Слайд 1 - Tuorla Observatory
... parameters are more accurate than for single star • (b) All stars are of the same age. Star clusters are the only objects that enable direct age estimate, study of the galactic evolution and the star-formation history • (c) All stars have nearly the same chemical composition, and the differences in ...
... parameters are more accurate than for single star • (b) All stars are of the same age. Star clusters are the only objects that enable direct age estimate, study of the galactic evolution and the star-formation history • (c) All stars have nearly the same chemical composition, and the differences in ...
CHP 13
... e. a supernova remnant. 5. Massive stars cannot generate energy through iron fusion because a. iron fusion requires very high density. b. stars contain very little iron. c. no star can get hot enough for iron fusion. d. iron is the most tightly bound of all nuclei. e. massive stars supernova before ...
... e. a supernova remnant. 5. Massive stars cannot generate energy through iron fusion because a. iron fusion requires very high density. b. stars contain very little iron. c. no star can get hot enough for iron fusion. d. iron is the most tightly bound of all nuclei. e. massive stars supernova before ...
Seeing Earth`s Orbit in the Stars: Parallax and Aberration
... This situation changed with the introduction of the Copernican system. Copernicus was well aware of parallax. In fact, parallax effects explain the motion of the Sun and certain aspects of planetary ...
... This situation changed with the introduction of the Copernican system. Copernicus was well aware of parallax. In fact, parallax effects explain the motion of the Sun and certain aspects of planetary ...
Copernicus
... planets, using combinations of circular motion known as epicycles. • An epicycle is an orbit within an orbit • Having set up this model, Ptolemy then went on to describe the mathematics which he needed in the rest of the work. ...
... planets, using combinations of circular motion known as epicycles. • An epicycle is an orbit within an orbit • Having set up this model, Ptolemy then went on to describe the mathematics which he needed in the rest of the work. ...
Lecture Topics 1023
... ASTR 1023 Lecture Topics These are the headings of the paragraphs into which ASTR 1023 lectures are divided. Use them to check your notes for completeness, and to see how the course is organized. It is also a good idea to cross-check these topics with your reading assignments, because some topics ar ...
... ASTR 1023 Lecture Topics These are the headings of the paragraphs into which ASTR 1023 lectures are divided. Use them to check your notes for completeness, and to see how the course is organized. It is also a good idea to cross-check these topics with your reading assignments, because some topics ar ...
Exercise 11
... 1. The first step is to make and calibrate your own scale for measuring angles. A transparent plastic strip marked off in 5° intervals is a simple and convenient scale since it can be car ried with you easily. The calibration procedure is illustrated in Figure 2-2. Stand a known distance from a wa ...
... 1. The first step is to make and calibrate your own scale for measuring angles. A transparent plastic strip marked off in 5° intervals is a simple and convenient scale since it can be car ried with you easily. The calibration procedure is illustrated in Figure 2-2. Stand a known distance from a wa ...
First Light Sources at the End of the Dark Ages: Direct
... emission detectable by large ground-based telescopes, and possibly a rest-frame ultraviolet continuum observable from the ground and/or with the JWST. By 2016, the JWST and/or ground-based surveys will regularly deliver deep infrared images that reveal the most massive star-forming galaxies and prot ...
... emission detectable by large ground-based telescopes, and possibly a rest-frame ultraviolet continuum observable from the ground and/or with the JWST. By 2016, the JWST and/or ground-based surveys will regularly deliver deep infrared images that reveal the most massive star-forming galaxies and prot ...
– 1 – 1. Chemical Evolution 1.1.
... one expects the SNII rate to increase by this factor as well. Greggio (2010, MNRAS, in press, see arXiv:1001.3033) gives rates for SNIa. Thes are believed to originate from degenerate binaries, both singly degenerate and systems where both components are degenerate (doubly degenerate). A detailed un ...
... one expects the SNII rate to increase by this factor as well. Greggio (2010, MNRAS, in press, see arXiv:1001.3033) gives rates for SNIa. Thes are believed to originate from degenerate binaries, both singly degenerate and systems where both components are degenerate (doubly degenerate). A detailed un ...
1 Controlled Assessment is the new name for Coursework! The
... the magnitudes of nearby bright reference stars to do this). For others, you will need to complete the analysis once data are collated or graphs have been drawn (for example shadow stick projects or those involving the light curve of a binary star). In some of the more descriptive projects, for exam ...
... the magnitudes of nearby bright reference stars to do this). For others, you will need to complete the analysis once data are collated or graphs have been drawn (for example shadow stick projects or those involving the light curve of a binary star). In some of the more descriptive projects, for exam ...
white dwarfs, neutron stars, black hole
... Compact stars are of special interest because they are the only places in nature where cold nuclear matter can reach densities above that of a single nucleus. To understand this and to introduce the underlying physical aspects, we will attest talk about them in their own right. The physics involved ...
... Compact stars are of special interest because they are the only places in nature where cold nuclear matter can reach densities above that of a single nucleus. To understand this and to introduce the underlying physical aspects, we will attest talk about them in their own right. The physics involved ...
Local Horizon View
... For our location at 45 degrees latitude, the pole star is at altitude 45 degrees as shown to the right. We can see that when we look up. This diagram shows that the altitude of Polaris above the horizon is the same as the observer's latitude. Note that the lines drawn to Polaris are parallel because ...
... For our location at 45 degrees latitude, the pole star is at altitude 45 degrees as shown to the right. We can see that when we look up. This diagram shows that the altitude of Polaris above the horizon is the same as the observer's latitude. Note that the lines drawn to Polaris are parallel because ...
Dennett-Thorpe-deBruyn,2002
... The determination of a peculiar velocity argues that the scattering structure is discrete. This measurement of the transverse velocity of the ionised scattering material cannot be directly compared to radial velocity measurements of HI, but we note that there is no anomalous feature known in this d ...
... The determination of a peculiar velocity argues that the scattering structure is discrete. This measurement of the transverse velocity of the ionised scattering material cannot be directly compared to radial velocity measurements of HI, but we note that there is no anomalous feature known in this d ...
10 September: Faint Stars and Bright Stars
... the right way to express it What are units of power in physics? ...
... the right way to express it What are units of power in physics? ...
Bright stars and faint stars: the stellar magnitude system Magnitudes
... • Apparent magnitude is the brightness of an object as it appears to you • System due to Hipparchos (2nd century BC) • Nowadays system made more precise • Magnitude changes are “logarithmic”, each magnitude means factor of 2.512 in brightness • See Table 16.2 (p382) ...
... • Apparent magnitude is the brightness of an object as it appears to you • System due to Hipparchos (2nd century BC) • Nowadays system made more precise • Magnitude changes are “logarithmic”, each magnitude means factor of 2.512 in brightness • See Table 16.2 (p382) ...
... there was no ice on the poles. Eighteen thousand years ago, there was ice nearly three kilometres thick in parts of Europe. As a result of the huge size of the ice sheets, the sea level was 130 metres lower. Studies show that in some parts of the world, swift dramatic changes took place around that ...
Ground-Based Astrometry 2010-2020
... lengths have yielded reliable distances for many, giving empirical heft to estimates of luminosities, white dwarf masses, and (ultimately) space densities (Thorstensen et al. 2008). Because of ground-based parallax efforts on planetary nebulae central stars, we now know their luminosities and how t ...
... lengths have yielded reliable distances for many, giving empirical heft to estimates of luminosities, white dwarf masses, and (ultimately) space densities (Thorstensen et al. 2008). Because of ground-based parallax efforts on planetary nebulae central stars, we now know their luminosities and how t ...
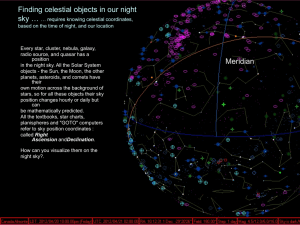
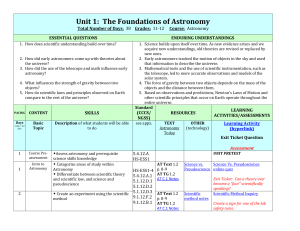
Unit 1: The Foundations of Astronomy
... 1. Science builds upon itself over time. As new evidence arises and we acquire new understandings, old theories are revised or replaced by new ones. 2. Early astronomers tracked the motion of objects in the sky and used that information to describe the universe. 3. Mathematical tools and the use of ...
... 1. Science builds upon itself over time. As new evidence arises and we acquire new understandings, old theories are revised or replaced by new ones. 2. Early astronomers tracked the motion of objects in the sky and used that information to describe the universe. 3. Mathematical tools and the use of ...
No. 2 - Society for Astronomical Sciences
... have been published) and unique information about the surface properties of asteroids. Robert Buchheim described his observation and data reduction methods, and presented two phase curves created from his observations of 1130 Skuld and 535 Montague. The very-nearest astronomical targets discussed th ...
... have been published) and unique information about the surface properties of asteroids. Robert Buchheim described his observation and data reduction methods, and presented two phase curves created from his observations of 1130 Skuld and 535 Montague. The very-nearest astronomical targets discussed th ...
cook - University of Glasgow
... Circle = most perfect form in nature All celestial motions are combinations of circular motions ...
... Circle = most perfect form in nature All celestial motions are combinations of circular motions ...
ASTRONOMY REVIEW Qs - Westhampton Beach School District
... 29. Base your answer to the following question on the passage below. A Newly Discovered Planet Scientists studying a Sun-like star named Ogle-Tr-3 discovered a planet that is, on the average, 3.5 million kilometers away from the star’s surface. The planet was discovered as a result of observing a cy ...
... 29. Base your answer to the following question on the passage below. A Newly Discovered Planet Scientists studying a Sun-like star named Ogle-Tr-3 discovered a planet that is, on the average, 3.5 million kilometers away from the star’s surface. The planet was discovered as a result of observing a cy ...
All_Stars
... and heat up to temperatures sufficient to ignite fusion in the “ash” left over from the previous core-burning stage. The final burning stage is silicon (Si) to iron (Fe) in the core. Fusion of lighter elements occurs in shells surrounding the core. ...
... and heat up to temperatures sufficient to ignite fusion in the “ash” left over from the previous core-burning stage. The final burning stage is silicon (Si) to iron (Fe) in the core. Fusion of lighter elements occurs in shells surrounding the core. ...
The Chemical Composition of an Extrasolar Kuiper-Belt
... lower limit to the accreted mass is ∼1022 g, which is about one hundred thousand times the typical mass of a shortperiod comet. In addition, WD 1425+540 has a wide binary companion, which could facilitate perturbing a Kuiper-Belt-Object analog into the white dwarf’s tidal radius. This finding shows t ...
... lower limit to the accreted mass is ∼1022 g, which is about one hundred thousand times the typical mass of a shortperiod comet. In addition, WD 1425+540 has a wide binary companion, which could facilitate perturbing a Kuiper-Belt-Object analog into the white dwarf’s tidal radius. This finding shows t ...
Part 2 - Aryabhat
... Procyon is a yellow-white main sequence star, twice the size and 7 times more luminous than the Sun. With the exception of Alpha Centauri, it is the least intrinsically luminous star on this list. Like Alpha Centauri it appears so bright only because at 11.4 light-years, it is relatively close. Proc ...
... Procyon is a yellow-white main sequence star, twice the size and 7 times more luminous than the Sun. With the exception of Alpha Centauri, it is the least intrinsically luminous star on this list. Like Alpha Centauri it appears so bright only because at 11.4 light-years, it is relatively close. Proc ...