Tutorial 3 Magnetostatics
... field. The magnetic flux density with 3.5 T experiences a magnetic force of magnitude 2x10-13 N. Determine the angle between the magnetic field and proton’s velocity? Biot- Savart Law Q5. The metal niobium becomes a superconductor with the zero electrical resistance when it is cooled to below 9 K, b ...
... field. The magnetic flux density with 3.5 T experiences a magnetic force of magnitude 2x10-13 N. Determine the angle between the magnetic field and proton’s velocity? Biot- Savart Law Q5. The metal niobium becomes a superconductor with the zero electrical resistance when it is cooled to below 9 K, b ...
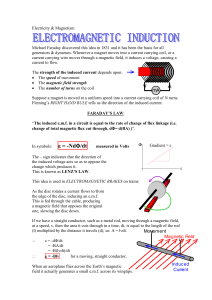
EM_INDUCTION
... The strength of the induced current depends upon: The speed of movement The magnetic field strength The number of turns on the coil Suppose a magnet is moved at a uniform speed into a current carrying coil of N turns. Fleming’s RIGHT HAND RULE tells us the direction of the induced current. FAR ...
... The strength of the induced current depends upon: The speed of movement The magnetic field strength The number of turns on the coil Suppose a magnet is moved at a uniform speed into a current carrying coil of N turns. Fleming’s RIGHT HAND RULE tells us the direction of the induced current. FAR ...
magnetismintrowebquest8word
... 4) 4) What is a magnetic domain? 5) Sketch two images of a material that has magnetic domains, one that is magnetized and one that is unmagnetized. 6) Sketch a bar magnet. Label the poles of the magnet with an “N” and an “S”. Draw magnetic field lines (with direction) both inside and outside of the ...
... 4) 4) What is a magnetic domain? 5) Sketch two images of a material that has magnetic domains, one that is magnetized and one that is unmagnetized. 6) Sketch a bar magnet. Label the poles of the magnet with an “N” and an “S”. Draw magnetic field lines (with direction) both inside and outside of the ...
Worksheet_18 - Iowa State University
... 1. An electron is traveling to the right with a speed of 8.5 x 106 m/s when a magnetic field is turned on. The strength of the magnetic field is 0.050 T, and it is directed into the paper. (a) Describe the path of the electron after the field has been turned on (assuming only magnetic effects). (b) ...
... 1. An electron is traveling to the right with a speed of 8.5 x 106 m/s when a magnetic field is turned on. The strength of the magnetic field is 0.050 T, and it is directed into the paper. (a) Describe the path of the electron after the field has been turned on (assuming only magnetic effects). (b) ...
Year 12 Physics Term 3 Unit 4 Plan
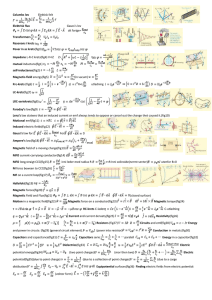
... 3 right hand rules for: current carrying wire & solenoids Magnetic Field Strength, Magnetic Flux Density, Magnetic Flux, Induced EMF, Force on charged particle, Electromagnetic Induction, Motors, Generators Induced EMF = Blvsinθ ; F = Bqvsinθ; φ = BAcosθ Equations for 3 cases: Magnetic Field Strengt ...
... 3 right hand rules for: current carrying wire & solenoids Magnetic Field Strength, Magnetic Flux Density, Magnetic Flux, Induced EMF, Force on charged particle, Electromagnetic Induction, Motors, Generators Induced EMF = Blvsinθ ; F = Bqvsinθ; φ = BAcosθ Equations for 3 cases: Magnetic Field Strengt ...
Class Problem 21 (1) The nuclear magneton is obtained from the
... Calculate the change in energy LlE of the proton when the magnetic moment relaxes to become parallel to the magnetic field ...
... Calculate the change in energy LlE of the proton when the magnetic moment relaxes to become parallel to the magnetic field ...
Slide ()
... Basic operations of the MRI scanner. A. The static magnetic field (Bo). The protons align parallel or antiparallel to the static magnetic field, creating a small net magnetization vector. While aligned to the magnetic field, the protons precess at the Larmor frequency. B. Transmission of radiofreque ...
... Basic operations of the MRI scanner. A. The static magnetic field (Bo). The protons align parallel or antiparallel to the static magnetic field, creating a small net magnetization vector. While aligned to the magnetic field, the protons precess at the Larmor frequency. B. Transmission of radiofreque ...
Magnetic stripe card
A magnetic stripe card is a type of card capable of storing data by modifying the magnetism of tiny iron-based magnetic particles on a band of magnetic material on the card. The magnetic stripe, sometimes called swipe card or magstripe, is read by swiping past a magnetic reading head. Magnetic stripe cards are commonly used in credit cards, identity cards, and transportation tickets. They may also contain an RFID tag, a transponder device and/or a microchip mostly used for business premises access control or electronic payment.Magnetic recording on steel tape and wire was invented during World War II for recording audio. In the 1950s, magnetic recording of digital computer data on plastic tape coated with iron oxide was invented. In 1960 IBM used the magnetic tape idea to develop a reliable way of securing magnetic stripes to plastic cards, under a contract with the US government for a security system. A number of International Organization for Standardization standards, ISO/IEC 7810, ISO/IEC 7811, ISO/IEC 7812, ISO/IEC 7813, ISO 8583, and ISO/IEC 4909, now define the physical properties of the card, including size, flexibility, location of the magstripe, magnetic characteristics, and data formats. They also provide the standards for financial cards, including the allocation of card number ranges to different card issuing institutions.