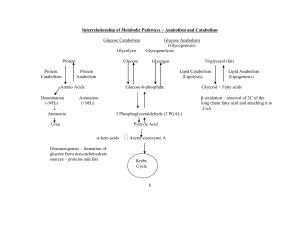
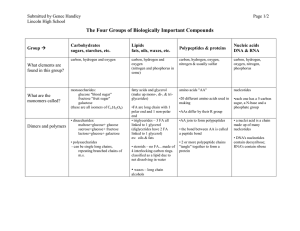
Gluconeogenesis
... Gluconeogenesis and starch/glycogen synthesis • In animals, lactate formed anaerobically in muscles is converted to glucose in liver and kidney and stored as glycogen or released as blood glucose. • In plants, G3P product of photosynthesis is converted to starch and stored in chloroplasts or conver ...
... Gluconeogenesis and starch/glycogen synthesis • In animals, lactate formed anaerobically in muscles is converted to glucose in liver and kidney and stored as glycogen or released as blood glucose. • In plants, G3P product of photosynthesis is converted to starch and stored in chloroplasts or conver ...
Diabetic Form
... _________Units if blood glucose is_________to_________mg/dl _________Units if blood glucose is_________to_________mg/dl _________Units if blood glucose is_________to_________mg/dl _________Units if blood glucose is_________to_________mg/dl Can student give own injections? ______yes ______no Can stud ...
... _________Units if blood glucose is_________to_________mg/dl _________Units if blood glucose is_________to_________mg/dl _________Units if blood glucose is_________to_________mg/dl _________Units if blood glucose is_________to_________mg/dl Can student give own injections? ______yes ______no Can stud ...
Endocrine Part 2 Powerpoint
... increased, body temperature increases, TSH inhibited • Glucose goes high: insulin released, glucose goes down, insulin inhibited • Glucose goes down: glucagon released, glucose goes ...
... increased, body temperature increases, TSH inhibited • Glucose goes high: insulin released, glucose goes down, insulin inhibited • Glucose goes down: glucagon released, glucose goes ...
Insulin-Dependent Diabetes - Wk 1-2
... Progressive abnormalities in β-cell function yield an apparent abrupt onset. This is due to the fact that clinically diagnosed hyperglycaemia is only present when 70-90% of β-cells have been damaged. Type I diabetes is often termed juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus as it commonly occurs during childh ...
... Progressive abnormalities in β-cell function yield an apparent abrupt onset. This is due to the fact that clinically diagnosed hyperglycaemia is only present when 70-90% of β-cells have been damaged. Type I diabetes is often termed juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus as it commonly occurs during childh ...
(i)
... 2. bio-electrical energy for transmission of nerve impulse or action potential along neuron. 3. heat energy for regulation of body temperature 4. other forms of energy for active transport e.g. absorption of foods in ileum, reabsorption in nephron of kidneys. TWO of the above forms. b. ATP is the ra ...
... 2. bio-electrical energy for transmission of nerve impulse or action potential along neuron. 3. heat energy for regulation of body temperature 4. other forms of energy for active transport e.g. absorption of foods in ileum, reabsorption in nephron of kidneys. TWO of the above forms. b. ATP is the ra ...
study guide - cvadultcma
... 6. What hormone is required for the normal use of glucose in the body? Insulin 7. The following instructions should be relayed to the patient regarding a fasting blood glucose test? Do not consume food or fluid (except water) for 12 hours before the test. 8. According to the American Diabetes Associ ...
... 6. What hormone is required for the normal use of glucose in the body? Insulin 7. The following instructions should be relayed to the patient regarding a fasting blood glucose test? Do not consume food or fluid (except water) for 12 hours before the test. 8. According to the American Diabetes Associ ...
Exercise 3 - HRD Press
... controlled by the supply of the simple sugar glucose. After eating, glucose levels in the blood rise. The pancreas excretes insulin to turn the excess glucose into glycogen, which is then stored by the liver. If glucose is consumed during exercise, the pancreas releases glucagons to turn glycogen in ...
... controlled by the supply of the simple sugar glucose. After eating, glucose levels in the blood rise. The pancreas excretes insulin to turn the excess glucose into glycogen, which is then stored by the liver. If glucose is consumed during exercise, the pancreas releases glucagons to turn glycogen in ...
study guide - cvadultcma
... 13. What term is used to describe an abnormally low level of glucose in the blood? hypoglycemia 14. What is the purpose of SMBG testing? To maintain good blood glucose control, to delay or prevent long-term complications of diabetes, to test blood glucose when a side effect common to diabetes occurs ...
... 13. What term is used to describe an abnormally low level of glucose in the blood? hypoglycemia 14. What is the purpose of SMBG testing? To maintain good blood glucose control, to delay or prevent long-term complications of diabetes, to test blood glucose when a side effect common to diabetes occurs ...
Laboratory Values
... Clinicians need to identify and classify systemic disorders and appropriately modify diagnosis and treatment planning in order to avoid systemic complications. Diagnosis is based on: previous history, medication lists, symptoms, clinical signs, clinical tests such as radiographs and laboratory data. ...
... Clinicians need to identify and classify systemic disorders and appropriately modify diagnosis and treatment planning in order to avoid systemic complications. Diagnosis is based on: previous history, medication lists, symptoms, clinical signs, clinical tests such as radiographs and laboratory data. ...
GlucoseHomeostasis1
... Write a paragraph in which you 1) identify the major objectives of the paper (the most important questions it addresses), and 2) a concise summary of their most important findings. Bring this text with you to lab, ready to turn in to the lab instructor. ...
... Write a paragraph in which you 1) identify the major objectives of the paper (the most important questions it addresses), and 2) a concise summary of their most important findings. Bring this text with you to lab, ready to turn in to the lab instructor. ...
Lecture 3b powerpoint
... -used to be called insulin dependent diabetes mellitus or juvenile diabetes -no cure at the moment -type 2 diabetes -insulin resistance followed by beta cell failure -used to be called-non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus(NIDDM) or adult onset diabetes -no cure at the moment -gestational diabetes ...
... -used to be called insulin dependent diabetes mellitus or juvenile diabetes -no cure at the moment -type 2 diabetes -insulin resistance followed by beta cell failure -used to be called-non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus(NIDDM) or adult onset diabetes -no cure at the moment -gestational diabetes ...
A1981LY47200002
... development of understanding of the "As a graduate student at Camprocess of fuel selection in mammalian bridge, I had worked on the rat muscle. I hope that it adequately diaphragm assay for insulin and anti-inrepresented and acknowledged the sulin factors in blood plasma. This excontribution of coll ...
... development of understanding of the "As a graduate student at Camprocess of fuel selection in mammalian bridge, I had worked on the rat muscle. I hope that it adequately diaphragm assay for insulin and anti-inrepresented and acknowledged the sulin factors in blood plasma. This excontribution of coll ...
Name the hormone responsible for the
... • What are glucose transporters (GLUT), how are they important, and where are they found? How does insulin act on these transporters to increase glucose uptake by insulin-sensitive cells? Are all cells insulinsensitive? Defend your answer. ...
... • What are glucose transporters (GLUT), how are they important, and where are they found? How does insulin act on these transporters to increase glucose uptake by insulin-sensitive cells? Are all cells insulinsensitive? Defend your answer. ...
glucose
... The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM is primarily responsible for regulating blood glucose. The two main hormones are INSULIN and GLUCAGON. ...
... The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM is primarily responsible for regulating blood glucose. The two main hormones are INSULIN and GLUCAGON. ...
Lab Blood Glucose & Diabetes
... – Glucagon signals liver cells to break down glycogen into glucose and release glucose into blood – Signals liver cells to convert amino acids and glycerol into glucose and release glucose into blood ...
... – Glucagon signals liver cells to break down glycogen into glucose and release glucose into blood – Signals liver cells to convert amino acids and glycerol into glucose and release glucose into blood ...
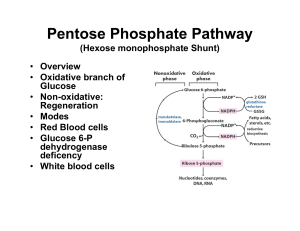
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
... sex-linked trait (11% of NA african americans, 5-10% of mediteranean and Middle eastern heritage cause oxidative stress under certain environmental conditions low levels of glutathione another genetic trait favored in ...
... sex-linked trait (11% of NA african americans, 5-10% of mediteranean and Middle eastern heritage cause oxidative stress under certain environmental conditions low levels of glutathione another genetic trait favored in ...
tAs
... antigen causes an immune response to produce antibodies specific for that antigen; antibodies produced in B-lymphocytes; B-lymphocytes produced in bone marrow; carried in blood; antigen presenting cell / helper T cell present antigen to B cell; ...
... antigen causes an immune response to produce antibodies specific for that antigen; antibodies produced in B-lymphocytes; B-lymphocytes produced in bone marrow; carried in blood; antigen presenting cell / helper T cell present antigen to B cell; ...
Metabolic Changes during Starvation
... phase’ and a delayed or ‘protein-sparing phase’ may be identified. The early response to starvation is concerned with the maintenance of adequate glucose release from the liver so as to meet the on-going needs of the brain. This is achieved by stimulation of hepatic glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesi ...
... phase’ and a delayed or ‘protein-sparing phase’ may be identified. The early response to starvation is concerned with the maintenance of adequate glucose release from the liver so as to meet the on-going needs of the brain. This is achieved by stimulation of hepatic glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesi ...
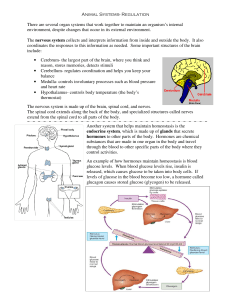
Animal Systems- Regulation There are several organ systems that
... result, the lungs release the excess carbon dioxide into the environment, and at the same time pick up more oxygen from the environment. ...
... result, the lungs release the excess carbon dioxide into the environment, and at the same time pick up more oxygen from the environment. ...
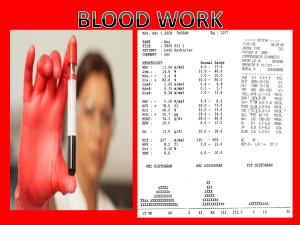
Blood Work - Mr. Lesiuk
... • Blood work is collected first thing in the morning after 8 hours of fasting • Fasting, as the name suggests, means refraining from eating of drinking any liquids other than water for eight hours. It is used as a test for diabetes. If Values • After fasting, a carbohydrate metabolism test is conduc ...
... • Blood work is collected first thing in the morning after 8 hours of fasting • Fasting, as the name suggests, means refraining from eating of drinking any liquids other than water for eight hours. It is used as a test for diabetes. If Values • After fasting, a carbohydrate metabolism test is conduc ...
5. Pancreas: Glucagon
... Type II Diabetes Mellitus • non-insulin-dependent (NIDDM; formerly mature-onset diabetes) • usually starts after age 40 • insulin levels are normal or elevated, but peripheral tissue become less sensitive to it • 25-30% of Americans carry gene that predisposes them to NIDDM, more likely in over-wei ...
... Type II Diabetes Mellitus • non-insulin-dependent (NIDDM; formerly mature-onset diabetes) • usually starts after age 40 • insulin levels are normal or elevated, but peripheral tissue become less sensitive to it • 25-30% of Americans carry gene that predisposes them to NIDDM, more likely in over-wei ...