Review of Thermodynamics
... Hence although we may like to discuss entropy and enthalpy for explaining spontaneous reactions, equilibria and phase behaviour, we must be aware that they are intrinsically linked ...
... Hence although we may like to discuss entropy and enthalpy for explaining spontaneous reactions, equilibria and phase behaviour, we must be aware that they are intrinsically linked ...
Chemistry - Plymouth Public Schools
... MA CHM 1.3 Describe the three normal states of matter (solid, liquid, gas) in terms of energy, particle motion, and phase transitions. Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry Central Concepts: Atomic models are used to explain atoms and help us understand the interaction of elements and compounds obs ...
... MA CHM 1.3 Describe the three normal states of matter (solid, liquid, gas) in terms of energy, particle motion, and phase transitions. Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry Central Concepts: Atomic models are used to explain atoms and help us understand the interaction of elements and compounds obs ...
ch14
... valence level. • H is similar to the other Group 4A elements in terms of – ionization energy, ...
... valence level. • H is similar to the other Group 4A elements in terms of – ionization energy, ...
Stage 2 Chemistry Intended Student Learning 2014
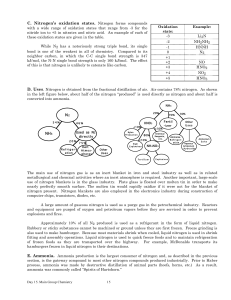
... Nitrogen may be converted into compounds by biological processes such as fixation or by reaction with oxygen during lightning discharges and at high temperatures such as those which occur in engines and furnaces. ...
... Nitrogen may be converted into compounds by biological processes such as fixation or by reaction with oxygen during lightning discharges and at high temperatures such as those which occur in engines and furnaces. ...
Unit 10: Structure and Bonding
... The diffusion of gases- The reaction between ammonia and hydrogen chloride Gases will diffuse at different rates. If one piece of cotton wool is soaked in concentrated ammonia solution and another is soaked in concentrated hydrochloric acid and these are put at either end of a dry ...
... The diffusion of gases- The reaction between ammonia and hydrogen chloride Gases will diffuse at different rates. If one piece of cotton wool is soaked in concentrated ammonia solution and another is soaked in concentrated hydrochloric acid and these are put at either end of a dry ...
Higher Chemistry summary 3a
... Therefore, for every 0.5 moles of methane 1 mole of oxygen would be required. Looking at the quantities of reactants from step 1 there is not enough oxygen to allow all of the methane to react therefore some methane will be left over at the end. The methane is said to be in excess and the oxygen wil ...
... Therefore, for every 0.5 moles of methane 1 mole of oxygen would be required. Looking at the quantities of reactants from step 1 there is not enough oxygen to allow all of the methane to react therefore some methane will be left over at the end. The methane is said to be in excess and the oxygen wil ...
Slide 1
... Catalysts and Reaction Order The synthesis of NH3 is carried out in the presence of catalysts. The order of the reaction depends on the composition and structure of this catalyst. ...
... Catalysts and Reaction Order The synthesis of NH3 is carried out in the presence of catalysts. The order of the reaction depends on the composition and structure of this catalyst. ...
Organic Chemistry
... Organic molecules are described more commonly by drawings or structural formulas, combinations of drawings and chemical symbols. The line-angle formula is simple and unambiguous. In this system, the endpoints and intersections of each line represent one carbon, and hydrogen atoms can either be notat ...
... Organic molecules are described more commonly by drawings or structural formulas, combinations of drawings and chemical symbols. The line-angle formula is simple and unambiguous. In this system, the endpoints and intersections of each line represent one carbon, and hydrogen atoms can either be notat ...
Test
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY
... Elements are divided between metals and nonmetals several elements with properties of both metals and nonmetals are called metalloids. Metals are elements that are generally solid, shiny in appearance, electrically conducting, and malleable (— )ليونةthat is, they can be pounded into flat sheets wi ...
... Elements are divided between metals and nonmetals several elements with properties of both metals and nonmetals are called metalloids. Metals are elements that are generally solid, shiny in appearance, electrically conducting, and malleable (— )ليونةthat is, they can be pounded into flat sheets wi ...
Atoms, Ions and Molecules
... properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary chemical reaction, no atom of any element disappears or is changed into an atom of another element. 3. Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. In a given compound, the relative numbers of at ...
... properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary chemical reaction, no atom of any element disappears or is changed into an atom of another element. 3. Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. In a given compound, the relative numbers of at ...
CHEM110P1_06_2015_Y_P1
... A large flask was evacuated and found to weigh 141.225 g. It was filled with an unknown gas to a pressure of 95.00 kPa at 26 °C and reweighed; its mass was 143.565 g. The flask was then filled with water at 26 °C and found to weigh 942.781 g. (The density of water at 26 °C is 0.9968 g cm–3.) Assumin ...
... A large flask was evacuated and found to weigh 141.225 g. It was filled with an unknown gas to a pressure of 95.00 kPa at 26 °C and reweighed; its mass was 143.565 g. The flask was then filled with water at 26 °C and found to weigh 942.781 g. (The density of water at 26 °C is 0.9968 g cm–3.) Assumin ...
"Introduction" Kinetics in Process Chemistry: Case Studies Baran Group Meeting Mike DeMartino
... acids or weakly nucleophilic amines often result in poor yields, or unacceptably long reaction times when done on-scale. In order to circumvent this problem, a catalyst is often used that can activate the carbonyl even more than the acyl imidazole. HOBt is one such catalyst. The potential for proces ...
... acids or weakly nucleophilic amines often result in poor yields, or unacceptably long reaction times when done on-scale. In order to circumvent this problem, a catalyst is often used that can activate the carbonyl even more than the acyl imidazole. HOBt is one such catalyst. The potential for proces ...