climate models
... Definition: A change in the net radiation at the top of the atmosphere due to some external factor. ...
... Definition: A change in the net radiation at the top of the atmosphere due to some external factor. ...
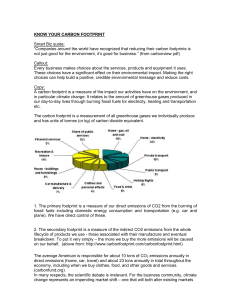
Know your carbon footprint
... The carbon footprint is a measurement of all greenhouse gases we individually produce and has units of tonnes (or kg) of carbon dioxide equivalent. ...
... The carbon footprint is a measurement of all greenhouse gases we individually produce and has units of tonnes (or kg) of carbon dioxide equivalent. ...
presentation - Globelics Academy
... Colored lines pre-2000 are proxy-based T reconstructions by different groups. Gray band 2000-2100 shows range of scenarios for future developed by Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Continuation of recent trends (middle of band) leads by 2100 to temperatures not reached since the Eocene (25- ...
... Colored lines pre-2000 are proxy-based T reconstructions by different groups. Gray band 2000-2100 shows range of scenarios for future developed by Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Continuation of recent trends (middle of band) leads by 2100 to temperatures not reached since the Eocene (25- ...
The global climate in 2011-2015: hot and wild Extreme weather
... rise. Increased ocean heat content accounts for about 40% of the observed global sea-level increase over the past 60 years. A number of studies have concluded that the contribution of continental ice sheets, particularly Greenland and west Antarctica, to sea-level rise is accelerating. During the sa ...
... rise. Increased ocean heat content accounts for about 40% of the observed global sea-level increase over the past 60 years. A number of studies have concluded that the contribution of continental ice sheets, particularly Greenland and west Antarctica, to sea-level rise is accelerating. During the sa ...
Advocacy Writing - Physicians for Social Responsibility
... Critics of the IPCC report focus on one uncertainty (constant temperature) while ignoring other salient facts: The oceans have become about 30% more acidic in the past century as they absorb CO2. Plankton, the base of the ocean food chain, is 50% less than in the 1950s. Polar ice caps, which have a ...
... Critics of the IPCC report focus on one uncertainty (constant temperature) while ignoring other salient facts: The oceans have become about 30% more acidic in the past century as they absorb CO2. Plankton, the base of the ocean food chain, is 50% less than in the 1950s. Polar ice caps, which have a ...
Document
... Relative changes in precipitation (in percent) for the period 2090–2099, relative to 1980–1999. Values are multi-model averages based on the medium emission scenario for December to February (left) and June to August (right). ...
... Relative changes in precipitation (in percent) for the period 2090–2099, relative to 1980–1999. Values are multi-model averages based on the medium emission scenario for December to February (left) and June to August (right). ...
file
... hectares a year, enough to obliterate it completely in our children’s lifetime. These rainforests are the second-largest source of water vapour on the planet, after the oceans. This means that they have a very strong impact on global weather patterns as well as being a huge and crucial carbon sink b ...
... hectares a year, enough to obliterate it completely in our children’s lifetime. These rainforests are the second-largest source of water vapour on the planet, after the oceans. This means that they have a very strong impact on global weather patterns as well as being a huge and crucial carbon sink b ...
OTBA material for class VIII - Kendriya Vidyalaya Anantapuram
... bonds with oxygen to form carbon di-oxide, adding to the greenhouse effect. Methane is formed when plants decay and where there is very little air. It is often called swamp gas. It stays in the atmosphere for only 10 years but traps 20 times more heat than carbon di-oxide. Nitrous oxide is another ...
... bonds with oxygen to form carbon di-oxide, adding to the greenhouse effect. Methane is formed when plants decay and where there is very little air. It is often called swamp gas. It stays in the atmosphere for only 10 years but traps 20 times more heat than carbon di-oxide. Nitrous oxide is another ...
PPT
... higher, and the atmosphere can 'hold' more water vapor. As a greenhouse gas, the higher concentration of water vapor is then able to absorb more thermal IR energy radiated from the Earth, thus further warming the atmosphere. The warmer atmosphere can then hold more water vapor and so on and so on. T ...
... higher, and the atmosphere can 'hold' more water vapor. As a greenhouse gas, the higher concentration of water vapor is then able to absorb more thermal IR energy radiated from the Earth, thus further warming the atmosphere. The warmer atmosphere can then hold more water vapor and so on and so on. T ...
0,48 MB - COMMIN.org
... No one has more to lose — or gain — from our climate crisis than farmers. • Agricultural producers have demonstrated their ability to adapt to changes in climate and other factors in the past, and they will continue to adapt in the future. • However, the key question for agriculture is whether adap ...
... No one has more to lose — or gain — from our climate crisis than farmers. • Agricultural producers have demonstrated their ability to adapt to changes in climate and other factors in the past, and they will continue to adapt in the future. • However, the key question for agriculture is whether adap ...
AOSS_NRE_480_L10_Feedbacks_20100216
... • That balance relies on water to exist in all three phases. – Too warm could run away to “greenhouse” – Too cold run away to “snowball” ice ...
... • That balance relies on water to exist in all three phases. – Too warm could run away to “greenhouse” – Too cold run away to “snowball” ice ...
Deforestation impacts global food production: Reveals
... sizes are increased, in theory, they cover very limited global area. A very recent research based on satellite data provides insight into how large-scale deforestation could impact global food production by triggering changes in local climate. The results seem to be highly comprehensive as the resea ...
... sizes are increased, in theory, they cover very limited global area. A very recent research based on satellite data provides insight into how large-scale deforestation could impact global food production by triggering changes in local climate. The results seem to be highly comprehensive as the resea ...
Climate Change: Science and Policy
... WEBSITE: https://sites.google.com/site/umclimatechangestudies/home TEXTBOOK: Robert Henson, The Thinking Person’s Guide to Climate Change (2014) Course Description and Objectives: This is an introductory course on the scientific and social dimensions of global climate change. The goal is to provide ...
... WEBSITE: https://sites.google.com/site/umclimatechangestudies/home TEXTBOOK: Robert Henson, The Thinking Person’s Guide to Climate Change (2014) Course Description and Objectives: This is an introductory course on the scientific and social dimensions of global climate change. The goal is to provide ...
No Slide Title
... Heat waves and wild fires Impacts on human health and mortality, economic impacts, ecosystem and wildlife impacts ...
... Heat waves and wild fires Impacts on human health and mortality, economic impacts, ecosystem and wildlife impacts ...
Global climate change and drought in the West
... Heat waves and wild fires Impacts on human health and mortality, economic impacts, ecosystem and wildlife impacts ...
... Heat waves and wild fires Impacts on human health and mortality, economic impacts, ecosystem and wildlife impacts ...
3 - biodiversity
... • Help developing countries benefit from reduced emissions, including trading schemes. ...
... • Help developing countries benefit from reduced emissions, including trading schemes. ...
Climate Change & Allergic Airway Disease
... Climate change and air pollution have, to a large extent, a common cause –emissions from fossil fuel burning. The combustion of fossil fuel leads to emissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs) (CO2, methane, nitrous oxide) GHGs accumulate in the atmosphere, warming its lower layers and causing knock-on eff ...
... Climate change and air pollution have, to a large extent, a common cause –emissions from fossil fuel burning. The combustion of fossil fuel leads to emissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs) (CO2, methane, nitrous oxide) GHGs accumulate in the atmosphere, warming its lower layers and causing knock-on eff ...
class14b
... What’s causing global warming? • Carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane • Naturally occurring, but increase with human activity • Rising CO2 since Industrial Revolution • Product of fossil fuels • 90-99% confidence (IPCC) ...
... What’s causing global warming? • Carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane • Naturally occurring, but increase with human activity • Rising CO2 since Industrial Revolution • Product of fossil fuels • 90-99% confidence (IPCC) ...
Global/Climate Changes
... What’s causing global warming? • Carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane • Naturally occurring, but increase with human activity • Rising CO2 since Industrial Revolution • Product of fossil fuels • 90-99% confidence (IPCC) ...
... What’s causing global warming? • Carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane • Naturally occurring, but increase with human activity • Rising CO2 since Industrial Revolution • Product of fossil fuels • 90-99% confidence (IPCC) ...
Deepwater Project
... headlines earlier this year after completing the first circumnavigation of the world in a boat powered only by solar energy. The MS Tûranor Planet Solar is the largest solar vessel ever built, and contains state of the art technology in the field of composite manufacturing and storage of solar energ ...
... headlines earlier this year after completing the first circumnavigation of the world in a boat powered only by solar energy. The MS Tûranor Planet Solar is the largest solar vessel ever built, and contains state of the art technology in the field of composite manufacturing and storage of solar energ ...
Climate Change - Challenges
... likely to spread and worsen over time with increased warming. These dangers could include Arctic Sea ice retreat, boreal forest fires, and increases in frequency of drought, and they could become determinative over time or taken together with other dangers. • Regional dangers are widespread dangers ...
... likely to spread and worsen over time with increased warming. These dangers could include Arctic Sea ice retreat, boreal forest fires, and increases in frequency of drought, and they could become determinative over time or taken together with other dangers. • Regional dangers are widespread dangers ...
nrm glossary of terms - Climate Change in Australia
... vapour (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrous oxide (N2O), methane (CH4) and ozone (O3) are the primary greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere. ...
... vapour (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrous oxide (N2O), methane (CH4) and ozone (O3) are the primary greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere. ...
to David Karoly`s PP
... ‘The atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, and nitrous oxide have increased to levels unprecedented in at least the last 800,000 years. CO2 concentrations have increased by 40% since preindustrial times, primarily from fossil fuel emissions and secondarily from net land use ch ...
... ‘The atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, and nitrous oxide have increased to levels unprecedented in at least the last 800,000 years. CO2 concentrations have increased by 40% since preindustrial times, primarily from fossil fuel emissions and secondarily from net land use ch ...
Attribution of recent climate change
Attribution of recent climate change is the effort to scientifically ascertain mechanisms responsible for recent changes observed in the Earth's climate, commonly known as 'global warming'. The effort has focused on changes observed during the period of instrumental temperature record, when records are most reliable; particularly in the last 50 years, when human activity has grown fastest and observations of the troposphere have become available. The dominant mechanisms (to which recent climate change has been attributed) are anthropogenic, i.e., the result of human activity. They are: increasing atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases global changes to land surface, such as deforestation increasing atmospheric concentrations of aerosols.There are also natural mechanisms for variation including climate oscillations, changes in solar activity, and volcanic activity.According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), it is ""extremely likely"" that human influence was the dominant cause of global warming between 1951 and 2010. The IPCC defines ""extremely likely"" as indicating a probability of 95 to 100%, based on an expert assessment of all the available evidence.Multiple lines of evidence support attribution of recent climate change to human activities: A basic physical understanding of the climate system: greenhouse gas concentrations have increased and their warming properties are well-established. Historical estimates of past climate changes suggest that the recent changes in global surface temperature are unusual. Computer-based climate models are unable to replicate the observed warming unless human greenhouse gas emissions are included. Natural forces alone (such as solar and volcanic activity) cannot explain the observed warming.The IPCC's attribution of recent global warming to human activities is a view shared by most scientists, and is also supported by 196 other scientific organizations worldwide (see also: scientific opinion on climate change).