Fast-Acting, Long Lasting Soil Conditioner
... contains sulfates or phosphates, as it will reduce the effectiveness of Remediator. Can I apply liquid or granular fertilizer before or after using Remediator?: Yes. Remediator also works very well when incorporated with organic soil amendments. Can Remediator be used on food-bearing plants and tree ...
... contains sulfates or phosphates, as it will reduce the effectiveness of Remediator. Can I apply liquid or granular fertilizer before or after using Remediator?: Yes. Remediator also works very well when incorporated with organic soil amendments. Can Remediator be used on food-bearing plants and tree ...
15 mts and erosion handout
... b. Some of this sinks into the ground through the soil (seeps) c. It keeps sinking and then ____________________________________________ d. Travels all the way down to a layer of rock that it can’t pass through o This layer is considered _____________________________ ( ...
... b. Some of this sinks into the ground through the soil (seeps) c. It keeps sinking and then ____________________________________________ d. Travels all the way down to a layer of rock that it can’t pass through o This layer is considered _____________________________ ( ...
Chapter One
... plants with all the water the plant needs – Roots are the best water absorbing body . ...
... plants with all the water the plant needs – Roots are the best water absorbing body . ...
pdf version
... impose on agriculture activities through such factors as erosion, soil thickness, angle of slope and salinity, can be studied on a broad scale or at the micro-level. If one looks at the soil potentially of Iran (see Figure 1), one is struck by the fact that the areas possessing few or no soil limita ...
... impose on agriculture activities through such factors as erosion, soil thickness, angle of slope and salinity, can be studied on a broad scale or at the micro-level. If one looks at the soil potentially of Iran (see Figure 1), one is struck by the fact that the areas possessing few or no soil limita ...
APES 10 Things-Weathering and Erosion
... Rock Cycle- weathering and erosion are important to creation of sedimentary rock 4. Weathering- breaks down rocks into loose material, aka sediments. 5. Erosion- moves the sediment to a location conducive to creation of sedimentary rocks 6. Material cycling- long term loops of every cycle- Phosphoru ...
... Rock Cycle- weathering and erosion are important to creation of sedimentary rock 4. Weathering- breaks down rocks into loose material, aka sediments. 5. Erosion- moves the sediment to a location conducive to creation of sedimentary rocks 6. Material cycling- long term loops of every cycle- Phosphoru ...
WeatheringandErosion
... Soil horizons • Horizon A – top layer of soil – litter of leaves twigs and other organic material – litter prevents erosion – topsoil – dark and fertile • Horizon B – below A – lighter in color – no litter – less fertile – leaching – removal of dissolved minerals – move from A to B • Horizon C - bo ...
... Soil horizons • Horizon A – top layer of soil – litter of leaves twigs and other organic material – litter prevents erosion – topsoil – dark and fertile • Horizon B – below A – lighter in color – no litter – less fertile – leaching – removal of dissolved minerals – move from A to B • Horizon C - bo ...
Chapter 4 Notes: Weathering and Soil
... • The oxygen in air is also involved in chemical weathering. • Many common minerals contain iron. When these minerals dissolve in water, oxygen in the air and the water combines to produce rust. ...
... • The oxygen in air is also involved in chemical weathering. • Many common minerals contain iron. When these minerals dissolve in water, oxygen in the air and the water combines to produce rust. ...
A: Q: What Is a Watershed?
... fun also picks up and suspends material, carrying everything from soil to gravel to trash and pollutants. Sediment, trash, and even biological organisms are transported until they are deposited in slowermoving sections of a watershed. In addition to its ability to transport materials, water—often ca ...
... fun also picks up and suspends material, carrying everything from soil to gravel to trash and pollutants. Sediment, trash, and even biological organisms are transported until they are deposited in slowermoving sections of a watershed. In addition to its ability to transport materials, water—often ca ...
Back To Organic Farming
... The top 9 inches of our soil is where plant growth is sustained and therefore this is the area that is the mainspring of our agricultural production. Our health and indeed, our life itself depend on the change taking place in these 9 inches of soil. According to Nature’s design, trees and the ’micro ...
... The top 9 inches of our soil is where plant growth is sustained and therefore this is the area that is the mainspring of our agricultural production. Our health and indeed, our life itself depend on the change taking place in these 9 inches of soil. According to Nature’s design, trees and the ’micro ...
Chapter 5, Lesson 4
... How might building dams damage soil? The water and nutrient rich sediments held in a dam might not be available to plants downriver, so these plants might die. With less water and less plant life, soil can become dry, and wind can blow it away. ...
... How might building dams damage soil? The water and nutrient rich sediments held in a dam might not be available to plants downriver, so these plants might die. With less water and less plant life, soil can become dry, and wind can blow it away. ...
organic - Txstate
... Size of the soil particles How much organic matter is in the soil The minerals that make up the soil ...
... Size of the soil particles How much organic matter is in the soil The minerals that make up the soil ...
Soil Water
... 2. Weight of cylinder + wet soil = 1000 g 3. Weight of cylinder + oven dry (1050C) soil = 860 g Volume of cylinder = p*r2*h = 3.14*(7.6/2)2*7.6 = 345 cm3 Weight of wet soil = 1000 – 300 = 700 g Weight of dry soil = 860 – 300 = 560 g ...
... 2. Weight of cylinder + wet soil = 1000 g 3. Weight of cylinder + oven dry (1050C) soil = 860 g Volume of cylinder = p*r2*h = 3.14*(7.6/2)2*7.6 = 345 cm3 Weight of wet soil = 1000 – 300 = 700 g Weight of dry soil = 860 – 300 = 560 g ...
Irrigation for Home Gardens
... will be small and misshapen. Tomatoes may develop blossom-end rot and salad crops, such as celery, may have tough fibers. There are critical periods of growth when water stress can be most detrimental. It is imperative that a good moisture supply be maintained during seed germination and seedling em ...
... will be small and misshapen. Tomatoes may develop blossom-end rot and salad crops, such as celery, may have tough fibers. There are critical periods of growth when water stress can be most detrimental. It is imperative that a good moisture supply be maintained during seed germination and seedling em ...
Rocks, Soil AP Env Sci Class 14 Dr. Mike Sowa
... • Soil – several ways to define: – Unconsolidated material overlying bedrock – * Material capable of supporting plant growth * • Soil is produced by weathering – Physical, Chemical, Biological Processes – Climate, topography, source material composition, and time are factors ...
... • Soil – several ways to define: – Unconsolidated material overlying bedrock – * Material capable of supporting plant growth * • Soil is produced by weathering – Physical, Chemical, Biological Processes – Climate, topography, source material composition, and time are factors ...
Media release - Positive findings for Southeast
... including trichloroethene (TCE) in the Southeast Edwardstown area have been released with some good news for residents. Environment Protection Authority (EPA) Operations Director Science, Assessment and Planning, Peter Dolan, said that “Levels are considered to be safe and no testing is required in ...
... including trichloroethene (TCE) in the Southeast Edwardstown area have been released with some good news for residents. Environment Protection Authority (EPA) Operations Director Science, Assessment and Planning, Peter Dolan, said that “Levels are considered to be safe and no testing is required in ...
Coastal Ecosystems
... Most species release pollen into the current to reproduce They maintain an internally salinity the same as the surrounding water so they do not need to collect and excrete excess salt They are edible and provide food for fish, turtles,etc ...
... Most species release pollen into the current to reproduce They maintain an internally salinity the same as the surrounding water so they do not need to collect and excrete excess salt They are edible and provide food for fish, turtles,etc ...
Ecology of Wetlands - Minnesota Division Izaak Walton League of
... of the types of wetlands that can be commonly found in the United States are swamps, marshes and bogs. There are many different definitions of wetlands, some scientific and some legal, which affect wetland regulations and wetland protection. For example, in order to be protected under the Clean Wate ...
... of the types of wetlands that can be commonly found in the United States are swamps, marshes and bogs. There are many different definitions of wetlands, some scientific and some legal, which affect wetland regulations and wetland protection. For example, in order to be protected under the Clean Wate ...
SP0549 Audit of Soils-Related Education and Awareness
... all natural things. It is designed to take the visitor into the soil so that they see the world from the eyes of a soil animal. There are also urban exhibits where there is pointedly no soil. The exhibition attracts 100,000 visitors a year and numbers are not dropping off. The exhibition is widely a ...
... all natural things. It is designed to take the visitor into the soil so that they see the world from the eyes of a soil animal. There are also urban exhibits where there is pointedly no soil. The exhibition attracts 100,000 visitors a year and numbers are not dropping off. The exhibition is widely a ...
soil makeup
... • There is a constant fluctuation in the amount of air and water found in the soil. ...
... • There is a constant fluctuation in the amount of air and water found in the soil. ...
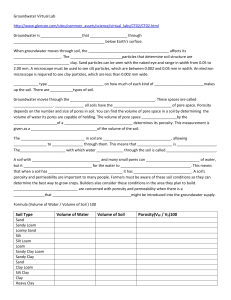
2015-2016 Groundwater Virtual Lab
... 5. Explain why surface runoff, or rain not absorbed by the soil, occurs much more often in areas with soils with high clay content. ...
... 5. Explain why surface runoff, or rain not absorbed by the soil, occurs much more often in areas with soils with high clay content. ...
Earth Systems Quick Study Card
... 10. Include a diagram of a soil texture triangle and give an example problem of how to use it to determine the soil type of a soil sample. ...
... 10. Include a diagram of a soil texture triangle and give an example problem of how to use it to determine the soil type of a soil sample. ...
Soil salinity control
Soil salinity control relates to controlling the problem of soil salinity and reclaiming salinized agricultural land.The aim of soil salinity control is to prevent soil degradation by salination and reclaim already salty (saline) soils. Soil reclamation is also called soil improvement, rehabilitation, remediation, recuperation, or amelioration.The primary man-made cause of salinization is irrigation. River water or groundwater used in irrigation contains salts, which remain behind in the soil after the water has evaporated.The primary method of controlling soil salinity is to permit 10-20% of the irrigation water to leach the soil, be drained and discharged through an appropriate drainage system. The salt concentration of the drainage water is normally 5 to 10 times higher than that of the irrigation water, thus salt export matches salt import and it will not accumulate.