Human Origins and Intelligent Design*
... ancestors of chimpanzees and other extant hominoids. However, there are some fossils of "hominids" which some paleoanthropologists believe represent very close relatives or direct ancestors of humans. The vast majority of hominid fossils have been divided into two basic categories: those of the genu ...
... ancestors of chimpanzees and other extant hominoids. However, there are some fossils of "hominids" which some paleoanthropologists believe represent very close relatives or direct ancestors of humans. The vast majority of hominid fossils have been divided into two basic categories: those of the genu ...
Homo - Carol Lee Lab
... The hyoid is a small bone that connects the musculature of the tongue and the larynx, and allows a wider range of tongue and laryngeal movements. The bone found in Neanderthals is virtually identical to that of modern humans. The presence of this bone implies that structured speech was anatomically ...
... The hyoid is a small bone that connects the musculature of the tongue and the larynx, and allows a wider range of tongue and laryngeal movements. The bone found in Neanderthals is virtually identical to that of modern humans. The presence of this bone implies that structured speech was anatomically ...
Ecological dominance and the final sprint in hominid evolution
... Homo sapiens sapiens can we discern very clear traces of mass hunting techniques that probably have driven many prey species into extinction ("prehistoric overkill", Martin, 1967). At the same time many large species of mammals go extinct. Although some of these extinction coincides with climatic ch ...
... Homo sapiens sapiens can we discern very clear traces of mass hunting techniques that probably have driven many prey species into extinction ("prehistoric overkill", Martin, 1967). At the same time many large species of mammals go extinct. Although some of these extinction coincides with climatic ch ...
Does cultural evolution need matriliny?
... unlikely that syntactical speech – a low-cost, intrinsically unreliable system of communication – could have evolved in our own species independently of comparable confidence-building strategies and displays of social commitment rendering such signals worth listening to (Deacon 1997; Knight 1998). I ...
... unlikely that syntactical speech – a low-cost, intrinsically unreliable system of communication – could have evolved in our own species independently of comparable confidence-building strategies and displays of social commitment rendering such signals worth listening to (Deacon 1997; Knight 1998). I ...
Survival of the Adaptable - Smithsonian`s Human Origins
... Without medicine, even minor infirmities could be fatal. The robust appearance of the Kabwe cranium from Zambia belies the possibility that this Homo heidelbergensis individual died from a small but fatal infection. This individual is one of the oldest known to have had tooth cavities, including ten ...
... Without medicine, even minor infirmities could be fatal. The robust appearance of the Kabwe cranium from Zambia belies the possibility that this Homo heidelbergensis individual died from a small but fatal infection. This individual is one of the oldest known to have had tooth cavities, including ten ...
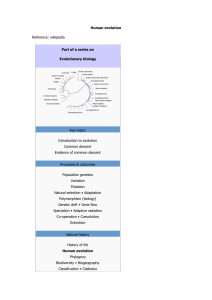
Human evolution (wikipedia)
... Family tree showing the extant hominoids: humans (genus Homo), chimpanzees and bonobos (genus Pan), gorillas (genus Gorilla), orangutans (genus Pongo), and gibbons (four genera of the family Hylobatidae: Hylobates, Hoolock, Nomascus, and Symphalangus). All except gibbons are hominids. The evidence ...
... Family tree showing the extant hominoids: humans (genus Homo), chimpanzees and bonobos (genus Pan), gorillas (genus Gorilla), orangutans (genus Pongo), and gibbons (four genera of the family Hylobatidae: Hylobates, Hoolock, Nomascus, and Symphalangus). All except gibbons are hominids. The evidence ...
Explaining robust humans
... not be so. But a longer maturation period would not necessarily follow from changes in developmental processes, nor is it necessarily a concomitant to longevity. As distinct from Cuozzo, I believe that the key features of the Neandertal morphology arose (influenced to varying degrees by environmenta ...
... not be so. But a longer maturation period would not necessarily follow from changes in developmental processes, nor is it necessarily a concomitant to longevity. As distinct from Cuozzo, I believe that the key features of the Neandertal morphology arose (influenced to varying degrees by environmenta ...
Homo erectus/ergaster and Out of Africa: Recent Developments in
... hominids who were responsible for the first movement “Out of Africa” and their possible timescal for the migration is reviewed here in the light of recent developments. There was a general concept that the early homo did not move outside Africa until 1 Ma ago, which has been changed due to various n ...
... hominids who were responsible for the first movement “Out of Africa” and their possible timescal for the migration is reviewed here in the light of recent developments. There was a general concept that the early homo did not move outside Africa until 1 Ma ago, which has been changed due to various n ...
The New Science of Human Evolution
... and chimp DNA differ by no more than 1.2 percent, and DNA changes at a fairly regular rate. That lets scientists use this rate to calibrate a "molecular clock" whose tick-tocks measure how long ago a genetic change occurred. The fact that the DNA of living chimps and humans differ by about 35 millio ...
... and chimp DNA differ by no more than 1.2 percent, and DNA changes at a fairly regular rate. That lets scientists use this rate to calibrate a "molecular clock" whose tick-tocks measure how long ago a genetic change occurred. The fact that the DNA of living chimps and humans differ by about 35 millio ...
What happened in the origin of human consciousness?
... At some point in its evolutionary history, our species Homo sapiens ceased to be a nonlinguistic, nonsymbolic organism, living in the world as presented to it by Nature, and instead began to exist in a world that it reconstructs in its own mind. Most scientists since Darwin have been content to expl ...
... At some point in its evolutionary history, our species Homo sapiens ceased to be a nonlinguistic, nonsymbolic organism, living in the world as presented to it by Nature, and instead began to exist in a world that it reconstructs in its own mind. Most scientists since Darwin have been content to expl ...
Untitled - Serge De Vrindt
... prove to be, let us say, as nearly unlinear in reality as human evolution was held to be up until the 1970s, when the single-species model finally became untenable. But, as we will see presently, the single-species hypothesis has reared its head again, though not through an analysis of fossil materi ...
... prove to be, let us say, as nearly unlinear in reality as human evolution was held to be up until the 1970s, when the single-species model finally became untenable. But, as we will see presently, the single-species hypothesis has reared its head again, though not through an analysis of fossil materi ...
Homo Habilis: Handy Man
... • 1974 – Donald Johnson discovered a partial skeleton in Africa. • Johnson found a piece of a skull, a jawbone, a rib, and leg bones. • After careful analysis, Johnson concluded that the bones belonged to a female hominid who lived more that 3 MILLION years ago. • Johnson called her Lucy. ...
... • 1974 – Donald Johnson discovered a partial skeleton in Africa. • Johnson found a piece of a skull, a jawbone, a rib, and leg bones. • After careful analysis, Johnson concluded that the bones belonged to a female hominid who lived more that 3 MILLION years ago. • Johnson called her Lucy. ...
Chapter 23: How Humans Evolved
... We now know australopithecines from hundreds of fossils. The structure of these fossils clearly indicates that australopithecines walked upright. These early hominids weighed about 18 kilograms and were about 1 meter tall. Their dentition was distinctly hominid, but their brains were not any larger ...
... We now know australopithecines from hundreds of fossils. The structure of these fossils clearly indicates that australopithecines walked upright. These early hominids weighed about 18 kilograms and were about 1 meter tall. Their dentition was distinctly hominid, but their brains were not any larger ...
in the history of life on Earth
... Largely intact skeleton discovered in Ethiopia in the 1970s Bipedal (known from pelvic structure) Long arms, short legs, grasping feet Brain size similar to chimpanzee 450 cc (Homo sapiens is 1,400 cc) The Evolution of Human Beings ...
... Largely intact skeleton discovered in Ethiopia in the 1970s Bipedal (known from pelvic structure) Long arms, short legs, grasping feet Brain size similar to chimpanzee 450 cc (Homo sapiens is 1,400 cc) The Evolution of Human Beings ...
The evoluTion of life
... similar to modern humans, but they are often called archaic Homo sapiens because there are physical differences between them and modern humans. Their mean brain size of 1,220 ml was about 85 per cent that of modern humans. The best-known subset of these archaic humans is the Neanderthals, who diverg ...
... similar to modern humans, but they are often called archaic Homo sapiens because there are physical differences between them and modern humans. Their mean brain size of 1,220 ml was about 85 per cent that of modern humans. The best-known subset of these archaic humans is the Neanderthals, who diverg ...
the hominization process - European Anthropological Association
... adaptation to nonarboreal ecological niches were more important for early hominid evolution. However these divergent views are ultimately resolved, it is interesting to learn how far back human technology and culture can be traced. ...
... adaptation to nonarboreal ecological niches were more important for early hominid evolution. However these divergent views are ultimately resolved, it is interesting to learn how far back human technology and culture can be traced. ...
HUMAN EVOLUTION CART
... years, fossils representing this species have been unearthed and studied by a large international team with diverse areas of expertise. In the October 2, 2009 issue of Science, Ardipithecus ramidus was described in great detail. To the surprise of many researchers, the female skeleton of Ar. ramidus ...
... years, fossils representing this species have been unearthed and studied by a large international team with diverse areas of expertise. In the October 2, 2009 issue of Science, Ardipithecus ramidus was described in great detail. To the surprise of many researchers, the female skeleton of Ar. ramidus ...
historyppt-131202092752-phpapp02
... • The other theory is the multiregional model, which states that development from earlier hominids to modern humans occurred in different locations in Africa, Asia, and Europe at different times. ...
... • The other theory is the multiregional model, which states that development from earlier hominids to modern humans occurred in different locations in Africa, Asia, and Europe at different times. ...
Human Evolution - Princeton University Press
... however, mainly in Africa and later in Europe and West Asia, people shaped core tools into symmetrical tools with long edges, called hand axes. The resulting Acheulean stone industry persisted for some 1.3 million years. Along with stone, archaeologists know that Pleistocene humans often used fire, ...
... however, mainly in Africa and later in Europe and West Asia, people shaped core tools into symmetrical tools with long edges, called hand axes. The resulting Acheulean stone industry persisted for some 1.3 million years. Along with stone, archaeologists know that Pleistocene humans often used fire, ...
article - British Academy
... the sum of its parts. Particular aspects of the individual genome cannot be differentially passed along to the next generation in isolation from others. Those specific attributes that we can, with sufficient ingenuity, characterise as ‘adaptations,’ are strongly, sometimes indissolubly, linked with ...
... the sum of its parts. Particular aspects of the individual genome cannot be differentially passed along to the next generation in isolation from others. Those specific attributes that we can, with sufficient ingenuity, characterise as ‘adaptations,’ are strongly, sometimes indissolubly, linked with ...
Origin and Dispersal of Modern Humans
... – By 50,000 y.a., Sahul, the area including New Guinea and Australia, was inhabited by modern humans. – Archeological sites in Australia: 55,000 y.a. Human fossils: 30,000 y.a. – Earliest dat ...
... – By 50,000 y.a., Sahul, the area including New Guinea and Australia, was inhabited by modern humans. – Archeological sites in Australia: 55,000 y.a. Human fossils: 30,000 y.a. – Earliest dat ...
Human Evolution - Professor Sherry Bowen
... thickened brow ridges were reported to be similar to those of some later fossil hominids (notably Homo erectus), whereas this morphology differs from that observed in all australopithecines, most fossil hominids and extant humans. ...
... thickened brow ridges were reported to be similar to those of some later fossil hominids (notably Homo erectus), whereas this morphology differs from that observed in all australopithecines, most fossil hominids and extant humans. ...
Ch 22 ppt
... • Briefly describe the following early hominins: Orrorin, Ardipithecus, and Australopithecus anamensis, A. afarensis, and A. africanus • Distinguish among the following members of genus Homo: H. habilis, H. ergaster, H. erectus, H. antecessor, H. heidelbergensis, H. neanderthalensis, and H. sapiens ...
... • Briefly describe the following early hominins: Orrorin, Ardipithecus, and Australopithecus anamensis, A. afarensis, and A. africanus • Distinguish among the following members of genus Homo: H. habilis, H. ergaster, H. erectus, H. antecessor, H. heidelbergensis, H. neanderthalensis, and H. sapiens ...
A. afarensis
... thickened brow ridges were reported to be similar to those of some later fossil hominids (notably Homo erectus), whereas this morphology differs from that observed in all australopithecines, most fossil hominids and extant humans. ...
... thickened brow ridges were reported to be similar to those of some later fossil hominids (notably Homo erectus), whereas this morphology differs from that observed in all australopithecines, most fossil hominids and extant humans. ...
Teaching Human Evolution - the Biology Department
... and skull bones contrast with their stout but small bodies. There are few limb bones for these forms, but in body proportions they were similar to Australopithecus africanus. They are found mainly in deposits of former open, bushy grasslands. Early Homo Homo habilis remains have been found in Tanzan ...
... and skull bones contrast with their stout but small bodies. There are few limb bones for these forms, but in body proportions they were similar to Australopithecus africanus. They are found mainly in deposits of former open, bushy grasslands. Early Homo Homo habilis remains have been found in Tanzan ...
Homo heidelbergensis

Homo heidelbergensis – sometimes called Homo rhodesiensis – is an extinct species of the genus Homo which lived in Africa, Europe and western Asia between 600 and 200 thousand years ago. Its brain was nearly as large as that of a modern Homo sapiens. First discovered near Heidelberg in Germany in 1907, it was described and named by Otto Schoetensack.Neanderthals, Denisovans, and modern humans (H. s. sapiens) are all descended from H. heidelbergensis. Between 300,000 and 400,000 years ago, an ancestral group of H. heidelbergensis became independent of others shortly after they had left Africa. One group branched northwest into Europe and West Asia, and eventually evolved into Neanderthals. The other group ventured eastwards throughout Asia, eventually developing into Denisovans. H. heidelbergensis evolved into H. sapiens approximately 130,000 years ago.