A general rule for how a pickup coil will respond to a magnetic field
... Digital Data Sheets and simulators are available using links provided by your instructor. Magnetism Questionnaire Answer the following questions based upon your reading. 1. What creates a magnetic field? _____________________________________________________________ 2. How are magnetic poles labeled? ...
... Digital Data Sheets and simulators are available using links provided by your instructor. Magnetism Questionnaire Answer the following questions based upon your reading. 1. What creates a magnetic field? _____________________________________________________________ 2. How are magnetic poles labeled? ...
magnetic field - Broadneck High School Physics Web Site
... cobalt. A variety of rare earth elements, such as neodymium and gadolinium, produce permanent magnets that are extremely strong for their size. Example 1 ...
... cobalt. A variety of rare earth elements, such as neodymium and gadolinium, produce permanent magnets that are extremely strong for their size. Example 1 ...
document
... compendium of important military techniques) describes the magnetized iron “fish” that floats in water and can be used for finding south; about the same time Chinese began applying the compass for navigation, most likely using the iron “fish” (1084 AD) ...
... compendium of important military techniques) describes the magnetized iron “fish” that floats in water and can be used for finding south; about the same time Chinese began applying the compass for navigation, most likely using the iron “fish” (1084 AD) ...
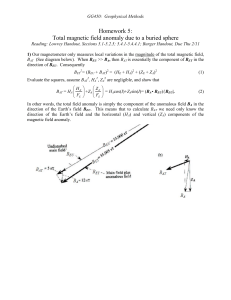
Total field anomaly over a sphere
... BAT along a South-to-North profile centered over the buried sphere (see diagram to the right). It turns out that the magnetic field due to a sphere with uniform magnetization M and radius a is identical to that of a magnetic dipole with a dipole moment m = (4/3a3)M. The Matlab function “dipole.m” t ...
... BAT along a South-to-North profile centered over the buried sphere (see diagram to the right). It turns out that the magnetic field due to a sphere with uniform magnetization M and radius a is identical to that of a magnetic dipole with a dipole moment m = (4/3a3)M. The Matlab function “dipole.m” t ...
abstract
... The main effect of the static magnetic field on the growth dynamics of the bacterium S. aureus is shown in Fig. 1. Each symbol is an average from 4 independent measurements performed previously. We found that the number of CFU increases with the time of exposure and decreases with the magnitude of t ...
... The main effect of the static magnetic field on the growth dynamics of the bacterium S. aureus is shown in Fig. 1. Each symbol is an average from 4 independent measurements performed previously. We found that the number of CFU increases with the time of exposure and decreases with the magnitude of t ...
Magnets
... If a permanent magnetic is cut in half repeatedly, you will still have a north and a south pole This differs from electric charges ...
... If a permanent magnetic is cut in half repeatedly, you will still have a north and a south pole This differs from electric charges ...
make it magnetic
... The properties of paramagnetic susceptibility Positive (Typically 10−5 to 10−3) Temperature-dependent Saturates for large B or low T ...
... The properties of paramagnetic susceptibility Positive (Typically 10−5 to 10−3) Temperature-dependent Saturates for large B or low T ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... If resistance of coil is 100 ohms what are current, energy dissipated, and average force required? • I = emf/R = 1.5v/100 ohms = 15mA •E = Pt = I2Rt= 2.25 x 10-3 J • F = work required to pull coil out/distance = energy dissipated in coil/distance = W/d = 0.050 N Use d = 0.05 m since no flux change u ...
... If resistance of coil is 100 ohms what are current, energy dissipated, and average force required? • I = emf/R = 1.5v/100 ohms = 15mA •E = Pt = I2Rt= 2.25 x 10-3 J • F = work required to pull coil out/distance = energy dissipated in coil/distance = W/d = 0.050 N Use d = 0.05 m since no flux change u ...
The Magnetic Field of a Permanent Magnet
... 2. How well does the inverse-cube model fit your experimental data? From the comparison, does your magnet show the magnetic field pattern of a dipole? 3. The computer adjusted the parameter A so the equation’s curve comes as close as possible to your data points. Relating the parameter A to the fiel ...
... 2. How well does the inverse-cube model fit your experimental data? From the comparison, does your magnet show the magnetic field pattern of a dipole? 3. The computer adjusted the parameter A so the equation’s curve comes as close as possible to your data points. Relating the parameter A to the fiel ...
Divergence and Curl of the Magnetic Field
... Finally, let me prove that the integral (23) indeed evaluates to zero. Note that G(r − r′ ) depends only on the difference r − r′ , hence its derivatives WRT to components of the r and the r′ are related by sign reversal, ∂Gi (r − r′ ) ∂Gi (r − r′ ) ...
... Finally, let me prove that the integral (23) indeed evaluates to zero. Note that G(r − r′ ) depends only on the difference r − r′ , hence its derivatives WRT to components of the r and the r′ are related by sign reversal, ∂Gi (r − r′ ) ∂Gi (r − r′ ) ...
SAC: Solution to a scientific or technological problem
... AOS 1: How do things move without contact? SAC: Separation of particles Description: Your challenge is to come up with a design for a device that separates particles according to their mass and type using electric, magnetic and gravitational fields. You can assume that the first step of your device ...
... AOS 1: How do things move without contact? SAC: Separation of particles Description: Your challenge is to come up with a design for a device that separates particles according to their mass and type using electric, magnetic and gravitational fields. You can assume that the first step of your device ...
magsources
... side has current I = 4.00 A flowing around it. The current flows N = 500 times around. What is the total magnetic field at the center? •Draw in the two directions from the center to the corners of one segment •Top angle is one-sixth of a circle, or 60 degrees •Total angles in circle is 180, so other ...
... side has current I = 4.00 A flowing around it. The current flows N = 500 times around. What is the total magnetic field at the center? •Draw in the two directions from the center to the corners of one segment •Top angle is one-sixth of a circle, or 60 degrees •Total angles in circle is 180, so other ...
Magnetism Review
... Explanation: A force is exerted on charged particles only when they move at an angle to magnetic field lines. The force is greatest when motion is at right angles to the magnetic field. ...
... Explanation: A force is exerted on charged particles only when they move at an angle to magnetic field lines. The force is greatest when motion is at right angles to the magnetic field. ...
Magnetometer

Magnetometers are measurement instruments used for two general purposes: to measure the magnetization of a magnetic material like a ferromagnet, or to measure the strength and, in some cases, the direction of the magnetic field at a point in space.The first magnetometer was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall Effect which is still widely used.Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field and in geophysical surveys to detect magnetic anomalies of various types. They are also used militarily to detect submarines. Consequently, some countries, such as the USA, Canada and Australia classify the more sensitive magnetometers as military technology, and control their distribution.Magnetometers can be used as metal detectors: they can detect only magnetic (ferrous) metals, but can detect such metals at a much larger depth than conventional metal detectors; they are capable of detecting large objects, such as cars, at tens of metres, while a metal detector's range is rarely more than 2 metres.In recent years magnetometers have been miniaturized to the extent that they can be incorporated in integrated circuits at very low cost and are finding increasing use as compasses in consumer devices such as mobile phones and tablet computers.