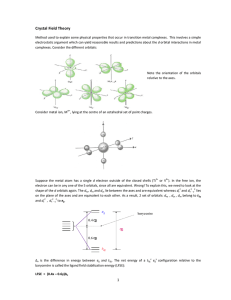
MRI Homework
... the same. The energy difference between the spin-up and spin-down states would increase. b. In order to obtain a 3-D image of the tissue within the body, an MRI device will use electromagnets to vary the strength of the magnetic field across the large hollow cylindrical magnet into which the person ...
... the same. The energy difference between the spin-up and spin-down states would increase. b. In order to obtain a 3-D image of the tissue within the body, an MRI device will use electromagnets to vary the strength of the magnetic field across the large hollow cylindrical magnet into which the person ...
Magnetism
... which is a galvanometer and which is an electric motor. How can you tell the difference between the two? a. In a galvanometer, the current changes direction every time the coil makes a half revolution. b. In an electric motor, the current changes direction every time the coil makes a half revolution ...
... which is a galvanometer and which is an electric motor. How can you tell the difference between the two? a. In a galvanometer, the current changes direction every time the coil makes a half revolution. b. In an electric motor, the current changes direction every time the coil makes a half revolution ...
Physical Science Insight
... The number of field lines in any given region indicates the relative strength of the field Although the magnetic field is invisible you can see its effect around a magnet by placing a piece of paper on top of a magnet and then sprinkling iron fillings over the paper If you were to place a magne ...
... The number of field lines in any given region indicates the relative strength of the field Although the magnetic field is invisible you can see its effect around a magnet by placing a piece of paper on top of a magnet and then sprinkling iron fillings over the paper If you were to place a magne ...
Equations of the electromagnetic field in dispersive media
... oil and gas (Safonov et al., 1996). It was shown by mathematical modeling that the IP effect can be considered as one of the probable causes of the phenomenon. However, its mechanism was not explained in the framework of classic electrodynamic theory and is still not fully understood. Terms like “no ...
... oil and gas (Safonov et al., 1996). It was shown by mathematical modeling that the IP effect can be considered as one of the probable causes of the phenomenon. However, its mechanism was not explained in the framework of classic electrodynamic theory and is still not fully understood. Terms like “no ...
ppt_ch14
... completely, the retentivity BR must be reduced to zero. To demagnetize a magnetic material completely, the retentivity BR must be reduced to zero. A practical way to do so is to magnetize and demagnetize the material with a decreasing hysteresis loop. This method of demagnetization is called degauss ...
... completely, the retentivity BR must be reduced to zero. To demagnetize a magnetic material completely, the retentivity BR must be reduced to zero. A practical way to do so is to magnetize and demagnetize the material with a decreasing hysteresis loop. This method of demagnetization is called degauss ...
Magnets - BAschools.org
... • Occurs when a permanent magnet is rubbed along a piece of iron, steel, or cobalt • Magnetic field cannot be turned off, however it doesn’t ...
... • Occurs when a permanent magnet is rubbed along a piece of iron, steel, or cobalt • Magnetic field cannot be turned off, however it doesn’t ...
Chemical work
... Dielectrics are materials where the molecules may orient or displace their center of positive and negative charge in response to an electric field, but which cannot directly support an electric current because the electrons are not free to leave the molecules. (Such materials are thus insulators). M ...
... Dielectrics are materials where the molecules may orient or displace their center of positive and negative charge in response to an electric field, but which cannot directly support an electric current because the electrons are not free to leave the molecules. (Such materials are thus insulators). M ...
Earth`s Magnetic Field
... Magnetic Forces on Moving Charged Particles If the charged particle moves in a magnetic field, the charged particle experiences a deflecting force. • This force is greatest when the particle moves in a direction perpendicular to the magnetic field lines. • At other angles, the force is less. • The ...
... Magnetic Forces on Moving Charged Particles If the charged particle moves in a magnetic field, the charged particle experiences a deflecting force. • This force is greatest when the particle moves in a direction perpendicular to the magnetic field lines. • At other angles, the force is less. • The ...
engineering physics ii magnetic materials
... Ina diamagnetic material, the electron orbits are more or less random, and mostly all the magnetic moments are cancelled. Similarly all the spin moments are almost paired i.e., they have even number of electrons and has equal number of electrons spinning in two opposite directions. Hence the net mag ...
... Ina diamagnetic material, the electron orbits are more or less random, and mostly all the magnetic moments are cancelled. Similarly all the spin moments are almost paired i.e., they have even number of electrons and has equal number of electrons spinning in two opposite directions. Hence the net mag ...
Document
... Convenient to describe the interaction at a distance between magnets with the notion of magnetic field. Magnetic objects are surrounded a magnetic field. Moving electrical charges are also surrounded by a magnetic field (in addition to the electrical field). A vector quantity: magnitude and directio ...
... Convenient to describe the interaction at a distance between magnets with the notion of magnetic field. Magnetic objects are surrounded a magnetic field. Moving electrical charges are also surrounded by a magnetic field (in addition to the electrical field). A vector quantity: magnitude and directio ...
19.8: Magnetic force between two parallel conductors
... Magnetic materials owe their properties to magnetic dipole moments of electrons in atoms Classical model for electrons in atoms: 1.Orbital motion of electron: like a loop current (but B-field produced by 1 electron can be cancelled out by an oppositely revolving electron in the same atom) 2. “spin” ...
... Magnetic materials owe their properties to magnetic dipole moments of electrons in atoms Classical model for electrons in atoms: 1.Orbital motion of electron: like a loop current (but B-field produced by 1 electron can be cancelled out by an oppositely revolving electron in the same atom) 2. “spin” ...