1 Slinking round Learning Objectives: 1. Explore the Earthss
... 2. Determine the relationship between magnetic field and the length of a coil. 3. Use a Magnetic Field Sensor to measure the field at the center of a coil. 4. Determine the relationship between magnetic field and the number of turns in a coil. 5. Determine the relationship between magnetic field and ...
... 2. Determine the relationship between magnetic field and the length of a coil. 3. Use a Magnetic Field Sensor to measure the field at the center of a coil. 4. Determine the relationship between magnetic field and the number of turns in a coil. 5. Determine the relationship between magnetic field and ...
magnetic fields - Northside Middle School
... For each statement below, write true or rewrite the italicized part to make the statement true. ...
... For each statement below, write true or rewrite the italicized part to make the statement true. ...
Magnetism
... Lodestones were found in Greece some 2000 years ago. The Chinese later used them for navigating ships. In the 18th century, Charles Coulomb conducted a study of the forces between lodestones. ...
... Lodestones were found in Greece some 2000 years ago. The Chinese later used them for navigating ships. In the 18th century, Charles Coulomb conducted a study of the forces between lodestones. ...
Magnetic Resonance TOPIC 3
... A magnetic field is produced by passing an electric current through the coils. The electrical resistance of the wire produces heat and limits the maximum magnetic field strength of resistive magnets. The heat produced is conducted away from the magnet by cooling system. ...
... A magnetic field is produced by passing an electric current through the coils. The electrical resistance of the wire produces heat and limits the maximum magnetic field strength of resistive magnets. The heat produced is conducted away from the magnet by cooling system. ...
Geomagnetism. - Brock University
... 1. The strength of the RMS (a measure of the Earth's field strength when the rock formed). 2. The direction of the RMS (the direction to the Earth's magnetic poles at the time of rock formation). 3. The inclination of the RMS (the inclination of the Earth's field which reflects the latitude at which ...
... 1. The strength of the RMS (a measure of the Earth's field strength when the rock formed). 2. The direction of the RMS (the direction to the Earth's magnetic poles at the time of rock formation). 3. The inclination of the RMS (the inclination of the Earth's field which reflects the latitude at which ...
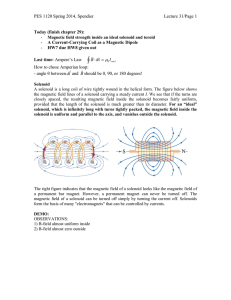
PES 1120 Spring 2014, Spendier Lecture 31/Page 1 Today (finish
... - A Current-Carrying Coil as a Magnetic Dipole - HW7 due HW8 given out Last time: Ampere’s Law ...
... - A Current-Carrying Coil as a Magnetic Dipole - HW7 due HW8 given out Last time: Ampere’s Law ...
Magnetic Torch - (EU
... causes the movement of the magnetic field. Change of magnetic field causes current to be generated in the wire. It is worth noting that the diode does not light up before shaking the test-tube, that is, for current to be induced magnetic field must change. This should shield us against a typical mis ...
... causes the movement of the magnetic field. Change of magnetic field causes current to be generated in the wire. It is worth noting that the diode does not light up before shaking the test-tube, that is, for current to be induced magnetic field must change. This should shield us against a typical mis ...
1 PHYS:1200 LECTURE 27 — ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM (5
... clusters of atoms line up and produce microscopic regions called domains that are fully magnetized. However, not all the domains in the material are aligned, so that every piece of iron is not a magnet. In an ordinary nail, the domains in the nail are randomly oriented. They c ...
... clusters of atoms line up and produce microscopic regions called domains that are fully magnetized. However, not all the domains in the material are aligned, so that every piece of iron is not a magnet. In an ordinary nail, the domains in the nail are randomly oriented. They c ...
ch7 sec2
... In this Investigate, you will map the magnetic field of a currentcarrying coil of wire (a solenoid) and compare it to that of a bar magnet. You will then determine how the number of turns, current size, and core material affect the strength of the magnetic field of a solenoid. 1. Wind 50 turns of wi ...
... In this Investigate, you will map the magnetic field of a currentcarrying coil of wire (a solenoid) and compare it to that of a bar magnet. You will then determine how the number of turns, current size, and core material affect the strength of the magnetic field of a solenoid. 1. Wind 50 turns of wi ...
Forces on Current Carrying Wires in Magnetic Fields
... and the other the south pole. In a compass the north pole of the magnet points toward the geographic north pole of the earth and the south pole of the magnet points toward the geographic south pole of the earth. Like electric charges – magnetic material follow the property that opposites attract ...
... and the other the south pole. In a compass the north pole of the magnet points toward the geographic north pole of the earth and the south pole of the magnet points toward the geographic south pole of the earth. Like electric charges – magnetic material follow the property that opposites attract ...
Compass
A compass is an instrument used for navigation and orientation that shows direction relative to the geographic cardinal directions, or ""points"". Usually, a diagram called a compass rose, shows the directions north, south, east, and west as abbreviated initials marked on the compass. When the compass is used, the rose can be aligned with the corresponding geographic directions, so, for example, the ""N"" mark on the rose really points to the north. Frequently, in addition to the rose or sometimes instead of it, angle markings in degrees are shown on the compass. North corresponds to zero degrees, and the angles increase clockwise, so east is 90 degrees, south is 180, and west is 270. These numbers allow the compass to show azimuths or bearings, which are commonly stated in this notation.The magnetic compass was first invented as a device for divination as early as the Chinese Han Dynasty (since about 206 BC), and later adopted for navigation by the Song Dynasty Chinese during the 11th century. The use of a compass is recorded in Western Europe and in Persia around the early 13th century.