a) Direct current
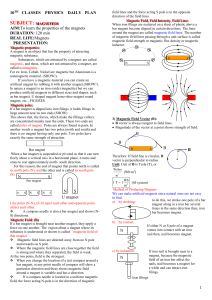
... 2) Magnetic field due to a current carrying conductor :If a magnetic compass is placed near a conductor carrying current (wire), the needle is deflected. This shows that a conductor carrying current has a magnetic field around it. If the direction of the current is from north to south, the deflecti ...
... 2) Magnetic field due to a current carrying conductor :If a magnetic compass is placed near a conductor carrying current (wire), the needle is deflected. This shows that a conductor carrying current has a magnetic field around it. If the direction of the current is from north to south, the deflecti ...
Big Ideas
... (A) classify matter based on its physical properties including magnetism, physical state, and the ability to conduct or insulate heat, electricity, and sound; (B) demonstrate that some mixtures maintain the physical properties of their ingredients; (C) identify changes that can occur in the physical ...
... (A) classify matter based on its physical properties including magnetism, physical state, and the ability to conduct or insulate heat, electricity, and sound; (B) demonstrate that some mixtures maintain the physical properties of their ingredients; (C) identify changes that can occur in the physical ...
The Atom`s Family
... wire Does the same thing happen to the compass at each place? Flip the battery around How does the compass direction compare to the direction found with the battery in its original ...
... wire Does the same thing happen to the compass at each place? Flip the battery around How does the compass direction compare to the direction found with the battery in its original ...
Magnetism Leaflet
... pole. Since opposite types of magnetic pole attract each other, the pole in the northern hemisphere, although called the north magnetic pole, is itself of the south-seeking type, and vice versa for the opposite hemisphere. ...
... pole. Since opposite types of magnetic pole attract each other, the pole in the northern hemisphere, although called the north magnetic pole, is itself of the south-seeking type, and vice versa for the opposite hemisphere. ...
chapter link
... Energy Effects of Magnetic Fields In a magnetic field, the energy is modified as a result of the interaction of the magnetic field with the magnetic dipole moments of the electrons and neutrons. This leads to shifts in the energy levels with the magnetic field, called the Zeeman Effect. Generally, f ...
... Energy Effects of Magnetic Fields In a magnetic field, the energy is modified as a result of the interaction of the magnetic field with the magnetic dipole moments of the electrons and neutrons. This leads to shifts in the energy levels with the magnetic field, called the Zeeman Effect. Generally, f ...
Word version of Episode 411
... TAP 411-2: Brush up on magnetism Use some permanent magnets and a current-carrying coil to review your knowledge of the nature and behaviour of magnetic fields. The purpose of this sheet is to help you to brush up your knowledge of magnets before you learn how magnetism is used with trains. ...
... TAP 411-2: Brush up on magnetism Use some permanent magnets and a current-carrying coil to review your knowledge of the nature and behaviour of magnetic fields. The purpose of this sheet is to help you to brush up your knowledge of magnets before you learn how magnetism is used with trains. ...
Sea-Floor spreading
... The molten iron flows creates an electric current (flow of electrons) & a magnetic field that surrounds the planet. • The magnetic field created in the center of the planet makes your compass point north • Protects the Earth from solar winds. ...
... The molten iron flows creates an electric current (flow of electrons) & a magnetic field that surrounds the planet. • The magnetic field created in the center of the planet makes your compass point north • Protects the Earth from solar winds. ...
PWE 19-3: Magnetic Levitation
... We know from Equation 19-5 that to maximize the magnetic force, the current direction should s. be perpendicular to the magnetic field B The right-hand rule then shows that the current should flow from west to east so that the magnetic force is directed upward. We’re not given the mass of the wire ...
... We know from Equation 19-5 that to maximize the magnetic force, the current direction should s. be perpendicular to the magnetic field B The right-hand rule then shows that the current should flow from west to east so that the magnetic force is directed upward. We’re not given the mass of the wire ...
Class Notes - Ms. Shevlin`s Website
... • These are two easy ways to make your own compass. • Give one a try but remember you must magnetise your needle first. ...
... • These are two easy ways to make your own compass. • Give one a try but remember you must magnetise your needle first. ...