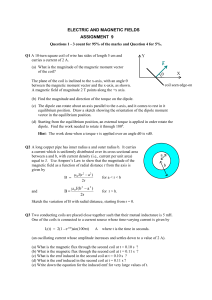
Magnetic Forces Practice
... to the plane formed by the field and the moving charge, and is greatest when the magnetic field and current are perpendicular to each other. The force on the current carrying wire shown above is therefore into the plane of the page and is determined by using the left-hand finger rule. ...
... to the plane formed by the field and the moving charge, and is greatest when the magnetic field and current are perpendicular to each other. The force on the current carrying wire shown above is therefore into the plane of the page and is determined by using the left-hand finger rule. ...
Assignment 9.
... (b) Find the magnitude and direction of the torque on the dipole. (c) The dipole can rotate about an axis parallel to the z-axis, and it comes to rest in it equilibrium position. Draw a sketch showing the orientation of the dipole moment vector in the equilibrium position. (d) Starting from the equi ...
... (b) Find the magnitude and direction of the torque on the dipole. (c) The dipole can rotate about an axis parallel to the z-axis, and it comes to rest in it equilibrium position. Draw a sketch showing the orientation of the dipole moment vector in the equilibrium position. (d) Starting from the equi ...
notes13-- Interactions of electrons with an electromagnetic field
... general relation between the magnetic dipole moment and angular momentum. In the present case, g L =1. The last equality shows that is an elementary unit of the magnetic dipole moment. The last expression can be generalized to any particle and the orbital angular momentum can be replaced by the sp ...
... general relation between the magnetic dipole moment and angular momentum. In the present case, g L =1. The last equality shows that is an elementary unit of the magnetic dipole moment. The last expression can be generalized to any particle and the orbital angular momentum can be replaced by the sp ...
Attention Graduate Students Introduction to Plasma Physics Physics
... http://www-istp.gsfc.nasa.gov/Education/wtrap1.html Charged particles--ions and electrons--can be trapped by the Earth's magnetic field. Their motions are an elaborate dance--a blend of three periodic motions which take place simultaneously: ...
... http://www-istp.gsfc.nasa.gov/Education/wtrap1.html Charged particles--ions and electrons--can be trapped by the Earth's magnetic field. Their motions are an elaborate dance--a blend of three periodic motions which take place simultaneously: ...
Physics 2102 Lecture 15
... "Rail guns are hyper-velocity weapons that shoot aluminum or clay rounds at just below the speed of light. In our film, we've taken existing stealth technology one step further and given them an X-ray scope sighting system," notes director Russell. "These guns represent a whole new technology in wea ...
... "Rail guns are hyper-velocity weapons that shoot aluminum or clay rounds at just below the speed of light. In our film, we've taken existing stealth technology one step further and given them an X-ray scope sighting system," notes director Russell. "These guns represent a whole new technology in wea ...
Magnetism - District 196
... Rules for Magnetic Field lines. 1. They show the shape of the field 2. They exit the North pole and enter the South Pole. 3. If the lines are close together the field is stronger. 4. The lines may never cross. 5. Use arrows to show the direction the north pole of a ...
... Rules for Magnetic Field lines. 1. They show the shape of the field 2. They exit the North pole and enter the South Pole. 3. If the lines are close together the field is stronger. 4. The lines may never cross. 5. Use arrows to show the direction the north pole of a ...
Magnetic stripes - Earth Learning Idea
... resources, for teacher educators and teachers of Earth science through school-level geography or science, with an online discussion around every idea in order to develop a global support network. ‘Earthlearningidea’ has little funding and is produced largely by voluntary effort. Copyright is waived ...
... resources, for teacher educators and teachers of Earth science through school-level geography or science, with an online discussion around every idea in order to develop a global support network. ‘Earthlearningidea’ has little funding and is produced largely by voluntary effort. Copyright is waived ...
Evidence card - Contemporary Science Issues
... Iron-nickel meteorites are much denser than most Earth rocks. They are even denser than rock samples that have been drilled from beneath the crust (from the mantle). ...
... Iron-nickel meteorites are much denser than most Earth rocks. They are even denser than rock samples that have been drilled from beneath the crust (from the mantle). ...
EM-UWA122B054T
... at point A, so the magnitude will increase. ii. [5 pts] Does the magnitude of the magnetic field at point B increase, decrease, or remain the same? Explain. The new magnet will contribute magnetic field directed to the left. Since the original field at point B pointed left, the magnitude of the magn ...
... at point A, so the magnitude will increase. ii. [5 pts] Does the magnitude of the magnetic field at point B increase, decrease, or remain the same? Explain. The new magnet will contribute magnetic field directed to the left. Since the original field at point B pointed left, the magnitude of the magn ...
cp19
... 8.0A running anti-parallel to each other. They are both parallel to the z-axis, and are located on the xaxis at x=3.0m and x=0.0m respectively. Find the magnetic field at the following points on the x-y plane: (a) (5,0,0) (b) (1,0,0) (c) (3,1,0) ...
... 8.0A running anti-parallel to each other. They are both parallel to the z-axis, and are located on the xaxis at x=3.0m and x=0.0m respectively. Find the magnetic field at the following points on the x-y plane: (a) (5,0,0) (b) (1,0,0) (c) (3,1,0) ...
Magnetic stripe card
A magnetic stripe card is a type of card capable of storing data by modifying the magnetism of tiny iron-based magnetic particles on a band of magnetic material on the card. The magnetic stripe, sometimes called swipe card or magstripe, is read by swiping past a magnetic reading head. Magnetic stripe cards are commonly used in credit cards, identity cards, and transportation tickets. They may also contain an RFID tag, a transponder device and/or a microchip mostly used for business premises access control or electronic payment.Magnetic recording on steel tape and wire was invented during World War II for recording audio. In the 1950s, magnetic recording of digital computer data on plastic tape coated with iron oxide was invented. In 1960 IBM used the magnetic tape idea to develop a reliable way of securing magnetic stripes to plastic cards, under a contract with the US government for a security system. A number of International Organization for Standardization standards, ISO/IEC 7810, ISO/IEC 7811, ISO/IEC 7812, ISO/IEC 7813, ISO 8583, and ISO/IEC 4909, now define the physical properties of the card, including size, flexibility, location of the magstripe, magnetic characteristics, and data formats. They also provide the standards for financial cards, including the allocation of card number ranges to different card issuing institutions.