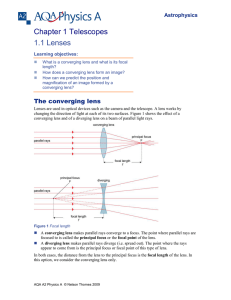
Chapter 1 Telescopes 1.1 Lenses
... the diameter of the objective of a telescope, the greater the number of stars that can be seen. Planets and other astronomical objects in the solar system are magnified using a telescope (unlike stars which are point objects and are seen through telescopes as point images no matter how large the mag ...
... the diameter of the objective of a telescope, the greater the number of stars that can be seen. Planets and other astronomical objects in the solar system are magnified using a telescope (unlike stars which are point objects and are seen through telescopes as point images no matter how large the mag ...
Part IV: Stars
... role of mathematical modeling in science and to explain how we can be so certain of what’s going on when we can’t see the core and can’t send in a probe to observe what’s going on there. Up to this point in the course, we’ve been discussing planets, which some students regard as “more real” because ...
... role of mathematical modeling in science and to explain how we can be so certain of what’s going on when we can’t see the core and can’t send in a probe to observe what’s going on there. Up to this point in the course, we’ve been discussing planets, which some students regard as “more real” because ...
Lecture18
... Extrasolar planets Many hundreds now known! Very difficult to detect (star much much brighter)... indirect “wobble” methods used based on velocity (Doppler shift) or position (Astrometry) of the star, “transits” (planet blocks starlight). Which detection method can be used depends on orientation of ...
... Extrasolar planets Many hundreds now known! Very difficult to detect (star much much brighter)... indirect “wobble” methods used based on velocity (Doppler shift) or position (Astrometry) of the star, “transits” (planet blocks starlight). Which detection method can be used depends on orientation of ...
The Magnitude System
... Magnitudes have to be somehow related to the brightness of stars. And brightness is a measure of the total number of photons of energy E that are emitted from the star per second and that pass though the area of our detectors. The unit of brightness is ergs/sec/cm2, or if you use SI units, it is Wat ...
... Magnitudes have to be somehow related to the brightness of stars. And brightness is a measure of the total number of photons of energy E that are emitted from the star per second and that pass though the area of our detectors. The unit of brightness is ergs/sec/cm2, or if you use SI units, it is Wat ...
18_Testbank - Lick Observatory
... a star supported against gravity by ordinary pressure. C) The white dwarf immediately collapses into a black hole, disappearing from view. D) A white dwarf can never gain enough mass to reach the limit because a strong stellar wind prevents the material from reaching it in the first place. Answer: A ...
... a star supported against gravity by ordinary pressure. C) The white dwarf immediately collapses into a black hole, disappearing from view. D) A white dwarf can never gain enough mass to reach the limit because a strong stellar wind prevents the material from reaching it in the first place. Answer: A ...
Millisecond Pulsar Binaries at Transition
... •Basically the same as PSR J1023+0038 •After the transition: • a P=1.69 ms pulsar is seen •X-rays are orbitally modulated •Gamma-ray flux has decreased by a factor of 2 ...
... •Basically the same as PSR J1023+0038 •After the transition: • a P=1.69 ms pulsar is seen •X-rays are orbitally modulated •Gamma-ray flux has decreased by a factor of 2 ...
Dust and molecular gas in the most distant quasars
... Discussion – star formation in the z~6 quasars • About 30% of the optically selected quasars at z~6 have been detected, and most of the detections show FIR excesses in their SEDs. • The MAMBO undetected quasars at z~6: – The average FIR-to-radio SED is consistent with the templates of local optical ...
... Discussion – star formation in the z~6 quasars • About 30% of the optically selected quasars at z~6 have been detected, and most of the detections show FIR excesses in their SEDs. • The MAMBO undetected quasars at z~6: – The average FIR-to-radio SED is consistent with the templates of local optical ...
Comparison of low- and high-mass star formation
... constantly replenished by the global collapse. The most massive object is located near the minimum of the global potential well and accretes the global collapse-fed material at a rate higher than any other object. Nevertheless, its accretion rate is only ∼10% of the total rate. In other words, the v ...
... constantly replenished by the global collapse. The most massive object is located near the minimum of the global potential well and accretes the global collapse-fed material at a rate higher than any other object. Nevertheless, its accretion rate is only ∼10% of the total rate. In other words, the v ...
... use the time delay between a light pulse sent to an object and the return of the reflected light pulse plus the finite speed of light to measure distances. However, stars are so far away and such poor reflectors that this approach is impractical (though it is used to determine distances to planets i ...
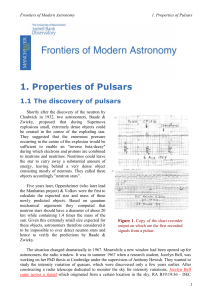
1: Properties of Pulsars
... from the central "strange" star, identifying it as a pulsar. It turned out later, that these "giant pulses" which they observed, occur every two minutes or so, and that the true pulse period was in fact as short as 33 milliseconds. The short period of 33 milliseconds ruled out white dwarfs for being ...
... from the central "strange" star, identifying it as a pulsar. It turned out later, that these "giant pulses" which they observed, occur every two minutes or so, and that the true pulse period was in fact as short as 33 milliseconds. The short period of 33 milliseconds ruled out white dwarfs for being ...
Lab PDF - NMSU Astronomy
... regardless of their luminosity or surface temperature, will lie along this line. In which corner of the diagram (upper right, upper left, lower right, or lower left) would stars with radii 1000 times larger than that of the Sun be plotted? In which corner would stars with radii 1000 times smaller th ...
... regardless of their luminosity or surface temperature, will lie along this line. In which corner of the diagram (upper right, upper left, lower right, or lower left) would stars with radii 1000 times larger than that of the Sun be plotted? In which corner would stars with radii 1000 times smaller th ...