Usama Bin Laden: “The Way to Save the Earth”
... and social sciences that America’s star is waning, its economy is shriveling and the dollar’s ship is sinking. And happy is he who learns from other’s mistakes.” “In closing, the world has before it a rare and historic opportunity to liberate itself from servitude to America, as the latter finds its ...
... and social sciences that America’s star is waning, its economy is shriveling and the dollar’s ship is sinking. And happy is he who learns from other’s mistakes.” “In closing, the world has before it a rare and historic opportunity to liberate itself from servitude to America, as the latter finds its ...
Climate Stabilization Targets - The National Academies of Sciences
... Anthropocene, in which human activities will largely control the evolution of Earth’s environment. Carbon emissions during this century will essentially determine the magnitude of eventual impacts and whether the Anthropocene is a short-term, relatively minor change from the current climate or an ex ...
... Anthropocene, in which human activities will largely control the evolution of Earth’s environment. Carbon emissions during this century will essentially determine the magnitude of eventual impacts and whether the Anthropocene is a short-term, relatively minor change from the current climate or an ex ...
article
... it cold and, because much of Europe is usually above freezing at this time of year, making the rain fall instead as snow. It also allowed warm air to flow into the Arctic, making it 10°C above normal in some places. The combination of this warm air and the push of the unusual winds lead to a decreas ...
... it cold and, because much of Europe is usually above freezing at this time of year, making the rain fall instead as snow. It also allowed warm air to flow into the Arctic, making it 10°C above normal in some places. The combination of this warm air and the push of the unusual winds lead to a decreas ...
Global climate - Gordon College Faculty
... Sea level rise, global, from University of Colorado. Graph from : http://sealevel.colorado.edu/current/sl_noib_global.jpg But the problem is that the pattern looks like you would expect if sea level is rising with fluctuations around a fairly steep slope. It’s really hard to look at this graph and c ...
... Sea level rise, global, from University of Colorado. Graph from : http://sealevel.colorado.edu/current/sl_noib_global.jpg But the problem is that the pattern looks like you would expect if sea level is rising with fluctuations around a fairly steep slope. It’s really hard to look at this graph and c ...
Winguth et al, 2005
... Geophys. Res. Lett., 29(10), 1405, doi:10.1029/2001GL013777. Feely, R., R. Wanninkhof, T. Takahashi, and P. Tans (1999), Influence of El Nino on the equatorial Pacific contribution to atmospheric CO2, ...
... Geophys. Res. Lett., 29(10), 1405, doi:10.1029/2001GL013777. Feely, R., R. Wanninkhof, T. Takahashi, and P. Tans (1999), Influence of El Nino on the equatorial Pacific contribution to atmospheric CO2, ...
The rate of global temperature rise may have hit a
... closer to 450 ppm. Ironically, if the world burns significantly less coal, that would lessen CO2 emissions but also reduce aerosols in the atmosphere that block the sun (such as sulfate particulates), so we would have to limit CO2 to below roughly 405 ppm. We are well on our way to surpassing these ...
... closer to 450 ppm. Ironically, if the world burns significantly less coal, that would lessen CO2 emissions but also reduce aerosols in the atmosphere that block the sun (such as sulfate particulates), so we would have to limit CO2 to below roughly 405 ppm. We are well on our way to surpassing these ...
Manish Climatic change Montereal Protocol
... 1...."Adverse effects of climate change" means changes in the physical environment or biota resulting from climate change which have significant deleterious effects on the composition, resilience or productivity of natural and managed ecosystems or on the operation of socio-economic systems or on hu ...
... 1...."Adverse effects of climate change" means changes in the physical environment or biota resulting from climate change which have significant deleterious effects on the composition, resilience or productivity of natural and managed ecosystems or on the operation of socio-economic systems or on hu ...
Lesson 1
... warming and human activities. Since the start of the Industrial Revolution, the average temperature of the planet has increased by slightly less than one degree Celsius to its present level of about 16°C (60°F). This seemingly insignificant change represents a fairly rapid warming trend. According t ...
... warming and human activities. Since the start of the Industrial Revolution, the average temperature of the planet has increased by slightly less than one degree Celsius to its present level of about 16°C (60°F). This seemingly insignificant change represents a fairly rapid warming trend. According t ...
Last Lecture
... “Climate change is the most severe problem we are facing today.” - Sir David King, UK government’s chief science adviser ...
... “Climate change is the most severe problem we are facing today.” - Sir David King, UK government’s chief science adviser ...
Fossil Fuels and Renewable Energy Peat Coal Coal Burning Coal
... Carbon dioxide and ________________ are examples of ________________. We create these gases by burning fossil fuels, driving cars and burying our rubbish in landfills. These greenhouse gases create a layer around the Earth which traps the sun‛s energy. If this layer gets too thick, it can increase t ...
... Carbon dioxide and ________________ are examples of ________________. We create these gases by burning fossil fuels, driving cars and burying our rubbish in landfills. These greenhouse gases create a layer around the Earth which traps the sun‛s energy. If this layer gets too thick, it can increase t ...
The Kyoto Protocol and Global Warming - Imprimis
... • As a result of the human use of coal, oil and natural gas, the air’s carbon dioxide content (along with the content of other human-produced greenhouse gases like methane) is increasing. • The greenhouse gases absorb infrared radiation and, as a result, should retain some energy near the surface of ...
... • As a result of the human use of coal, oil and natural gas, the air’s carbon dioxide content (along with the content of other human-produced greenhouse gases like methane) is increasing. • The greenhouse gases absorb infrared radiation and, as a result, should retain some energy near the surface of ...
Greenhouse Gases, Aerosols And Ozone Layer
... The short wave solar radiation photons in ultraviolet and visible bands (wave length less than 0.7 μm) move almost unchanged through the cloudless atmosphere and are absorbed or scattered mostly by aerosols and by cloud particles. The absorbed by clouds and by the ground surface solar radiative ener ...
... The short wave solar radiation photons in ultraviolet and visible bands (wave length less than 0.7 μm) move almost unchanged through the cloudless atmosphere and are absorbed or scattered mostly by aerosols and by cloud particles. The absorbed by clouds and by the ground surface solar radiative ener ...
Topic Five - Science - Miami
... atmosphere and present information in small groups. Model the layers of the atmosphere. Relate how energy provided by the Sun influences global patterns of atmospheric movement and temperature differences between air, water, and land Differentiate between weather and climate. Classify the di ...
... atmosphere and present information in small groups. Model the layers of the atmosphere. Relate how energy provided by the Sun influences global patterns of atmospheric movement and temperature differences between air, water, and land Differentiate between weather and climate. Classify the di ...
the big picture chapter 19 global change
... The bottle with the black paper will absorb and convert the light to heat very easily. The bottle with the white paper will reflect more of the light and therefore not get as warm. The black paper represents land, plants, and water. The white paper represents clouds, ice, and water that are reflecti ...
... The bottle with the black paper will absorb and convert the light to heat very easily. The bottle with the white paper will reflect more of the light and therefore not get as warm. The black paper represents land, plants, and water. The white paper represents clouds, ice, and water that are reflecti ...
Cool response to Durban compromise
... greenhouse-gas emissions under control, it may one day become necessary to intervene actively in the Earth system. One widely discussed option is solar-radiation management (SRM), an example of which would be the injection of large amounts of sulphurous aerosols into the stratosphere to reflect inco ...
... greenhouse-gas emissions under control, it may one day become necessary to intervene actively in the Earth system. One widely discussed option is solar-radiation management (SRM), an example of which would be the injection of large amounts of sulphurous aerosols into the stratosphere to reflect inco ...
Climate and Atmospheric Changes
... More emitted radiation and increased More sunspots will increase the amount temperatures are found around sunspots of heat that stays within the atmosphere. ...
... More emitted radiation and increased More sunspots will increase the amount temperatures are found around sunspots of heat that stays within the atmosphere. ...
Pew Center. 2010. Antarctic Climate Change
... downward away from the surface (Parkinson 2004; Levitus et al. 2005). In fact, the signal of humaninduced ocean warming has been detected to a depth of at least 700 meters (Barnett et al. 2005). As in the north, southern-hemisphere warming has been greater at mid-latitudes than at the equator, but t ...
... downward away from the surface (Parkinson 2004; Levitus et al. 2005). In fact, the signal of humaninduced ocean warming has been detected to a depth of at least 700 meters (Barnett et al. 2005). As in the north, southern-hemisphere warming has been greater at mid-latitudes than at the equator, but t ...
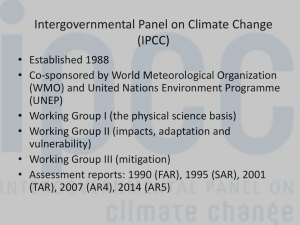
IPCC slides
... • Your task: What are your country’s/region’s interests in the climate change problematic? • What is your country’s contribution to global Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHGs)? • How will IPCC knowledge impact these interests? • Do you want stronger conclusions or weaker conclusions? • Do you want to tal ...
... • Your task: What are your country’s/region’s interests in the climate change problematic? • What is your country’s contribution to global Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHGs)? • How will IPCC knowledge impact these interests? • Do you want stronger conclusions or weaker conclusions? • Do you want to tal ...
Ch. 20 Notes – The Atmosphere: Climate, Climate Change and
... • Eleven of the twelve years in the period (1995-2006) rank among the top 12 warmest years in the instrumental record (since 1850, towards the end of the Little Ice Age). • Warming in the last 100 years has caused about a 0.74 °C increase in global average temperature. This is up from the 0.6 °C inc ...
... • Eleven of the twelve years in the period (1995-2006) rank among the top 12 warmest years in the instrumental record (since 1850, towards the end of the Little Ice Age). • Warming in the last 100 years has caused about a 0.74 °C increase in global average temperature. This is up from the 0.6 °C inc ...
MEMORANDUM TO THE PRESIDENT From: F. Sherwood Rowland
... Tropospheric ozone. The concentration of ozone near the Earth’s surface has increased during the past century by a factor of 5–8 in the Northern Hemisphere summer and by a factor of 2–4 in the Northern Hemisphere winter and during both seasons in the Southern Hemisphere. The added surface ozone is a ...
... Tropospheric ozone. The concentration of ozone near the Earth’s surface has increased during the past century by a factor of 5–8 in the Northern Hemisphere summer and by a factor of 2–4 in the Northern Hemisphere winter and during both seasons in the Southern Hemisphere. The added surface ozone is a ...
Global Warming The Basics
... Climate refers to the average weather conditions in a certain place over many years. For example, the climate in Minnesota is cold and snowy in the winter, and the climate in Honolulu, Hawaii, is warm and humid all year long. The climate in one area, like the Midwest or Hawaii, is called a regional ...
... Climate refers to the average weather conditions in a certain place over many years. For example, the climate in Minnesota is cold and snowy in the winter, and the climate in Honolulu, Hawaii, is warm and humid all year long. The climate in one area, like the Midwest or Hawaii, is called a regional ...
Power Point Summary
... that would limit warming to safe levels • Warming in the range of 1.5 -2 degrees Celsius clearly contains a significant risk of dangerous changes • Below 1.5 degrees Celsius there is still appears to be a risk of dangerous changes. Even at 1 degrees Celsius warming there remains a risk of significan ...
... that would limit warming to safe levels • Warming in the range of 1.5 -2 degrees Celsius clearly contains a significant risk of dangerous changes • Below 1.5 degrees Celsius there is still appears to be a risk of dangerous changes. Even at 1 degrees Celsius warming there remains a risk of significan ...
The Role of Sunspots and Solar Winds in Climate Change
... peer-reviewed studies available to back up that claim. Peter Foukal of the Massachusetts-based firm Heliophysics, Inc., who has tracked sunspot intensities from different spots around the globe dating back four centuries, also concludes that such solar disturbances have little or no impact on global ...
... peer-reviewed studies available to back up that claim. Peter Foukal of the Massachusetts-based firm Heliophysics, Inc., who has tracked sunspot intensities from different spots around the globe dating back four centuries, also concludes that such solar disturbances have little or no impact on global ...
MS Word
... dioxide have increased nearly 30%. These increases have enhanced the heat-trapping capability of the earth’s atmosphere. Why are greenhouse gas concentrations increasing? Scientists generally believe that the combustion of fossil fuels and other human activities are the primary reason for the increa ...
... dioxide have increased nearly 30%. These increases have enhanced the heat-trapping capability of the earth’s atmosphere. Why are greenhouse gas concentrations increasing? Scientists generally believe that the combustion of fossil fuels and other human activities are the primary reason for the increa ...
Week 3 Figures ()
... 6. The methane in the atmosphere and the oxidation of CH4 to CO2 (both greenhouse gases), cause a strong temperature spike (the PETM). 7. This increased global temperature causes more water evaporation, more coastal run-off, more nutrients into the ocean. 8. This increases biological productivity wh ...
... 6. The methane in the atmosphere and the oxidation of CH4 to CO2 (both greenhouse gases), cause a strong temperature spike (the PETM). 7. This increased global temperature causes more water evaporation, more coastal run-off, more nutrients into the ocean. 8. This increases biological productivity wh ...
Climate change feedback

Climate change feedback is important in the understanding of global warming because feedback processes may amplify or diminish the effect of each climate forcing, and so play an important part in determining the climate sensitivity and future climate state. Feedback in general is the process in which changing one quantity changes a second quantity, and the change in the second quantity in turn changes the first. Positive feedback amplifies the change in the first quantity while negative feedback reduces it.The term ""forcing"" means a change which may ""push"" the climate system in the direction of warming or cooling. An example of a climate forcing is increased atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases. By definition, forcings are external to the climate system while feedbacks are internal; in essence, feedbacks represent the internal processes of the system. Some feedbacks may act in relative isolation to the rest of the climate system; others may be tightly coupled; hence it may be difficult to tell just how much a particular process contributes. Forcings, feedbacks and the dynamics of the climate system determine how much and how fast the climate changes. The main positive feedback in global warming is the tendency of warming to increase the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere, which in turn leads to further warming. The main negative feedback comes from the Stefan–Boltzmann law, the amount of heat radiated from the Earth into space changes with the fourth power of the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere.Some observed and potential effects of global warming are positive feedbacks, which contribute directly to further global warming. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) Fourth Assessment Report states that ""Anthropogenic warming could lead to some effects that are abrupt or irreversible, depending upon the rate and magnitude of the climate change.""