The Origin of Stars
... object with an accretion disk and jets 4) When the young stellar object begins fusing hydrogen into helium it becomes a true star ...
... object with an accretion disk and jets 4) When the young stellar object begins fusing hydrogen into helium it becomes a true star ...
Scientists classify stars by
... 2. If the remaining mass of the star is about 1.4 times that of our Sun, it will collapse further to become a neutron star. 3. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse and what is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hol ...
... 2. If the remaining mass of the star is about 1.4 times that of our Sun, it will collapse further to become a neutron star. 3. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse and what is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hol ...
Handout 15: Virial Theorem E = P.E. + K.E = (1/2)P.E. = -K.E.
... For a star, gas is compressible, therefore density increases as r decreases Therefore more tightly bound than constant density Therefore PE is more negative than this ...
... For a star, gas is compressible, therefore density increases as r decreases Therefore more tightly bound than constant density Therefore PE is more negative than this ...
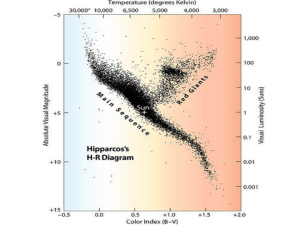
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature? - d
... On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own HertzsprungRussell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color, ...
... On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own HertzsprungRussell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color, ...
Quiz 1 Review
... Neutron stars spin extremely fast (1000 times per second). Any remaining electrons not fused with protons are excited by the stars rotation and interact with the neutron stars magnetic field. This interaction releases huge amounts of energy from the neutron stars N and S pole and they are seen as pu ...
... Neutron stars spin extremely fast (1000 times per second). Any remaining electrons not fused with protons are excited by the stars rotation and interact with the neutron stars magnetic field. This interaction releases huge amounts of energy from the neutron stars N and S pole and they are seen as pu ...
Astrophysics
... but continues to do so until it becomes nothing more than a point mass. Point mass singularity, and this breaks the laws of Physics. The strength of gravity inside a black hole is so massive that nothing can escape, not even light (which is why they are not visible). The perimeter at which light c ...
... but continues to do so until it becomes nothing more than a point mass. Point mass singularity, and this breaks the laws of Physics. The strength of gravity inside a black hole is so massive that nothing can escape, not even light (which is why they are not visible). The perimeter at which light c ...
S1E4 Extreme Stars
... What is a planetary nebula? (1) A large swarm of planets surrounding a star. (2) A disk of gas and dust around a young star. (3) Glowing gas in Earth’s upper atmosphere. (4) Ionized gas around a white dwarf star. ...
... What is a planetary nebula? (1) A large swarm of planets surrounding a star. (2) A disk of gas and dust around a young star. (3) Glowing gas in Earth’s upper atmosphere. (4) Ionized gas around a white dwarf star. ...
Astronomical distances and Stellar magnitudes
... 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate distance of the following in AU: (a) Sun to the E ...
... 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate distance of the following in AU: (a) Sun to the E ...
Chandra Sees the Atmosphere of a Neutron Star - Chandra X
... the central region of the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A. This interstellar cloud 14 light years across, is all that remains of a massive star that exploded 330 years ago. A careful analysis of the X-ray data has revealed that the dense neutron star left behind by the supernova has a thin carbon atm ...
... the central region of the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A. This interstellar cloud 14 light years across, is all that remains of a massive star that exploded 330 years ago. A careful analysis of the X-ray data has revealed that the dense neutron star left behind by the supernova has a thin carbon atm ...
File
... million K, the surface would be liquid form, while if it's cooler than that, it would be solid. Below that is a solid crust, about a kilometer thick. This crust is very hard and very smooth. Gravity would probably prevent any irregularities larger than half a centimeter. ...
... million K, the surface would be liquid form, while if it's cooler than that, it would be solid. Below that is a solid crust, about a kilometer thick. This crust is very hard and very smooth. Gravity would probably prevent any irregularities larger than half a centimeter. ...
chap17_s05_probs
... temperature relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third value is found using this relation, described on page 449 in the text. In solar units, L = R2 x T4 , substituting into the expression gives 64 = R2 x 24 , 64 = R2 x 16 Dividing each side of the expression by 16 gives, R2 = 4, there ...
... temperature relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third value is found using this relation, described on page 449 in the text. In solar units, L = R2 x T4 , substituting into the expression gives 64 = R2 x 24 , 64 = R2 x 16 Dividing each side of the expression by 16 gives, R2 = 4, there ...
Lec11_2D
... Accretion Disks and Black Holes The accretion disk around a black hole can extend very close to the event horizon. The gas speed there is very close to the speed of light, so the friction in the disk is extremely intense. This type of disk will produce the most-energetic x-rays. ...
... Accretion Disks and Black Holes The accretion disk around a black hole can extend very close to the event horizon. The gas speed there is very close to the speed of light, so the friction in the disk is extremely intense. This type of disk will produce the most-energetic x-rays. ...
chap17_f04_probs
... relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third is found using that relation, described on pg 449 in the text. In solar units, L = R2 x T4 , substituting into the expression gives 64 = R2 x 24 , 64 = R2 x 16 Dividing each side of the expression by 16 gives, R2 = 4, therefore R = 2. The star ...
... relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third is found using that relation, described on pg 449 in the text. In solar units, L = R2 x T4 , substituting into the expression gives 64 = R2 x 24 , 64 = R2 x 16 Dividing each side of the expression by 16 gives, R2 = 4, therefore R = 2. The star ...
Name: Period: Date: The Celestial Sphere What is the Celestial
... The “road of the sun” on the Celestial Sphere 1. The sun has a _________________ (daily) motion from east to west due to the earth’s spinning around its axis, ~ 24 h 2. The sun also changes its ____________________ in the sky ~ 1 degree per day, ~ 365.25 days What is the ecliptic? ...
... The “road of the sun” on the Celestial Sphere 1. The sun has a _________________ (daily) motion from east to west due to the earth’s spinning around its axis, ~ 24 h 2. The sun also changes its ____________________ in the sky ~ 1 degree per day, ~ 365.25 days What is the ecliptic? ...
10 relativity, black holes_
... Depends on the gravity between you and the object you want to escape! For a black hole, the escape velocity (inside the event horizon) is greater than the speed of light! ...
... Depends on the gravity between you and the object you want to escape! For a black hole, the escape velocity (inside the event horizon) is greater than the speed of light! ...
Stars
... • Then, star collapses under the weight and because it is electron degenerate, energy created will not expand the star and shut off the fusion. • So, entire star (carbon, mostly) undergoes fusion at once. What a star normally takes billions of years to burn, this star burns all at once. BIG explosio ...
... • Then, star collapses under the weight and because it is electron degenerate, energy created will not expand the star and shut off the fusion. • So, entire star (carbon, mostly) undergoes fusion at once. What a star normally takes billions of years to burn, this star burns all at once. BIG explosio ...