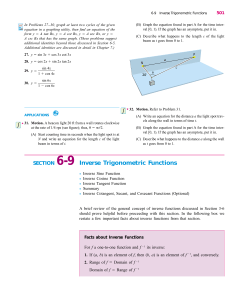
Solutions to Exercises, Section 2.1
... which equals 3. Thus each line parallel to it also has slope 3. The line containing the points (t, 2) and (3, 5) has slope ...
... which equals 3. Thus each line parallel to it also has slope 3. The line containing the points (t, 2) and (3, 5) has slope ...
Module 3 Lesson 7 - Peoria Public Schools
... • What do the partial products for 24 × 9 represent in the context of the word problem? • Talk to your partner about which method you prefer: writing the partial products or using a place value chart with disks? Is one of these methods easier for you to understand? Does one of them help you solve th ...
... • What do the partial products for 24 × 9 represent in the context of the word problem? • Talk to your partner about which method you prefer: writing the partial products or using a place value chart with disks? Is one of these methods easier for you to understand? Does one of them help you solve th ...
Time Series Prediction and Online Learning
... a hypothesis derived by application of an online-to-batch conversion technique to the sequence of hypotheses output by an online algorithm, in the general setting of a non-stationary non-mixing process? What other benefits can such combinations of the statistical learning and on-line learning tools ...
... a hypothesis derived by application of an online-to-batch conversion technique to the sequence of hypotheses output by an online algorithm, in the general setting of a non-stationary non-mixing process? What other benefits can such combinations of the statistical learning and on-line learning tools ...
Mathematical optimization

In mathematics, computer science and operations research, mathematical optimization (alternatively, optimization or mathematical programming) is the selection of a best element (with regard to some criteria) from some set of available alternatives.In the simplest case, an optimization problem consists of maximizing or minimizing a real function by systematically choosing input values from within an allowed set and computing the value of the function. The generalization of optimization theory and techniques to other formulations comprises a large area of applied mathematics. More generally, optimization includes finding ""best available"" values of some objective function given a defined domain (or a set of constraints), including a variety of different types of objective functions and different types of domains.