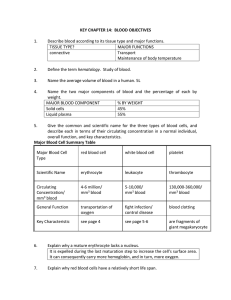
Smor gas bord, January 16 2012 Blood Donation Month
... Approximately 32,000 pints of blood are used each day in the United States. Every three seconds someone needs blood. One out of every 10 people entering a hospital needs blood Just one pint of donated blood can help save as many as three people's lives. There are four main blood types: A, B, AB, and ...
... Approximately 32,000 pints of blood are used each day in the United States. Every three seconds someone needs blood. One out of every 10 people entering a hospital needs blood Just one pint of donated blood can help save as many as three people's lives. There are four main blood types: A, B, AB, and ...
CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES
... Explain why the solid portion of blood, formed elements, packed cell volume, or hematocrit are all composed of approximately 99% erythrocytes. Because they are the most abundant blood cell. 11. Distinguish between granulocytes and agranulocytes, name the leukocytes in each category, list the specifi ...
... Explain why the solid portion of blood, formed elements, packed cell volume, or hematocrit are all composed of approximately 99% erythrocytes. Because they are the most abundant blood cell. 11. Distinguish between granulocytes and agranulocytes, name the leukocytes in each category, list the specifi ...
Motion of red blood cells in a glass microchannel: a global
... R. Lima, T. Ishikawa, Y. Imai, M. Takeda, S. Wada and T. Yamaguchi, Radial dispersion of red blood cells in blood flowing through glass capillaries: The role of hematocrit and geometry, Journal of Biomechanics, 41, 2188−2196 (2008). R. Lima, M. Nakamura, T. Omori, T. Ishikawa, S. Wada, and T. Yamagu ...
... R. Lima, T. Ishikawa, Y. Imai, M. Takeda, S. Wada and T. Yamaguchi, Radial dispersion of red blood cells in blood flowing through glass capillaries: The role of hematocrit and geometry, Journal of Biomechanics, 41, 2188−2196 (2008). R. Lima, M. Nakamura, T. Omori, T. Ishikawa, S. Wada, and T. Yamagu ...
File
... 11. Which blood type is the universal donor? 12. If an injured area becomes red, swollen, warm to the touch and blood work indicates increased white blood cells, what process is probably occurring? 13. AB+ blood types can donate blood to which blood type? 14. What happens to veins when they are not ...
... 11. Which blood type is the universal donor? 12. If an injured area becomes red, swollen, warm to the touch and blood work indicates increased white blood cells, what process is probably occurring? 13. AB+ blood types can donate blood to which blood type? 14. What happens to veins when they are not ...
Unit 6 Review - CSI: Coronado
... Example: A drop of blood found at a crime scene measures 5 mm by 15 mm. The point of convergence is found to be 120 cm away. At what height, in cm, was the wound that caused the blood droplet? What is the height in ft? 8. What is the composition of blood? 9. Name and describe the 3 types of blood ce ...
... Example: A drop of blood found at a crime scene measures 5 mm by 15 mm. The point of convergence is found to be 120 cm away. At what height, in cm, was the wound that caused the blood droplet? What is the height in ft? 8. What is the composition of blood? 9. Name and describe the 3 types of blood ce ...
Blood groups
... (antigens and recessive c , d and e ) antigens. -These antigens were also found in the human red cells. -Antigen D has the strongest antigenic effect So : If D antigen is present → Rh +ve. If D antigen is absent → Rh -ve. ...
... (antigens and recessive c , d and e ) antigens. -These antigens were also found in the human red cells. -Antigen D has the strongest antigenic effect So : If D antigen is present → Rh +ve. If D antigen is absent → Rh -ve. ...
Blood Web Activity
... 15. How many white blood cells are contained in a drop of blood? ________________________________________________________________________ 16. A significantly high white blood cell count can be an indicator that a patient has what disease? _____________________________________________________________ ...
... 15. How many white blood cells are contained in a drop of blood? ________________________________________________________________________ 16. A significantly high white blood cell count can be an indicator that a patient has what disease? _____________________________________________________________ ...
SYNTHESIS OF HEMOGLOBIN
... Ferrous iron -> HCL -> soluble. Ferrous acted upon by ferric reductase -> ferric iron. ...
... Ferrous iron -> HCL -> soluble. Ferrous acted upon by ferric reductase -> ferric iron. ...
Powerpoint - Blood Journal
... by Alexandre P. A. Theocharides, Pontus Lundberg, Asvin K. K. Lakkaraju, Veronika Lysenko, Renier Myburgh, Adriano Aguzzi, Radek C. Skoda, and Markus G. Manz ...
... by Alexandre P. A. Theocharides, Pontus Lundberg, Asvin K. K. Lakkaraju, Veronika Lysenko, Renier Myburgh, Adriano Aguzzi, Radek C. Skoda, and Markus G. Manz ...
Sickle Cell Disease
... New red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow every day to replace old blood cells. In a child with sickle cell anemia a red blood cell will last about 14 days. A red blood cell will last about four months in the child with normal hemoglobin. Because the red blood cells do not last long and be ...
... New red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow every day to replace old blood cells. In a child with sickle cell anemia a red blood cell will last about 14 days. A red blood cell will last about four months in the child with normal hemoglobin. Because the red blood cells do not last long and be ...
MR Imaging Artifacts of Intravascular Iron: A Case
... MRI of the body due to reticuloendothelial uptake by the spleen, liver and bone marrow. They may not be feasible in clinical situations where urgent neuroimaging is required, as in our case. ...
... MRI of the body due to reticuloendothelial uptake by the spleen, liver and bone marrow. They may not be feasible in clinical situations where urgent neuroimaging is required, as in our case. ...
Blood Plasma - El Camino College
... 11. ----------- are rarest of white blood cells, stain dark purple and release histamine to set an inflammatory response at the time of injury and infection. 12. ------------ are smallest white blood cells with very large nucleus and fight infections. Recap 2 Blood 1. ---------- are the largest whit ...
... 11. ----------- are rarest of white blood cells, stain dark purple and release histamine to set an inflammatory response at the time of injury and infection. 12. ------------ are smallest white blood cells with very large nucleus and fight infections. Recap 2 Blood 1. ---------- are the largest whit ...
Chapter 18: Blood
... Normally RBC are flexible and round, moving easily through your blood vessels. In sickle cell anemia, the RBC become rigid and sticky and are shaped like sickles or crescent moons. These irregularly shaped cells can get stuck in small blood vessels, which can slow or block flow and oxygen to parts ...
... Normally RBC are flexible and round, moving easily through your blood vessels. In sickle cell anemia, the RBC become rigid and sticky and are shaped like sickles or crescent moons. These irregularly shaped cells can get stuck in small blood vessels, which can slow or block flow and oxygen to parts ...
Regulation of Iron Metabolism Harnish and Hariom Yadav NATIONAL AGRI FOOD BIOTECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE,MOHALI
... So when hepicidin levels are low ,iron exporting cells have abundant ferroportin and thus releases iron into plasma.When hepicidin concentration increases it binds to ferroportin and thus iron is retained in the cells. ...
... So when hepicidin levels are low ,iron exporting cells have abundant ferroportin and thus releases iron into plasma.When hepicidin concentration increases it binds to ferroportin and thus iron is retained in the cells. ...
Blood Web Quest Name Go to the following Web site: http://health
... 14. What are the 3 main types of blood cells? 15. What are antibodies? 16. Which 3 organs does blood carry waste products to for elimination from the body? 17. List and discuss 3 diseases or disorders related to the blood. ...
... 14. What are the 3 main types of blood cells? 15. What are antibodies? 16. Which 3 organs does blood carry waste products to for elimination from the body? 17. List and discuss 3 diseases or disorders related to the blood. ...
MLAB 1415: Hematology Keri Brophy-Martinez Erythrocytes: Part Two
... Protects the RBC from oxidative injury. Most common defect is deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6PD). If the pathway is deficient, intracellular oxidants can’t be neutralized and globin denatures then precipitates. The precipitates are referred to as Heinz bodies ...
... Protects the RBC from oxidative injury. Most common defect is deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6PD). If the pathway is deficient, intracellular oxidants can’t be neutralized and globin denatures then precipitates. The precipitates are referred to as Heinz bodies ...
Quiz #7
... Instructor: Elmar Schmid, Ph.D. Q. 7: Which of the following is an example of incomplete dominance in humans ...
... Instructor: Elmar Schmid, Ph.D. Q. 7: Which of the following is an example of incomplete dominance in humans ...
Hemolytic Transfusion Reactions: Immune and Non
... red or brown urine (i.e., hemoglobinuria) is rarely seen; fever and chills may be the only manifestation in conscious patients. For patients under anesthesia, or in coma, DIC may be the initial clue of an AHTR. When an AHTR is suspected, the transfusion must be stopped immediately, the patient hydra ...
... red or brown urine (i.e., hemoglobinuria) is rarely seen; fever and chills may be the only manifestation in conscious patients. For patients under anesthesia, or in coma, DIC may be the initial clue of an AHTR. When an AHTR is suspected, the transfusion must be stopped immediately, the patient hydra ...
S-nitrosylation boon to blood transfusions
... Red blood cell transfusions are among the most commonly performed medical procedures, but the capacity of the transfused cells to transport oxygen is often reduced because of biochemical changes in the cells during storage. Now, Case Western Reserve University and Duke University Medical Center rese ...
... Red blood cell transfusions are among the most commonly performed medical procedures, but the capacity of the transfused cells to transport oxygen is often reduced because of biochemical changes in the cells during storage. Now, Case Western Reserve University and Duke University Medical Center rese ...
Association of Fluid Retention With Anemia and Clinical Outcomes
... defined by OH, was negatively correlated with hemoglobin concentrations at baseline (r= 0.438, P<0.001) (Figure 2). In multivariate regression analysis, OH remained an independent predictor of hemoglobin concentrations, second only to eGFR. We stratified the entire study cohort into 3 groups (no anemi ...
... defined by OH, was negatively correlated with hemoglobin concentrations at baseline (r= 0.438, P<0.001) (Figure 2). In multivariate regression analysis, OH remained an independent predictor of hemoglobin concentrations, second only to eGFR. We stratified the entire study cohort into 3 groups (no anemi ...
Case Studies - Oxford Academic
... susceptibility to infections. It has also been observed5 that pregnant women with sickle cell disease are at risk of pre-eclampsia, low birth weight, and fetal loss. Severity of disease in coinheritance of HbS with β-thalassemia and/or α-thalassemia determinants depends on the number and type of gen ...
... susceptibility to infections. It has also been observed5 that pregnant women with sickle cell disease are at risk of pre-eclampsia, low birth weight, and fetal loss. Severity of disease in coinheritance of HbS with β-thalassemia and/or α-thalassemia determinants depends on the number and type of gen ...
Sickle Cell Disease
... New red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow every day to replace old blood cells. In a child with sickle cell anemia a red blood cell will last about 14 days. A red blood cell will last about four months in the child with normal hemoglobin. Because the red blood cells do not last long and be ...
... New red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow every day to replace old blood cells. In a child with sickle cell anemia a red blood cell will last about 14 days. A red blood cell will last about four months in the child with normal hemoglobin. Because the red blood cells do not last long and be ...
Anemia

Anemia or anaemia (/əˈniːmiə/; also spelled anæmia) is usually defined as a decrease in the amount of red blood cells (RBCs) or hemoglobin in the blood. It can also be defined as a lowered ability of the blood to carry oxygen. When anemia comes on slowly the symptoms are often vague and may include: feeling tired, weakness, shortness of breath or a poor ability to exercise. Anemia that comes on quickly often has greater symptoms which may include: confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause.There are three main types of anemia: that due to blood loss, that due to decreased red blood cell production, and that due to increased red blood cell breakdown. Causes of blood loss include trauma and gastrointestinal bleeding, among others. Causes of decreased production include iron deficiency, a lack of vitamin B12, thalassemia and a number of neoplasms of the bone marrow among others. Causes of increased breakdown include a number of genetic conditions such as sickle cell anemia, infections like malaria and some autoimmune diseases among others. It can also be classified based on the size of red blood cells and amount of hemoglobin in each cell. If the cells are small it is microcytic anemia, if they are large it is macrocytic anemia and if they are normal sized it is normocytic anemia. Diagnosis in men is based on a hemoglobin of less than 130 to 140 g/L (13 to 14 g/dL), while in women it must be less than 120 to 130 g/L (12 to 13 g/dL). Further testing is then required to determine the cause.Certain groups of individuals, such as pregnant women, benefit from the use of iron pills for prevention. Dietary supplementation, without determining the specific cause, is not recommended. The use of blood transfusions is typically based on a person's signs and symptoms. In those without symptoms they are not recommended unless hemoglobin levels are less than 60 to 80 g/L (6 to 8 g/dL). These recommendations may also apply to some people with acute bleeding. Erythropoiesis-stimulating medications are only recommended in those with severe anemia.Anemia is the most common disorder of the blood with it affecting about a quarter of people globally. Iron-deficiency anemia affects nearly 1 billion. In 2013 anemia due to iron deficiency resulted in about 183,000 deaths – down from 213,000 deaths in 1990. It is more common in females than males, among children, during pregnancy, and in the elderly. Anemia increases costs of medical care and lowers a person's productivity through a decreased ability to work. The name is derived from Ancient Greek: ἀναιμία anaimia, meaning ""lack of blood"", from ἀν- an-, ""not"" + αἷμα haima, ""blood"".