbors have found better routes. • Information provided from neighbors – Outgoing line used for destination – Estimate of time or distance • can be ...
EMC SMARTS NETWORK PROTOCOL MANAGER Management That Enables Service Assurance for
... Information Model™ to model the routing protocol domain, and EMC Codebook Correlation Technology™ to pinpoint the root cause of the alarms it generates. The unique cross-domain correlation capability enables Smarts to correlate routing network failure as the root cause, and routing protocol failures ...
... Information Model™ to model the routing protocol domain, and EMC Codebook Correlation Technology™ to pinpoint the root cause of the alarms it generates. The unique cross-domain correlation capability enables Smarts to correlate routing network failure as the root cause, and routing protocol failures ...