Climate Change History
... natural to seek for the probable effects of such a change. From the best laboratory observations it appears that the principal result of increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide . . . would be a gradual increase in the mean temperature of the colder regions of the earth.” ...
... natural to seek for the probable effects of such a change. From the best laboratory observations it appears that the principal result of increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide . . . would be a gradual increase in the mean temperature of the colder regions of the earth.” ...
Climate Sustainability: The Road from Rio to Copenhagen
... We each have a leadership role to play in these steps forward. This is part of our journey to sustainability. ...
... We each have a leadership role to play in these steps forward. This is part of our journey to sustainability. ...
Economic implications of projected changes to tuna
... • Main features of region’s climate system • We are affecting the climate system - climate is already changing • Future will be warmer • Extreme weather likely to be more extreme Our climate will be changing for foreseeable future ...
... • Main features of region’s climate system • We are affecting the climate system - climate is already changing • Future will be warmer • Extreme weather likely to be more extreme Our climate will be changing for foreseeable future ...
2: The Causes of Climatic Change
... output and, hence, Earth's climate? Despite many studies, the evidence is still controversial. Sunspot cycles have been found in climate parameters, but the fluctuations are weak and tend to appear and disappear without reason. The 11-year sunspot cycle itself varies in strength on timescale of 80 y ...
... output and, hence, Earth's climate? Despite many studies, the evidence is still controversial. Sunspot cycles have been found in climate parameters, but the fluctuations are weak and tend to appear and disappear without reason. The 11-year sunspot cycle itself varies in strength on timescale of 80 y ...
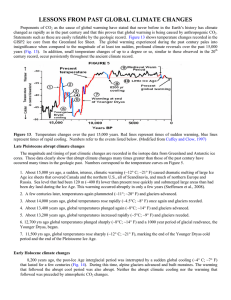
LESSONS FROM PAST GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGES
... Proponents of CO2 as the cause of global warming have stated that never before in the Earth’s history has climate changed as rapidly as in the past century and that this proves that global warming is being caused by anthropogenic CO2. Statements such as these are easily refutable by the geologic rec ...
... Proponents of CO2 as the cause of global warming have stated that never before in the Earth’s history has climate changed as rapidly as in the past century and that this proves that global warming is being caused by anthropogenic CO2. Statements such as these are easily refutable by the geologic rec ...
Poster
... and animal communities had to adapt to changing environment conditions. Climate change is a compounding factor to major drivers of freshwater biogeochemistry, but evidence is still often based on small scale. The effect of climate change cannot be quantified yet on a Baltic Basin wide-scale. Scenari ...
... and animal communities had to adapt to changing environment conditions. Climate change is a compounding factor to major drivers of freshwater biogeochemistry, but evidence is still often based on small scale. The effect of climate change cannot be quantified yet on a Baltic Basin wide-scale. Scenari ...
Climate of the Earth: CO2 and Climate Change
... Hard Way • The scientific studies and journal papers backing up and expanding on the content of this powerpoint can be found on my website’s climate page: Click here. I urge you to read it. • This is your future more than it is mine. ...
... Hard Way • The scientific studies and journal papers backing up and expanding on the content of this powerpoint can be found on my website’s climate page: Click here. I urge you to read it. • This is your future more than it is mine. ...
WFSC 420 Chapter 21 - Streetsboro City Schools
... – Deep water spreads southward to south Africa and joined by cold Antarctic waters – Spread northward into Indian and Pacific oceans as deep currents – Current slows down, warms up, becomes less dense, rises to the surface and moves back to North Atlantic – Produces a warm climate in Europe ...
... – Deep water spreads southward to south Africa and joined by cold Antarctic waters – Spread northward into Indian and Pacific oceans as deep currents – Current slows down, warms up, becomes less dense, rises to the surface and moves back to North Atlantic – Produces a warm climate in Europe ...
Toby Garfield, NOAA Southwest Fisheries Science Center
... MEI: Multivariate El Niño Index indicating interannual variability of temperature The three indices are suggesting that at the end of 2013 there occurred a transition from favorable productivity conditions to generally low productivity conditions! ...
... MEI: Multivariate El Niño Index indicating interannual variability of temperature The three indices are suggesting that at the end of 2013 there occurred a transition from favorable productivity conditions to generally low productivity conditions! ...
Global Interdependence
... Their ability to synthesis and apply the information they’ve gathered can be assessed in the class discussion to demonstrate their grasp of the theory of climate change. Do they identify examples of how climate change impacts the earth’s geo-spheres? Do they use the example of climate change to desc ...
... Their ability to synthesis and apply the information they’ve gathered can be assessed in the class discussion to demonstrate their grasp of the theory of climate change. Do they identify examples of how climate change impacts the earth’s geo-spheres? Do they use the example of climate change to desc ...
Climate Change and Ozone Depletion
... warmer troposphere can decrease the ability of the ocean to remove and store CO2 by decreasing the nutrient supply for phytoplankton and increasing the acidity of ocean water. Global warming will lead to prolonged heat waves and droughts in some areas and prolonged heavy rains and increased floodi ...
... warmer troposphere can decrease the ability of the ocean to remove and store CO2 by decreasing the nutrient supply for phytoplankton and increasing the acidity of ocean water. Global warming will lead to prolonged heat waves and droughts in some areas and prolonged heavy rains and increased floodi ...
Global Climate Change and You
... increased about 30% since the Industrial Revolution, indicates that humans have a significant role in the globally increased temperature – Its believed that the main source of carbon dioxide emissions are through the burning of fossil fuels ...
... increased about 30% since the Industrial Revolution, indicates that humans have a significant role in the globally increased temperature – Its believed that the main source of carbon dioxide emissions are through the burning of fossil fuels ...
Radiation and Climate_Global Warming
... Disagreement Among Scientists • Although most climate specialists agree that Earth’s average temperature will increase, there is still some disagreement about causes of this predicted warming. • New data indicate that the lower atmosphere may not be warming at the same rate as Earth’s surface, whic ...
... Disagreement Among Scientists • Although most climate specialists agree that Earth’s average temperature will increase, there is still some disagreement about causes of this predicted warming. • New data indicate that the lower atmosphere may not be warming at the same rate as Earth’s surface, whic ...
Plants will run out of time to grow under ongoing climate change
... today. The researchers then used climate projections to count the number of days in a year that will fall within these suitable climate ranges for plant growth in the future. Although the study did find that warming trends will increase the number of days above freezing at higher latitudes by 7%, th ...
... today. The researchers then used climate projections to count the number of days in a year that will fall within these suitable climate ranges for plant growth in the future. Although the study did find that warming trends will increase the number of days above freezing at higher latitudes by 7%, th ...
Talk 5 - Research needs for decadal to centennial climate prediction
... Much of the uncertainty arises from global model input ...
... Much of the uncertainty arises from global model input ...
Innovative Solutions to Global Warming
... near-surface air and oceans since the mid-20th century and its projected continuation. Global surface temperature increased 0.74 ± 0.18 °C (1.33 ± 0.32 °F) during the last century. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concludes that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations resulting ...
... near-surface air and oceans since the mid-20th century and its projected continuation. Global surface temperature increased 0.74 ± 0.18 °C (1.33 ± 0.32 °F) during the last century. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concludes that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations resulting ...
An Overview of Canada`s Changing Climate Contents of the 2014
... • Increases in wave activity in areas with reduced sea ice • Widespread increasing ocean acidity and decreasing subsurface oxygen ...
... • Increases in wave activity in areas with reduced sea ice • Widespread increasing ocean acidity and decreasing subsurface oxygen ...
The Physical Science Basis
... concentrations were to be stabilized today. Models indicate: • It is very likely (greater than 90% probability) that hot extremes, heat waves and heavy precipitation events will become more frequent. • If global average temperatures were to exceed 1.9 to 4.6 degrees C (3.4 to 8.3 degrees F) compared ...
... concentrations were to be stabilized today. Models indicate: • It is very likely (greater than 90% probability) that hot extremes, heat waves and heavy precipitation events will become more frequent. • If global average temperatures were to exceed 1.9 to 4.6 degrees C (3.4 to 8.3 degrees F) compared ...
Global warming hiatus
A global warming hiatus, also sometimes referred to as a global warming pause or a global warming slowdown, is a period of relatively little change in globally averaged surface temperatures. In the current episode of global warming many such periods are evident in the surface temperature record, along with robust evidence of the long term warming trend.The exceptionally warm El Niño year of 1998 was an outlier from the continuing temperature trend, and so gave the appearance of a hiatus: by January 2006 assertions had been made that this showed that global warming had stopped. A 2009 study showed that decades without warming were not exceptional, and in 2011 a study showed that if allowances were made for known variability, the rising temperature trend continued unabated. There was increased public interest in 2013 in the run-up to publication of the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report, and despite concerns that a 15-year period was too short to determine a meaningful trend, the IPCC included a section on a hiatus, which it defined as a much smaller increasing linear trend over the 15 years from 1998 to 2012, than over the 60 years from 1951 to 2012. Various studies examined possible causes of the short term slowdown. Even though the overall climate system had continued to accumulate energy due to Earth's positive energy budget, the available temperature readings at the earth's surface indicated slower rates of increase in surface warming than in the prior decade. Since measurements at the top of the atmosphere show that Earth is receiving more energy than it is radiating back into space, the retained energy should be producing warming in at least one of the five parts of Earth's climate system.A July 2015 paper on the updated NOAA dataset cast doubt on the existence of this supposed hiatus, and found no indication of a slowdown. This analysis incorporated the latest corrections for known biases in ocean temperature measurements, and new land temperature data. Scientists working on other datasets welcomed this study, though the view was expressed that the short term warming trend had been slower than in previous periods of the same length.