Chapter 9 Study Guide - Merrillville Community School
... After reading this chapter you should be able to: Describe how each community, North and South, connected to its soldiers at war, including a comparison of the two communities. Outline the immediate outbreak of the war from Fort Sumter to Bull Run, including initial strategies and the relative stren ...
... After reading this chapter you should be able to: Describe how each community, North and South, connected to its soldiers at war, including a comparison of the two communities. Outline the immediate outbreak of the war from Fort Sumter to Bull Run, including initial strategies and the relative stren ...
The Civil War - Marion County Public Schools
... as the nation approached its third year of bloody civil war. The proclamation declared "that all persons held as slaves" within the rebellious states "are, and henceforward shall be free." Despite this expansive wording, the Emancipation Proclamation was limited in many ways. It applied only to st ...
... as the nation approached its third year of bloody civil war. The proclamation declared "that all persons held as slaves" within the rebellious states "are, and henceforward shall be free." Despite this expansive wording, the Emancipation Proclamation was limited in many ways. It applied only to st ...
Study help for Unit 6 test Clicker questions with answers
... 12. Although no slaves were immediately freed by the Emancipation Proclamation, it was important because: a. Union troops would free slaves as they took over Confederate territory b. Confederate states eventually freed their slaves c. It meant that Britain would help the Confederacy in the war d. S ...
... 12. Although no slaves were immediately freed by the Emancipation Proclamation, it was important because: a. Union troops would free slaves as they took over Confederate territory b. Confederate states eventually freed their slaves c. It meant that Britain would help the Confederacy in the war d. S ...
Standards 4
... 12. How did the division in the Democratic Party allow Lincoln to be elected president? 13. Why did Southern states feel they no longer had a political voice in the federal government after the Presidential election of 1860? 14. What course of action did Southern states take in order to prevent thei ...
... 12. How did the division in the Democratic Party allow Lincoln to be elected president? 13. Why did Southern states feel they no longer had a political voice in the federal government after the Presidential election of 1860? 14. What course of action did Southern states take in order to prevent thei ...
Unit 8 - PowerPoints - The American Civil War
... in Northern and Western states before the Civil War. Abolitionists wanted slaves to be freed. Some abolitionists favored relocating them in Africa. Many, but not all, abolitionists believed African-American slaves should have the same freedoms as their owners. Southern states opposed the abolition o ...
... in Northern and Western states before the Civil War. Abolitionists wanted slaves to be freed. Some abolitionists favored relocating them in Africa. Many, but not all, abolitionists believed African-American slaves should have the same freedoms as their owners. Southern states opposed the abolition o ...
American History
... secede.” But I have no right to stop them from doing so.” Lincoln; “The president’s duty is to enforce the law to preserve the gov’t.”; warns, no state can lawfully get out of the union © 2009 abcteach.com ...
... secede.” But I have no right to stop them from doing so.” Lincoln; “The president’s duty is to enforce the law to preserve the gov’t.”; warns, no state can lawfully get out of the union © 2009 abcteach.com ...
April—Charleston Harbor
... January 1861 -- The South Secedes. When Abraham Lincoln, a known opponent of slavery, was elected president, the South Carolina legislature perceived a threat. Calling a state convention, the delegates voted to remove the state of South Carolina from the union known as the United States of America. ...
... January 1861 -- The South Secedes. When Abraham Lincoln, a known opponent of slavery, was elected president, the South Carolina legislature perceived a threat. Calling a state convention, the delegates voted to remove the state of South Carolina from the union known as the United States of America. ...
The Furnace of Civil War
... Union turned to 6-part strategy of total war 1. Suffocate South by blockading its ports 2. Free the slaves to undermine economy of South 3. Cut Confederacy in 1/2 by taking control of Mississippi River 4. Cut Confederacy into pieces by sending troops into Georgia and Carolinas 5. Take Confederate ca ...
... Union turned to 6-part strategy of total war 1. Suffocate South by blockading its ports 2. Free the slaves to undermine economy of South 3. Cut Confederacy in 1/2 by taking control of Mississippi River 4. Cut Confederacy into pieces by sending troops into Georgia and Carolinas 5. Take Confederate ca ...
Vocab 22 - The Civil War
... averting hostilities between the two nations, although he failed to stop the sailing of the Alabama, a raider built in Great Britain for the Confederacy. Alabama claims: There were a series of claims for indemnity made by the United States upon Great Britain in 1862. The claims were for compensation ...
... averting hostilities between the two nations, although he failed to stop the sailing of the Alabama, a raider built in Great Britain for the Confederacy. Alabama claims: There were a series of claims for indemnity made by the United States upon Great Britain in 1862. The claims were for compensation ...
The First Two Years of the Civil War
... The First Two Years of the Civil War Chapter 18 section 2 ...
... The First Two Years of the Civil War Chapter 18 section 2 ...
Civil War
... Ø September, 1862 – EmancipaJon ProclamaJon announced by Abraham Lincoln: • To take effect in 1863 (unless Southern states gave up rebellion against United States) • Seen, by Lincoln, as a necessary step to win the war • Slavery not enJrely destroyed (onl ...
... Ø September, 1862 – EmancipaJon ProclamaJon announced by Abraham Lincoln: • To take effect in 1863 (unless Southern states gave up rebellion against United States) • Seen, by Lincoln, as a necessary step to win the war • Slavery not enJrely destroyed (onl ...
Civil War - mrbeckwithhistory
... – Confederate diplomats travel aboard a British merchant ship (the Trent) in order to gain British recognition of the Confederacy • Trent is stopped by Union naval ship and the two diplomats are arrested – Britain threatens war against the Union and sends 8000 troops into Canada » Lincoln orders the ...
... – Confederate diplomats travel aboard a British merchant ship (the Trent) in order to gain British recognition of the Confederacy • Trent is stopped by Union naval ship and the two diplomats are arrested – Britain threatens war against the Union and sends 8000 troops into Canada » Lincoln orders the ...
M / C Review Chapter 15
... it prevented the Confederacy from being able to purchase several warships from Britain and France for use against Union shipping. C. it was the first clear case of treason by a United States official and it badly embarrassed the administration of John Adams. D. it resulted in the sinking of the Conf ...
... it prevented the Confederacy from being able to purchase several warships from Britain and France for use against Union shipping. C. it was the first clear case of treason by a United States official and it badly embarrassed the administration of John Adams. D. it resulted in the sinking of the Conf ...
How Did the North Win the Civil War?
... soldiers • Only had to defend their land – not attack North ...
... soldiers • Only had to defend their land – not attack North ...
American Civil War
... The Trent Affair (1861) November 1861: Union warship stops British steamer Trent at gunpoint in neutral waters Two Confederate delegates heading to London arrested Britain outraged at "violation of their sovereignty" North convinced that Britain is secretly supporting the South Britain sends 1 ...
... The Trent Affair (1861) November 1861: Union warship stops British steamer Trent at gunpoint in neutral waters Two Confederate delegates heading to London arrested Britain outraged at "violation of their sovereignty" North convinced that Britain is secretly supporting the South Britain sends 1 ...
Antietam
... 2. Emancipation Proclamation - What did Lincoln consider in his decision to draft the Emancipation Proclamation and who was involved in the decision? How did the Emancipation Proclamation affect society in the short-term and the long-term? 3. Lincoln’s Cabinet - In the summer of 1862, Lincoln’s cabi ...
... 2. Emancipation Proclamation - What did Lincoln consider in his decision to draft the Emancipation Proclamation and who was involved in the decision? How did the Emancipation Proclamation affect society in the short-term and the long-term? 3. Lincoln’s Cabinet - In the summer of 1862, Lincoln’s cabi ...
ARGUMENTS OVER THE EMANCIPATION PROCLAMATION
... • Lincoln does NOT believe govt. can abolish slavery • HOWEVER, Union army can seize “contraband”= to hurt South’s war effort • Antietam’s “victory” gives Lincoln the “opportunity” to issue preliminary proclamation on Sept. 23, 1862. • Emancipates only those slaves in states still in rebellion, NOT ...
... • Lincoln does NOT believe govt. can abolish slavery • HOWEVER, Union army can seize “contraband”= to hurt South’s war effort • Antietam’s “victory” gives Lincoln the “opportunity” to issue preliminary proclamation on Sept. 23, 1862. • Emancipates only those slaves in states still in rebellion, NOT ...
Document
... Lincoln moved to stop the rioting…he suspended “habeas corpus” (right to be charged or have a hearing before being jailed) 14,000 people arrested, most were never charged or brought to trial…they were just held and then released ...
... Lincoln moved to stop the rioting…he suspended “habeas corpus” (right to be charged or have a hearing before being jailed) 14,000 people arrested, most were never charged or brought to trial…they were just held and then released ...
Chapter 11 Section 2
... covering the hull of wooden ships. The first of these was the Merrimack, which had been captured from the Union and renamed the Virginia. Point of the iron was to withstand cannon fire. March 8, 1862: worst day of the war for the Union Navy. 240 sailors were killed when two ships sank that had b ...
... covering the hull of wooden ships. The first of these was the Merrimack, which had been captured from the Union and renamed the Virginia. Point of the iron was to withstand cannon fire. March 8, 1862: worst day of the war for the Union Navy. 240 sailors were killed when two ships sank that had b ...
CIVIL WAR - Brookwood High School
... • But did Federal Gov’t have authority to abolish it where it already existed? ...
... • But did Federal Gov’t have authority to abolish it where it already existed? ...
ch. 20 girding for war
... surrendered The North’s Economic Boom a. Economic Successes of the War i. New Factories – 1. Helped by the protective tariff 2. Manufacturers and businesspeople made lots of money ii. Millionaire Class 1. War bred a millionaire class for the first time 2. Many were speculators and peculators (people ...
... surrendered The North’s Economic Boom a. Economic Successes of the War i. New Factories – 1. Helped by the protective tariff 2. Manufacturers and businesspeople made lots of money ii. Millionaire Class 1. War bred a millionaire class for the first time 2. Many were speculators and peculators (people ...
The Furnace of Civil War
... – Serious student of warfare; had served in Mexican War, observed Crimean War – Excellent organizer and drillmaster – Extremely cautious; refused to move unless everything was perfect (and it never was) – Always believed enemy outnumbered him – Spoke to president disrespectfully and arrogantly – Fin ...
... – Serious student of warfare; had served in Mexican War, observed Crimean War – Excellent organizer and drillmaster – Extremely cautious; refused to move unless everything was perfect (and it never was) – Always believed enemy outnumbered him – Spoke to president disrespectfully and arrogantly – Fin ...
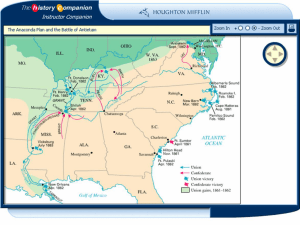
Study Questions for Chapter 21 and 22 Test
... 2. What were the three steps of the Anaconda Plan? ...
... 2. What were the three steps of the Anaconda Plan? ...
The Furnace of Civil War
... – Serious student of warfare; had served in Mexican War, observed Crimean War – Excellent organizer and drillmaster – Extremely cautious; refused to move unless everything was perfect (and it never was) – Always believed enemy outnumbered him – Spoke to president disrespectfully and arrogantly – Fin ...
... – Serious student of warfare; had served in Mexican War, observed Crimean War – Excellent organizer and drillmaster – Extremely cautious; refused to move unless everything was perfect (and it never was) – Always believed enemy outnumbered him – Spoke to president disrespectfully and arrogantly – Fin ...
481-485
... Like other South Carolinians, Emma Holmes got caught up in the passions that led her state to secede. In her diary, she wrote about South Carolina’s attack on Fort Sumter, a federal fort in Charleston’s harbor. ...
... Like other South Carolinians, Emma Holmes got caught up in the passions that led her state to secede. In her diary, she wrote about South Carolina’s attack on Fort Sumter, a federal fort in Charleston’s harbor. ...
Confederate privateer

The Confederate privateers were privately owned ships that were authorized by the government of the Confederate States of America to attack the shipping of the United States. Although the appeal was to profit by capturing merchant vessels and seizing their cargoes, the government was most interested in diverting the efforts of the Union Navy away from the blockade of Southern ports, and perhaps to encourage European intervention in the conflict.At the beginning of the American Civil War, the Confederate government sought to counter the United States Navy in part by appealing to private enterprise world-wide to engage in privateering against United States Shipping. [[