Applications of Light to Astronomy
... o Observing which wavelengths are missing after reflection tells you about the composition of the reflecting surface! o Observing which wavelengths are missing after passing through material (e.g. atmosphere of a planet or star) tells you about that material Most of the stuff in the universe is hy ...
... o Observing which wavelengths are missing after reflection tells you about the composition of the reflecting surface! o Observing which wavelengths are missing after passing through material (e.g. atmosphere of a planet or star) tells you about that material Most of the stuff in the universe is hy ...
Slide 1
... hot gas which looks like planetary disk, and called Planetary Nebulae (PNe) (nothing to do with planets per se) • PNe cores continue to cool and become White Dwarfs (94% stars end up as WDs) ...
... hot gas which looks like planetary disk, and called Planetary Nebulae (PNe) (nothing to do with planets per se) • PNe cores continue to cool and become White Dwarfs (94% stars end up as WDs) ...
Our Universe - Etiwanda E
... Most asteroids are between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter captured by gravity. Some asteroids are the moons of planets. ...
... Most asteroids are between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter captured by gravity. Some asteroids are the moons of planets. ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 9
... 27.1 & 27.2 – Formation & Models of the Solar System 1. What is a solar nebula? 2. What is the nebular hypothesis? 3. How did the land and atmosphere of Earth form? 4. How do the theories of Aristotle and Copernicus differ? 5. What did Ptolemy propose about the solar system? 6. What is a protoplanet ...
... 27.1 & 27.2 – Formation & Models of the Solar System 1. What is a solar nebula? 2. What is the nebular hypothesis? 3. How did the land and atmosphere of Earth form? 4. How do the theories of Aristotle and Copernicus differ? 5. What did Ptolemy propose about the solar system? 6. What is a protoplanet ...
Stars Answers - Science Skool!
... 1. What happens to cause the stable period in the life cycle of a star to end? It runs out of hydrogen so nuclear fusion slows down 2. What will happen to the Sun after the stable period ends? Temperature decreases and change to red giant, temperature increases and change to white dwarf 3. What happ ...
... 1. What happens to cause the stable period in the life cycle of a star to end? It runs out of hydrogen so nuclear fusion slows down 2. What will happen to the Sun after the stable period ends? Temperature decreases and change to red giant, temperature increases and change to white dwarf 3. What happ ...
STARS and GALAXIES
... • A large ball of gas held together by gravity that produces tremendous amounts of heat and light. • Some stars are very old and the size of planets or moons, and some no longer emit radiation (no light). ...
... • A large ball of gas held together by gravity that produces tremendous amounts of heat and light. • Some stars are very old and the size of planets or moons, and some no longer emit radiation (no light). ...
Unit D Test Review Electromagnetic Spectrum: Which
... What is the connection between wavelength of the radiation its energy? List the colors of visible light in order from shortest wavelength to longest. Complete the table: Type of Radiation ...
... What is the connection between wavelength of the radiation its energy? List the colors of visible light in order from shortest wavelength to longest. Complete the table: Type of Radiation ...
astronomy 2 review sheet - Hicksville Public Schools
... 9. What are eclipsing binary stars? A STAR SYSTEM WHERE ONE STAR BLOCKS THE LIGHT OF THE OTHER STAR AT REGULAR INTERVALS. 10. What are the different types of galaxies? SPIRAL. ELLIPTICAL, IRREGULAR. 11. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way? SPIRAL 12. What is the name of the theory that describes th ...
... 9. What are eclipsing binary stars? A STAR SYSTEM WHERE ONE STAR BLOCKS THE LIGHT OF THE OTHER STAR AT REGULAR INTERVALS. 10. What are the different types of galaxies? SPIRAL. ELLIPTICAL, IRREGULAR. 11. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way? SPIRAL 12. What is the name of the theory that describes th ...
Astronomy - Shelbyville Central Schools
... Stars differ in composition, age, and size. *young stars are rich in hydrogen *older stars use up hydrogen to produce more helium ...
... Stars differ in composition, age, and size. *young stars are rich in hydrogen *older stars use up hydrogen to produce more helium ...
Physical properties of stars
... that are 1,000 times larger than our sun. pg. 450 Temperature: Surface temperatures range from 3000K to 30,000K Color is an indication of temperature. Blue hottest White Yellow Orange Red coolest Mass While the size of stars varies widely the mass does not. 15 times our Sun’s mass to .2 times our Su ...
... that are 1,000 times larger than our sun. pg. 450 Temperature: Surface temperatures range from 3000K to 30,000K Color is an indication of temperature. Blue hottest White Yellow Orange Red coolest Mass While the size of stars varies widely the mass does not. 15 times our Sun’s mass to .2 times our Su ...
OP/IP27 Stars HR life of stars WS
... The Sun is classified as which type of star?___________________________________ ...
... The Sun is classified as which type of star?___________________________________ ...
ASTRO REVIEW 14
... 10. Compare and contrast the geocentric and the heliocentric models of the universe. ...
... 10. Compare and contrast the geocentric and the heliocentric models of the universe. ...
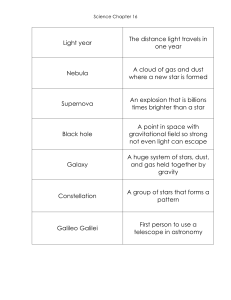
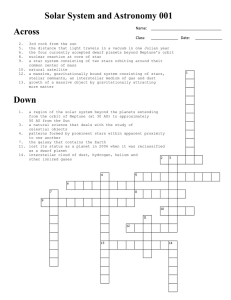
Solar System and Astronomy puzzle 001
... 3rd rock from the sun the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year the four currently accepted dwarf planets beyond Neptune's orbit nuclear reaction at core of star a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass 10. natural satellite 12. a massive ...
... 3rd rock from the sun the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year the four currently accepted dwarf planets beyond Neptune's orbit nuclear reaction at core of star a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass 10. natural satellite 12. a massive ...
Unit 11 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast the apparent and actual motion of stars. How can scientists know if a star or galaxy is moving toward ...
... Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast the apparent and actual motion of stars. How can scientists know if a star or galaxy is moving toward ...
New Directions in Star Cluster Research
... Consequences of Definition of a Star Stars must evolve (as they release energy) - changes in structure and/or chemical composition Death of a star can occur in 2 ways (a) Violation of first condition - self gravity (breakup of star scattering material into space) (b) Violation second condition - in ...
... Consequences of Definition of a Star Stars must evolve (as they release energy) - changes in structure and/or chemical composition Death of a star can occur in 2 ways (a) Violation of first condition - self gravity (breakup of star scattering material into space) (b) Violation second condition - in ...
Ginger Dublin 6th Grade Science
... Starlight Brightness • Apparent Magnitude: How bright a star appears to be from earth when viewed with the unaided eye. Distance can cause a dimmer star to appear to be brighter than a brighter star that is farther away. • Absolute Magnitude: The amount of light (brightness) a star actually has. Th ...
... Starlight Brightness • Apparent Magnitude: How bright a star appears to be from earth when viewed with the unaided eye. Distance can cause a dimmer star to appear to be brighter than a brighter star that is farther away. • Absolute Magnitude: The amount of light (brightness) a star actually has. Th ...