Cognitive Neurosciences and Strategic Management: Challenges
... blood oxygenation during ongoing cognitive tasks (Ogawa et al., 1990). The popular blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) contrast, used to measure brain activity, is based on the fact that hemoglobin has different magnetic properties depending on its state of oxygenation: oxyhemoglobin is diamagn ...
... blood oxygenation during ongoing cognitive tasks (Ogawa et al., 1990). The popular blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) contrast, used to measure brain activity, is based on the fact that hemoglobin has different magnetic properties depending on its state of oxygenation: oxyhemoglobin is diamagn ...
The Role of theThalamus in Human Consciousness
... Core cells specific projecting and dominate sensory nuclei Matrix cells diffusely projecting and dominate nuclei with more frontal connections Dynamic core associated with matrix (binding, integrative) thalamic relay neurons? E.G. Jones, 2009 ...
... Core cells specific projecting and dominate sensory nuclei Matrix cells diffusely projecting and dominate nuclei with more frontal connections Dynamic core associated with matrix (binding, integrative) thalamic relay neurons? E.G. Jones, 2009 ...
The human brain has on average 100 billion neurons, to each
... resolved and then analysed. What are EEGs? Electroencephalograms (EEGs) are measured scalp potentials as a result of cortical electrical activity amassed over scales larger than single neurons. They are obtained via the placement of electrodes at specific points over the surface area of the scalp. W ...
... resolved and then analysed. What are EEGs? Electroencephalograms (EEGs) are measured scalp potentials as a result of cortical electrical activity amassed over scales larger than single neurons. They are obtained via the placement of electrodes at specific points over the surface area of the scalp. W ...
The Brain - Midlands State University
... Possesses Motor Areas (Movement) Contralateral control Size of motor area directly related to number and complexity of skeletal muscle movements Contains Sensory Areas Somesthetic, Visual, Auditory, Olfactory ...
... Possesses Motor Areas (Movement) Contralateral control Size of motor area directly related to number and complexity of skeletal muscle movements Contains Sensory Areas Somesthetic, Visual, Auditory, Olfactory ...
PDF - 6 pages - Scholastic Heads Up
... who have been using drugs for a long time have a smaller prefrontal cortex than people who have not been using drugs. The prefrontal cortex is the area where decision making occurs. ...
... who have been using drugs for a long time have a smaller prefrontal cortex than people who have not been using drugs. The prefrontal cortex is the area where decision making occurs. ...
Music and the Brain: Areas and Networks
... their underlying brain networks all share many overlapping areas in the brain (Chapter 1.4 in this volume discusses this matter from a functional as well as neurological perspective). Such overlapping areas include (but are not limited to) a perisylvian network: regions surrounding the sylvian fissu ...
... their underlying brain networks all share many overlapping areas in the brain (Chapter 1.4 in this volume discusses this matter from a functional as well as neurological perspective). Such overlapping areas include (but are not limited to) a perisylvian network: regions surrounding the sylvian fissu ...
CE7427: Cognitive Neuroscience and Embedded Intelligence
... neurons and their microcurcuits. Event-related potentials (ERPs) are averaged responses to stimuli revealing brain reactions. Magnetoencephalography (MEG) records magnetic fields produced by electrical currents. ...
... neurons and their microcurcuits. Event-related potentials (ERPs) are averaged responses to stimuli revealing brain reactions. Magnetoencephalography (MEG) records magnetic fields produced by electrical currents. ...
Biopsychology – Paper 2
... Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue (the brain, spinal cord, PNS etc). They detect internal and external changes and form the communication link between the central nervous system, the brain and spinal cord and every part of the body. Neurons are microscopic in size and can be one of t ...
... Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue (the brain, spinal cord, PNS etc). They detect internal and external changes and form the communication link between the central nervous system, the brain and spinal cord and every part of the body. Neurons are microscopic in size and can be one of t ...
Your Amazing Brain:
... Did You Know…? Your brain contains 100 billion neurons and 60 trillion synapses (cortex) The average adult brain weighs about 1.4 kg (3 lbs) ...
... Did You Know…? Your brain contains 100 billion neurons and 60 trillion synapses (cortex) The average adult brain weighs about 1.4 kg (3 lbs) ...
Consciousness and Creativity in Brain
... • Phenomenal consciousness with inner life, self, unreliable processes? Is this desired in machines? • How reliable may machines with phenomenal C be? • First, can we build them? How to build a robot that feels, J.Kevin O'Regan at CogSys 2010 at ETH Zurich on 27/1/2010 • Sensorimotor account of acti ...
... • Phenomenal consciousness with inner life, self, unreliable processes? Is this desired in machines? • How reliable may machines with phenomenal C be? • First, can we build them? How to build a robot that feels, J.Kevin O'Regan at CogSys 2010 at ETH Zurich on 27/1/2010 • Sensorimotor account of acti ...
lab 8: central nervous system
... white matter - myelinated axons - called tracts: and basal or subcortical nuclei - groups of cell bodies (hence gray matter) found deep to the tracts. 1. surface features Note the ridges are called gyri (singular - gyrus) while the depressions or furrows are called sulci (singular = sulcus). Deep su ...
... white matter - myelinated axons - called tracts: and basal or subcortical nuclei - groups of cell bodies (hence gray matter) found deep to the tracts. 1. surface features Note the ridges are called gyri (singular - gyrus) while the depressions or furrows are called sulci (singular = sulcus). Deep su ...
ChapTer 3 - Physicians for Social Responsibility
... that the loss of a neurotransmitter so intimately involved in learning, memory, and cognition would be a common finding in dementia. Loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra is a cardinal feature of Parkinson’s disease. As cells in this region normally project to parts of the basal ...
... that the loss of a neurotransmitter so intimately involved in learning, memory, and cognition would be a common finding in dementia. Loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra is a cardinal feature of Parkinson’s disease. As cells in this region normally project to parts of the basal ...
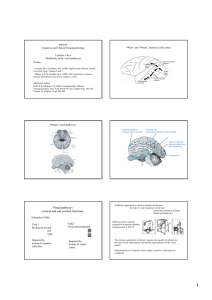
Visual pathways cortical and sub
... electrophysiological recordings from dorsal stream neurons neurons that fire during reaching neurons firing during saccades towards stationary objects neurons responding to moving objects if followed by gaze ...
... electrophysiological recordings from dorsal stream neurons neurons that fire during reaching neurons firing during saccades towards stationary objects neurons responding to moving objects if followed by gaze ...
Nervous System
... – 5. Go to the Daily Double slide just linked to, and right click once on the answer arrow at the bottom right, choose Hyperlink, and choose Edit Hyperlink. – 6. In the Action Settings window, make sure the Hyperlink button (to the left of “Hyperlink”) is selected, and in the select box underneath c ...
... – 5. Go to the Daily Double slide just linked to, and right click once on the answer arrow at the bottom right, choose Hyperlink, and choose Edit Hyperlink. – 6. In the Action Settings window, make sure the Hyperlink button (to the left of “Hyperlink”) is selected, and in the select box underneath c ...
Brain Compatible Learning Strategies
... hormones and emotions. It seeks balance or it can’t send information on to higher levels. – thalamus—information processing—receives all incoming information (except smell). It determines where to send info (visual cortex, auditory…). Keeps the brain updated on what is going on in the outside world. ...
... hormones and emotions. It seeks balance or it can’t send information on to higher levels. – thalamus—information processing—receives all incoming information (except smell). It determines where to send info (visual cortex, auditory…). Keeps the brain updated on what is going on in the outside world. ...
3A & 3B PowerPoint
... photons are emissions from radioactive substances What it shows: An image of the amount and localization of any molecules that can be injected in radioactive form, such as neurotransmitters, drugs, tracers for blood flow or glucose use (which indicates specific changes in neuronal activity) PET Scan ...
... photons are emissions from radioactive substances What it shows: An image of the amount and localization of any molecules that can be injected in radioactive form, such as neurotransmitters, drugs, tracers for blood flow or glucose use (which indicates specific changes in neuronal activity) PET Scan ...
Lecture 3
... • derived from hindbrain but not part of brain stem. • connected to pons and medulla by cerebellar peduncles that are made up of axons entering and leaving the cerebellum • 4th ventricle separates it from brain stem. ...
... • derived from hindbrain but not part of brain stem. • connected to pons and medulla by cerebellar peduncles that are made up of axons entering and leaving the cerebellum • 4th ventricle separates it from brain stem. ...
fMRI can see M1, premotor activity Corresponding to Individual
... brain activity can generally not be used to identify brain activity corresponding to activity of individual muscles. Further, it is believed that the spatial resolution of noninvasive brain imaging modalities is not sufficient to isolate neural activity related to individual muscles. However, this s ...
... brain activity can generally not be used to identify brain activity corresponding to activity of individual muscles. Further, it is believed that the spatial resolution of noninvasive brain imaging modalities is not sufficient to isolate neural activity related to individual muscles. However, this s ...
neurons
... – What does split brain mean? – Why did the woman have this procedure? – How were the woman’s language and perceptual abilities affected? – What do these cases show us about brain function? ...
... – What does split brain mean? – Why did the woman have this procedure? – How were the woman’s language and perceptual abilities affected? – What do these cases show us about brain function? ...
Understanding the brain by controlling neural activity
... development of more sophisticated methods for causal interference, such as nanostimulation and optogenetics, provide a more precise intervention with a greater flexibility. Nanostimulation permits activation of single brain cells in awake animals, facilitating the study of the importance of patterne ...
... development of more sophisticated methods for causal interference, such as nanostimulation and optogenetics, provide a more precise intervention with a greater flexibility. Nanostimulation permits activation of single brain cells in awake animals, facilitating the study of the importance of patterne ...
the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
... act directly on the pain receptors in the mouth and throat. The primary capsaicinoid, capsaicin, so hot that a single drop diluted in 100,000 drops of water will produce a blistering of the tongue. ...
... act directly on the pain receptors in the mouth and throat. The primary capsaicinoid, capsaicin, so hot that a single drop diluted in 100,000 drops of water will produce a blistering of the tongue. ...
Abnormal Brain Wiring as a Pathogenetic Mechanism in
... levels of connectivity of the left prefrontal cortex was found to be significantly correlated with negative symptoms, suggesting that a reduced functional coupling of prefrontal regions is related to more severe negative symptoms. Third, depressive symptoms were found to be related to lower levels o ...
... levels of connectivity of the left prefrontal cortex was found to be significantly correlated with negative symptoms, suggesting that a reduced functional coupling of prefrontal regions is related to more severe negative symptoms. Third, depressive symptoms were found to be related to lower levels o ...
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
... awareness are first processed in the brain. Mood and personality are mediated through the prefrontal cortex. This part of the brain is the center of higher cognitive and emotional functions. ...
... awareness are first processed in the brain. Mood and personality are mediated through the prefrontal cortex. This part of the brain is the center of higher cognitive and emotional functions. ...
Referring to Localized Cognitive Operations in
... (Bechtel & Richardson 1993; Bechtel & Abrahamsen 2005; Machamer, Darden, & Craver 2000). Differentiating parts and operations required the development of appropriate research techniques to decompose the brain structurally and functionally. Using staining techniques to differentiate the distribution ...
... (Bechtel & Richardson 1993; Bechtel & Abrahamsen 2005; Machamer, Darden, & Craver 2000). Differentiating parts and operations required the development of appropriate research techniques to decompose the brain structurally and functionally. Using staining techniques to differentiate the distribution ...
Functional magnetic resonance imaging

Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) is a functional neuroimaging procedure using MRI technology that measures brain activity by detecting associated changes in blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases.The primary form of fMRI uses the blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) contrast, discovered by Seiji Ogawa. This is a type of specialized brain and body scan used to map neural activity in the brain or spinal cord of humans or other animals by imaging the change in blood flow (hemodynamic response) related to energy use by brain cells. Since the early 1990s, fMRI has come to dominate brain mapping research because it does not require people to undergo shots, surgery, or to ingest substances, or be exposed to radiation, etc. Other methods of obtaining contrast are arterial spin labeling and diffusion MRI.The procedure is similar to MRI but uses the change in magnetization between oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood as its basic measure. This measure is frequently corrupted by noise from various sources and hence statistical procedures are used to extract the underlying signal. The resulting brain activation can be presented graphically by color-coding the strength of activation across the brain or the specific region studied. The technique can localize activity to within millimeters but, using standard techniques, no better than within a window of a few seconds.fMRI is used both in the research world, and to a lesser extent, in the clinical world. It can also be combined and complemented with other measures of brain physiology such as EEG and NIRS. Newer methods which improve both spatial and time resolution are being researched, and these largely use biomarkers other than the BOLD signal. Some companies have developed commercial products such as lie detectors based on fMRI techniques, but the research is not believed to be ripe enough for widespread commercialization.