Use of climate data and information for EEA climate
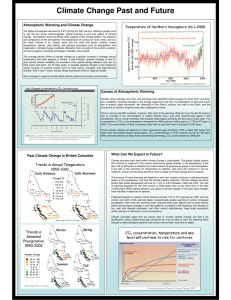
... according to different near-surface temperature observational analyses with anomalies close to 1oC. • the decade 2006-2015 was between 0.83 and 0.89 oC warmer than the period 1850-1899 (pre-industrial) ...
... according to different near-surface temperature observational analyses with anomalies close to 1oC. • the decade 2006-2015 was between 0.83 and 0.89 oC warmer than the period 1850-1899 (pre-industrial) ...
Uncertainty in Climate Predictions
... the changes in CO2 over time. A mapping F takes the state from time t to t + 1. It uses both the current state of the climate system, xt and the values of the external forces, y t to produce a dynamical result for the next time step. Concisely, xt+1 = F (xt , y t ). Here the individual time steps of ...
... the changes in CO2 over time. A mapping F takes the state from time t to t + 1. It uses both the current state of the climate system, xt and the values of the external forces, y t to produce a dynamical result for the next time step. Concisely, xt+1 = F (xt , y t ). Here the individual time steps of ...
IPCC Fifth Assessment Report: Climate Change 2013/14
... Emissions of greenhouse gases and aerosols due to human activities continue to alter the atmosphere in ways that are expected to affect the climate. Confidence in the ability of models to project future climate has increased There is new and stronger evidence that most of the warming observed over t ...
... Emissions of greenhouse gases and aerosols due to human activities continue to alter the atmosphere in ways that are expected to affect the climate. Confidence in the ability of models to project future climate has increased There is new and stronger evidence that most of the warming observed over t ...
Climate Change Past and Future
... will continue to respond to the excess greenhouse gases already in the atmosphere. It will take 100 to 300 years to stabilize the concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. It will take a few centuries for temperature to stabilize. Sea level will continue to rise for millennia. Human comm ...
... will continue to respond to the excess greenhouse gases already in the atmosphere. It will take 100 to 300 years to stabilize the concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. It will take a few centuries for temperature to stabilize. Sea level will continue to rise for millennia. Human comm ...
Climate change - is it really happening
... climate research • There’s still a big range in temperature projections – due to differences in model feedbacks (clouds especially) • Carbon cycle feedbacks … • Regional patterns and extremes – especially rainfall • Interactions between climate variability and climate change ...
... climate research • There’s still a big range in temperature projections – due to differences in model feedbacks (clouds especially) • Carbon cycle feedbacks … • Regional patterns and extremes – especially rainfall • Interactions between climate variability and climate change ...
Modelling Short Term Impacts of Climate Change
... • Weather charts – back to the late 1800s • Windspeed data – back to the 1960s • Re-analysis data • e.g. European Center Medium Range Weather Forecasting (ECMWF) ERA40 and ERAInterim • “best guess” snapshot of the world’s weather at six-hourly intervals since 1957 • Numerical models - mathematical m ...
... • Weather charts – back to the late 1800s • Windspeed data – back to the 1960s • Re-analysis data • e.g. European Center Medium Range Weather Forecasting (ECMWF) ERA40 and ERAInterim • “best guess” snapshot of the world’s weather at six-hourly intervals since 1957 • Numerical models - mathematical m ...
Impacts and costs
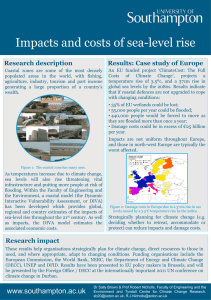
... • 55,000 people per year could be flooded; • 440,000 people would be forced to move as they are flooded more than once a year; • Damage costs could be in excess of €25 billion per year. Impacts are not uniform throughout Europe, and those in north-west Europe are typically the worst affected. ...
... • 55,000 people per year could be flooded; • 440,000 people would be forced to move as they are flooded more than once a year; • Damage costs could be in excess of €25 billion per year. Impacts are not uniform throughout Europe, and those in north-west Europe are typically the worst affected. ...
What we do not know in terms of adaptation
... A recent paper by Oreskes et al. in the journal Philosophy of Science asserts that “there is a gap between the scale on which models produce consistent information and the scale on which humans act”. While the large scales, such as the global mean, provide the best indicators of the state of earth’s ...
... A recent paper by Oreskes et al. in the journal Philosophy of Science asserts that “there is a gap between the scale on which models produce consistent information and the scale on which humans act”. While the large scales, such as the global mean, provide the best indicators of the state of earth’s ...
Main Findings of IPCC - UW Program on Climate Change
... How long have we got? We have to stabilize emissions of carbon dioxide within a decade, or temperatures will warm by more than one degree. That will be warmer than it has been for half a million years, and many things could become unstoppable.…We don't have much time left.” Dr. James Hansen, Directo ...
... How long have we got? We have to stabilize emissions of carbon dioxide within a decade, or temperatures will warm by more than one degree. That will be warmer than it has been for half a million years, and many things could become unstoppable.…We don't have much time left.” Dr. James Hansen, Directo ...
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
... methods. These activities have increased the amount of "greenhouse gases" in the atmosphere, especially carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. Such gases occur naturally -- they are critical for life on earth; they keep some of the sun's warmth from reflecting back into space, and without them ...
... methods. These activities have increased the amount of "greenhouse gases" in the atmosphere, especially carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. Such gases occur naturally -- they are critical for life on earth; they keep some of the sun's warmth from reflecting back into space, and without them ...
Introduction to Climate Change
... The Earth's climate has changed many times during the planet's history, with events ranging from ice ages to long periods of warmth. Historically, natural factors such as volcanic eruptions, changes in the Earth's orbit, and the amount of energy released from the Sun have affected the Earth's climat ...
... The Earth's climate has changed many times during the planet's history, with events ranging from ice ages to long periods of warmth. Historically, natural factors such as volcanic eruptions, changes in the Earth's orbit, and the amount of energy released from the Sun have affected the Earth's climat ...
global warming Defen..
... The new NASA guidelines prohibit the editing of reports to alter scientific data, as well as any public affairs management of NASA projects by non-agency institutions. ...
... The new NASA guidelines prohibit the editing of reports to alter scientific data, as well as any public affairs management of NASA projects by non-agency institutions. ...
Slide 2 - Climate Action Partnership
... and changing the distribution of disease vectors thus putting more people at risk. Temperature increases will enhance rates of extinction for many species. Changing rainfall patterns will effect water resources which are already under pressure. Increasing sea levels mean greater risk of storm surge ...
... and changing the distribution of disease vectors thus putting more people at risk. Temperature increases will enhance rates of extinction for many species. Changing rainfall patterns will effect water resources which are already under pressure. Increasing sea levels mean greater risk of storm surge ...
16 Mar 2014
... whereas CO2-induced warming should warm the troposphere but cool the stratosphere. According to the evidence, the stratosphere has cooled while the troposphere has warmed. The present rate of planetary warming is more than ten times that at end of the last ice age, and is faster than any known warm ...
... whereas CO2-induced warming should warm the troposphere but cool the stratosphere. According to the evidence, the stratosphere has cooled while the troposphere has warmed. The present rate of planetary warming is more than ten times that at end of the last ice age, and is faster than any known warm ...
Uncertainties
... Other complicated factors people have measured temperatures with different kinds of instruments, at different locations and even at different altitudes. Urban heat island effect The enormous range Concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere in 2100 is likely to exceed preindustrial levels ...
... Other complicated factors people have measured temperatures with different kinds of instruments, at different locations and even at different altitudes. Urban heat island effect The enormous range Concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere in 2100 is likely to exceed preindustrial levels ...
Fighting Climate Change(17.9.14)
... Brac University (BU) in collaboration with a global network of activists, Avaaz, yesterday urged the prime minister to ask industrialised countries to provide financial and technological assistance to the countries which are affected by climate change. The prime minister should also ask the industri ...
... Brac University (BU) in collaboration with a global network of activists, Avaaz, yesterday urged the prime minister to ask industrialised countries to provide financial and technological assistance to the countries which are affected by climate change. The prime minister should also ask the industri ...
Global_Temperature_Change_in_the_21st_Century
... must rely on perturbing simulated Earths rather than the actual Earth. It would be impossible in a physical simulation (such as a giant globe) to capture the processes in the Earth’s complex systems in a realistic and meaningful way. Researchers therefore rely on computer simulations that mathematic ...
... must rely on perturbing simulated Earths rather than the actual Earth. It would be impossible in a physical simulation (such as a giant globe) to capture the processes in the Earth’s complex systems in a realistic and meaningful way. Researchers therefore rely on computer simulations that mathematic ...
Climate Physics and the Problem of Abrupt Climate Change
... • Relative to what is observed in nature, climate models seem unusually stable. • There are many mysteries surrounding the cause and mechanisms of past abrupt climate change. • Although future abrupt climate change is considered unlikely, model predictions of future climate may be under-representing ...
... • Relative to what is observed in nature, climate models seem unusually stable. • There are many mysteries surrounding the cause and mechanisms of past abrupt climate change. • Although future abrupt climate change is considered unlikely, model predictions of future climate may be under-representing ...
Earth Science 4 - Learn More About Climate
... • How is climate influenced by changes in Earth’s energy balance? • How have climates changed over Earth’s history? • How does climate change impact all of Earth’s systems? • How have climate changes impacted human society? Relevance and Application: • Much of the data we receive about the ocean and ...
... • How is climate influenced by changes in Earth’s energy balance? • How have climates changed over Earth’s history? • How does climate change impact all of Earth’s systems? • How have climate changes impacted human society? Relevance and Application: • Much of the data we receive about the ocean and ...
Climate Change
... occurring trace elements. Water vapor is also important in creating cloud cover, which also traps heat. At the same time dense cloud cover reflects back the energy from the sun, if it is continuous and unbroken for days. Thus there is a great interplay of the properties of the atmosphere, land and o ...
... occurring trace elements. Water vapor is also important in creating cloud cover, which also traps heat. At the same time dense cloud cover reflects back the energy from the sun, if it is continuous and unbroken for days. Thus there is a great interplay of the properties of the atmosphere, land and o ...
Climate Change
... which releases the longstored CO2 back into the atmosphere. www.epa.gov/climatechange ...
... which releases the longstored CO2 back into the atmosphere. www.epa.gov/climatechange ...