article - British Academy
... enough for us to conclude that this is somehow the normal state of affairs, for this is what we are used to; but historically things have been otherwise and, in this regard at least, we should not permit the present to shape our expectations about the past. The dominant pattern we see throughout the ...
... enough for us to conclude that this is somehow the normal state of affairs, for this is what we are used to; but historically things have been otherwise and, in this regard at least, we should not permit the present to shape our expectations about the past. The dominant pattern we see throughout the ...
The Study of Molecular Evidences for Human Evolution, Gene Flow
... humans in Eurasia. Dart’s findings were dismissed for quite some time and then eventually accepted by the scientific community later in the twentieth century. Successively in late 1950s a number of other fossil bones were discovered in a cave from the northeast of Johannesburg, Africa which emphasiz ...
... humans in Eurasia. Dart’s findings were dismissed for quite some time and then eventually accepted by the scientific community later in the twentieth century. Successively in late 1950s a number of other fossil bones were discovered in a cave from the northeast of Johannesburg, Africa which emphasiz ...
What happened in the origin of human consciousness?
... At some point in its evolutionary history, our species Homo sapiens ceased to be a nonlinguistic, nonsymbolic organism, living in the world as presented to it by Nature, and instead began to exist in a world that it reconstructs in its own mind. Most scientists since Darwin have been content to expl ...
... At some point in its evolutionary history, our species Homo sapiens ceased to be a nonlinguistic, nonsymbolic organism, living in the world as presented to it by Nature, and instead began to exist in a world that it reconstructs in its own mind. Most scientists since Darwin have been content to expl ...
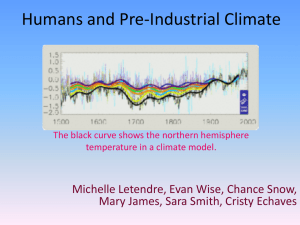
Humans and Preindustrial Climate
... (woodlands, grasslands, river margins) This leads to a different Hypothesis… The The Variability Selection Hypothesis: Rapid evolution occurred because rapidly changing climate put new demands on our ancestors, which favored those who were more adaptable. ...
... (woodlands, grasslands, river margins) This leads to a different Hypothesis… The The Variability Selection Hypothesis: Rapid evolution occurred because rapidly changing climate put new demands on our ancestors, which favored those who were more adaptable. ...
The Evolutionary Origins of Human Culture
... genus, Homo habilis, had evolved into Homo erectus, which extended the hominin range out of Africa. H. erectus had evolved into archaic H. sapiens by 300,000 years ago. Most scientists tend to exclude the Neandertals as ancestors of modern humans. Biological and cultural changes eventually led to an ...
... genus, Homo habilis, had evolved into Homo erectus, which extended the hominin range out of Africa. H. erectus had evolved into archaic H. sapiens by 300,000 years ago. Most scientists tend to exclude the Neandertals as ancestors of modern humans. Biological and cultural changes eventually led to an ...
S292 Explaining the emergence of humans
... African apes. Natural selection as a process is applicable to humans, as it is to all species, and the gulf between humans and other species is not especially great. Nevertheless, the big question for palaeoanthropologists today remains the same as it was in the 19th century: What makes a human? For ...
... African apes. Natural selection as a process is applicable to humans, as it is to all species, and the gulf between humans and other species is not especially great. Nevertheless, the big question for palaeoanthropologists today remains the same as it was in the 19th century: What makes a human? For ...
Grandmothering
... • Extended PRLS is unique to humans in this sense, because typically female nonhuman primates do not live for an extended amount of time after they stop reproducing. • Evidence for menopause has been exhibited in rhesus macaques and Japanese macaques as well as other species such as guppies and whal ...
... • Extended PRLS is unique to humans in this sense, because typically female nonhuman primates do not live for an extended amount of time after they stop reproducing. • Evidence for menopause has been exhibited in rhesus macaques and Japanese macaques as well as other species such as guppies and whal ...
versión PDF - U. de Chile
... attachment of powerful chewing muscles; and huge, thickly enameled molar teeth. (This is not to say that australopithecines never ate meat. They almost certainly did on occasion, just as chimps do today.) In contrast, early members of the genus Homo, which descended from the gracile australopithecin ...
... attachment of powerful chewing muscles; and huge, thickly enameled molar teeth. (This is not to say that australopithecines never ate meat. They almost certainly did on occasion, just as chimps do today.) In contrast, early members of the genus Homo, which descended from the gracile australopithecin ...
a revision of his definition and a new estimation of his emergence date
... fact the age of some erectus specimens show that erectus had seen life until about 30,000 years. Third, such a classification of species within Homo genus established on the basis of morphological features could not be maintained. In fact, the first note is based on the finding of the Wood and Colla ...
... fact the age of some erectus specimens show that erectus had seen life until about 30,000 years. Third, such a classification of species within Homo genus established on the basis of morphological features could not be maintained. In fact, the first note is based on the finding of the Wood and Colla ...
Primates - Cloudfront.net
... • Humans, apes, and most monkeys belong to a group called anthropoids, which means humanlike primates • This group split very early in its evolutionary history into two major branches: These branches became separated from each other as drifting continents moved apart – One branch, found today in Cen ...
... • Humans, apes, and most monkeys belong to a group called anthropoids, which means humanlike primates • This group split very early in its evolutionary history into two major branches: These branches became separated from each other as drifting continents moved apart – One branch, found today in Cen ...
Homo - Carol Lee Lab
... neanderthalensis. Because of its larger brain, we assumed that it had to be the same species as us ...
... neanderthalensis. Because of its larger brain, we assumed that it had to be the same species as us ...
Homo Habilis: Handy Man
... • This group had been around longer than the Australopithecus Afarensis and Homo Hablis. • This hominid group was discovered in 1891 in Java, Asia. • The Upright Man has been around longer than any other hominid group. • Scientists believe they were the first hominid group to migrate out of Africa. ...
... • This group had been around longer than the Australopithecus Afarensis and Homo Hablis. • This hominid group was discovered in 1891 in Java, Asia. • The Upright Man has been around longer than any other hominid group. • Scientists believe they were the first hominid group to migrate out of Africa. ...
historyppt-131202092752-phpapp02
... The most significant of these adaptations are • 1. bipedalism (1.9 million years ago), • 2. increased brain size, • 3. lengthened ontogeny (gestation and infancy), • 4. decreased sexual dimorphism. ...
... The most significant of these adaptations are • 1. bipedalism (1.9 million years ago), • 2. increased brain size, • 3. lengthened ontogeny (gestation and infancy), • 4. decreased sexual dimorphism. ...
the hominization process - European Anthropological Association
... words, tool-use and tool-making developed before hominid brain capacity had undergone remarkable increase. The old idea that a large brain and associated high intelligence were prerequisites for tool use is no longer tenable. The use of tools by primitive hominids may, in fact, have been a major fac ...
... words, tool-use and tool-making developed before hominid brain capacity had undergone remarkable increase. The old idea that a large brain and associated high intelligence were prerequisites for tool use is no longer tenable. The use of tools by primitive hominids may, in fact, have been a major fac ...
Evolution - Rosehill
... teeth, fragments of the arm, thigh bone, and a finger, from at least five different individuals have been found. The size and morphology of the teeth are intermediate between those of a chimpanzee and those of a human. ...
... teeth, fragments of the arm, thigh bone, and a finger, from at least five different individuals have been found. The size and morphology of the teeth are intermediate between those of a chimpanzee and those of a human. ...
Ecological dominance and the final sprint in hominid evolution
... Meat consumption? To find the origin of the uniquely human trends towards increasing brain size and probably the use of language we have to go back to 2.5 million years ago, when both the genus Homo and Paranthropus arose from some Australopithecine ancestor in a reaction to the first ice age. Both ...
... Meat consumption? To find the origin of the uniquely human trends towards increasing brain size and probably the use of language we have to go back to 2.5 million years ago, when both the genus Homo and Paranthropus arose from some Australopithecine ancestor in a reaction to the first ice age. Both ...
You Light Up My Life
... first species to evolve in Central Africa about 6 to 7 million years ago, during the time when the ancestors of humans were becoming distinct from the apes. Australopithecus afarensis is one of the species that walked upright across the African plain some 3.7 million years ago. ...
... first species to evolve in Central Africa about 6 to 7 million years ago, during the time when the ancestors of humans were becoming distinct from the apes. Australopithecus afarensis is one of the species that walked upright across the African plain some 3.7 million years ago. ...
Human evolution (wikipedia)
... known hominids, it was nicknamed 'handy man' by discoverer Louis Leakey due to its association with stone tools. Some scientists have proposed moving this species out of Homo and into Australopithecus due to the morphology of its skeleton being more adapted to living on trees rather than to moving o ...
... known hominids, it was nicknamed 'handy man' by discoverer Louis Leakey due to its association with stone tools. Some scientists have proposed moving this species out of Homo and into Australopithecus due to the morphology of its skeleton being more adapted to living on trees rather than to moving o ...
Untitled - Serge De Vrindt
... the three living species, bulldozes whole stands of trees and turns bush and forest into savannah or even desert, affecting the livelihood and abundance of the other mammals that live in the same habitat; so every year hundreds of elephants are shot in southern African game reserves and national par ...
... the three living species, bulldozes whole stands of trees and turns bush and forest into savannah or even desert, affecting the livelihood and abundance of the other mammals that live in the same habitat; so every year hundreds of elephants are shot in southern African game reserves and national par ...
Origin and Dispersal of Modern Humans
... – Klasies River Mouth and Border Cave all dated to the later time period. • Modern humans appeared in East Africa at about 200,000 ya, and migrated to southern Africa by 100,000 ya. • Consistent wi ...
... – Klasies River Mouth and Border Cave all dated to the later time period. • Modern humans appeared in East Africa at about 200,000 ya, and migrated to southern Africa by 100,000 ya. • Consistent wi ...
Paleoanth - HCC Learning Web
... • The bonobo has also been used, it is equally related to us, because these two species split from each other AFTER the hominin line had already diverged from them. ...
... • The bonobo has also been used, it is equally related to us, because these two species split from each other AFTER the hominin line had already diverged from them. ...
Homo erectus

Homo erectus (meaning ""upright man"", from the Latin ērigere, ""to put up, set upright"") is an extinct species of hominid that lived throughout most of the Pleistocene geological epoch. Its earliest fossil evidence dates to 1.9 million years ago and the most recent to 70,000 years ago. Its extinction is linked by some scientists to the Toba super-eruption catastrophe, but no sufficient case has been made to date for the idea. It is generally thought that H. erectus originated in Africa and spread from there, migrating throughout Eurasia as far as Georgia, India, Sri Lanka, China and Java. But other scientists posit that the species rose first, or separately, in Asia.Debate also continues about the classification, ancestry, and progeny of Homo erectus, especially vis-à-vis Homo ergaster, with two major positions: 1) H. erectus is the same species as H. ergaster, and thereby H. erectus is a direct ancestor of the later hominins including Homo heidelbergensis, Homo neanderthalensis, and Homo sapiens; or, 2) it is in fact an Asian species distinct from African H. ergaster.And there is another view—an alternative to 1): some palaeoanthropologists consider H. ergaster to be a variety, that is, the ""African"" variety, of H. erectus, and they offer the labels ""Homo erectus sensu stricto"" (strict sense) for the Asian species and ""Homo erectus sensu lato"" (broad sense) for the greater species comprising both Asian and African populations.A new debate appeared in 2013, with the documentation of the Dmanisi skulls. Considering the large morphological variation among all Dmanisi skulls, researchers now suggest that several early human ancestors variously classified, for example, as Homo ergaster, or Homo rudolfensis, and perhaps even Homo habilis, should instead be designated as Homo erectus.