Problem Solving and Computers in a Learning Environment
... Modelling thinking, in the technical use of the term, refers to the translation of objects or phenomena from the real world into mathematical equations (mathematical models) or computer relations (simulation models). It is choosing an appropriate representation or modelling the relevant aspects of a ...
... Modelling thinking, in the technical use of the term, refers to the translation of objects or phenomena from the real world into mathematical equations (mathematical models) or computer relations (simulation models). It is choosing an appropriate representation or modelling the relevant aspects of a ...
Document
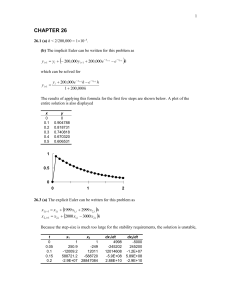
... Thus, to solve for the first time step, we substitute the initial conditions for the right-hand side and solve the 22 system of equations. The best way to do this is with LU decomposition since we will have to solve the system repeatedly. For the present case, because it’s easier to display, we wil ...
... Thus, to solve for the first time step, we substitute the initial conditions for the right-hand side and solve the 22 system of equations. The best way to do this is with LU decomposition since we will have to solve the system repeatedly. For the present case, because it’s easier to display, we wil ...
nature of metacognition in a dynamic geometry
... Lester (1985), I developed a model capturing together student’s cognitive and metacognitive behaviors when problem solving in DGS (Kuzle, 2011) and their complex interplay. On the contrary to Schoenfeld (1981, 1985) the planning/implementation episodes were separated into two episodes, as they do no ...
... Lester (1985), I developed a model capturing together student’s cognitive and metacognitive behaviors when problem solving in DGS (Kuzle, 2011) and their complex interplay. On the contrary to Schoenfeld (1981, 1985) the planning/implementation episodes were separated into two episodes, as they do no ...
Chapter 2: Equations, Inequalities and Problem Solving
... A car rental agency advertised renting a Buick Century for $24.95 per day and $0.29 per mile. If you rent this car for 2 days, how many whole miles can you drive on a $100 budget? 1.) Understand Read and reread the problem. Let’s propose that we drive a total of 100 miles over the 2 days. Then we ne ...
... A car rental agency advertised renting a Buick Century for $24.95 per day and $0.29 per mile. If you rent this car for 2 days, how many whole miles can you drive on a $100 budget? 1.) Understand Read and reread the problem. Let’s propose that we drive a total of 100 miles over the 2 days. Then we ne ...
Locality Preserving Hashing Kang Zhao, Hongtao Lu and Jincheng Mei
... be given by 12 (1 + yik ). Broadly, hashing methods can be roughly divided into two main categories (Gong and Lazebnik 2011; Liu et al. 2011): data-independent methods and data-dependent methods. Locality Sensitive Hashing (LSH) (Gionis et al. 1999) and its variants (Datar et al. 2004; Kulis, Jain, ...
... be given by 12 (1 + yik ). Broadly, hashing methods can be roughly divided into two main categories (Gong and Lazebnik 2011; Liu et al. 2011): data-independent methods and data-dependent methods. Locality Sensitive Hashing (LSH) (Gionis et al. 1999) and its variants (Datar et al. 2004; Kulis, Jain, ...
Free surface ow under gravity and surface tension due to an Applied
... Free surface flow due to an applied pressure distribution in the presence of a uniform stream has been a much-studied problem for more than a century, with applications to the forcing of water waves by atmospheric disturbances, or due to moving obstacles such as ships. For the two-dimensional flow o ...
... Free surface flow due to an applied pressure distribution in the presence of a uniform stream has been a much-studied problem for more than a century, with applications to the forcing of water waves by atmospheric disturbances, or due to moving obstacles such as ships. For the two-dimensional flow o ...
An Active Approach to Characterizing Dynamic Dependencies
... – compare to 140 potential dependencies (!) – one false negative most likely due to insufficient data – caveat: some glitches due to unmodeled interactions » manifested as small negative dependency strengths » solution: improve model or simply discard negative strengths ...
... – compare to 140 potential dependencies (!) – one false negative most likely due to insufficient data – caveat: some glitches due to unmodeled interactions » manifested as small negative dependency strengths » solution: improve model or simply discard negative strengths ...
Basis for the calculations of travel time curves in a 1D model
... the first arrival times, hence we are interested in the first point plotted at each of the receivers. The next step is to identify straight lines in our plot, or in other words, slopes and intercepts. By calculating the equation of the lines we are now able to find the slopes (hence the velocities) ...
... the first arrival times, hence we are interested in the first point plotted at each of the receivers. The next step is to identify straight lines in our plot, or in other words, slopes and intercepts. By calculating the equation of the lines we are now able to find the slopes (hence the velocities) ...