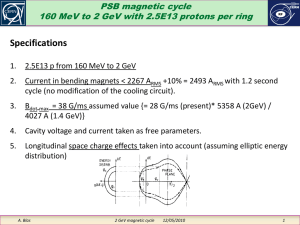
Experiments with Coler magnetic current apparatus
... main reason why this invention is not forgotten. Another important historical fact is the investigation of the device by the British Intelligence Objectives Sub-Committee (B.I.O.S.) and the confidential, later disclosed, positive report of this agency. The investigation was conducted by Hurst and Sa ...
... main reason why this invention is not forgotten. Another important historical fact is the investigation of the device by the British Intelligence Objectives Sub-Committee (B.I.O.S.) and the confidential, later disclosed, positive report of this agency. The investigation was conducted by Hurst and Sa ...
User Guide for FMT1000-series Magnetic Field Mapper
... distorted (warped) and causes an error in measured orientation if the magnetometers are used to estimate orientation. This is not the case in all filter profiles. However, the disturbance of the magnetic field caused by mounting the FMT on a ferromagnetic object can be corrected for using a speciali ...
... distorted (warped) and causes an error in measured orientation if the magnetometers are used to estimate orientation. This is not the case in all filter profiles. However, the disturbance of the magnetic field caused by mounting the FMT on a ferromagnetic object can be corrected for using a speciali ...
Electromagnets
... clusters of atoms to line up with each other. These clusters of aligned atoms are called magnetic domains. Each domain consists of billions of aligned iron atoms. When a current is sent through the wire wrapped around the iron-containing metal, the domains align so their tiny magnetic fields add to ...
... clusters of atoms to line up with each other. These clusters of aligned atoms are called magnetic domains. Each domain consists of billions of aligned iron atoms. When a current is sent through the wire wrapped around the iron-containing metal, the domains align so their tiny magnetic fields add to ...
Physical Science: Magnets Study Guide
... Attract things made of iron Have a north and south pole 15. Magnets are all different because they Can have different shapes Can be used in different ways 16. Temporary magnets are created by stroking objects made of iron or steel with a magnet. 17. There are many kinds of magnets. These inc ...
... Attract things made of iron Have a north and south pole 15. Magnets are all different because they Can have different shapes Can be used in different ways 16. Temporary magnets are created by stroking objects made of iron or steel with a magnet. 17. There are many kinds of magnets. These inc ...
rotationally supported disk? - Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares UNAM
... Alex Lazarian (U. Wisconsin) ...
... Alex Lazarian (U. Wisconsin) ...
Copyright 2009 Pearson
... A B-H curve is referred to as a magnetization curve for the case where the material is initially unmagnetized. The B-H curve differs for different materials; magnetic materials have in common much larger flux density for a given magnetic field intensity, such as the annealed iron shown here. Flux De ...
... A B-H curve is referred to as a magnetization curve for the case where the material is initially unmagnetized. The B-H curve differs for different materials; magnetic materials have in common much larger flux density for a given magnetic field intensity, such as the annealed iron shown here. Flux De ...
MRI
... encoding gradients. The phase encoding gradient is used to give a specific phase angle to the transverse magnetization vector. It acts in much the same way as the frequency encoding gradient when turned on. In this case each transverse magnetization vector has a unique Larmor frequency. However, the ...
... encoding gradients. The phase encoding gradient is used to give a specific phase angle to the transverse magnetization vector. It acts in much the same way as the frequency encoding gradient when turned on. In this case each transverse magnetization vector has a unique Larmor frequency. However, the ...
Fulltext PDF
... magnitude of the magnetoresistance is more than 100% at low temperatures. The French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) has awarded the Medaille dOr (Golden Medal) for 2005 to Prof A Fert. Application of G MR in the read heads of computer discs was developed by IBM in 1997, using thin fi ...
... magnitude of the magnetoresistance is more than 100% at low temperatures. The French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) has awarded the Medaille dOr (Golden Medal) for 2005 to Prof A Fert. Application of G MR in the read heads of computer discs was developed by IBM in 1997, using thin fi ...
magnetic orientation by hatchling loggerhead sea turtles
... record of the voltage output and thus of the movements and orientation of each turtle (accurate within 15°). Immediately before or after each experiment, the system was calibrated by obtaining chart recorder measurements for a series of known compass directions. Altering the magnetic field The satel ...
... record of the voltage output and thus of the movements and orientation of each turtle (accurate within 15°). Immediately before or after each experiment, the system was calibrated by obtaining chart recorder measurements for a series of known compass directions. Altering the magnetic field The satel ...
Magnetometer

Magnetometers are measurement instruments used for two general purposes: to measure the magnetization of a magnetic material like a ferromagnet, or to measure the strength and, in some cases, the direction of the magnetic field at a point in space.The first magnetometer was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall Effect which is still widely used.Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field and in geophysical surveys to detect magnetic anomalies of various types. They are also used militarily to detect submarines. Consequently, some countries, such as the USA, Canada and Australia classify the more sensitive magnetometers as military technology, and control their distribution.Magnetometers can be used as metal detectors: they can detect only magnetic (ferrous) metals, but can detect such metals at a much larger depth than conventional metal detectors; they are capable of detecting large objects, such as cars, at tens of metres, while a metal detector's range is rarely more than 2 metres.In recent years magnetometers have been miniaturized to the extent that they can be incorporated in integrated circuits at very low cost and are finding increasing use as compasses in consumer devices such as mobile phones and tablet computers.