Solutions to Homework #4, AST 203, Spring 2012
... rotation of the neutron star will be much shorter, as we expect. Substituting numbers, RNS /RCO = 10km/(0.5R ) ≈ 2×10−5 . The period is then PNS = (2×10−5 )2 ×30days ≈ 1 millisecond. This number is actually near the limit of how fast a neutron star can rotate. From observations of radio pulsars we ...
... rotation of the neutron star will be much shorter, as we expect. Substituting numbers, RNS /RCO = 10km/(0.5R ) ≈ 2×10−5 . The period is then PNS = (2×10−5 )2 ×30days ≈ 1 millisecond. This number is actually near the limit of how fast a neutron star can rotate. From observations of radio pulsars we ...
Ch12&13 Life and Death of Stars
... • Adding mass to a white dwarf increases its gravity, forcing electrons into a smaller space • In order to avoid being in the same state some of the electrons need to move faster ...
... • Adding mass to a white dwarf increases its gravity, forcing electrons into a smaller space • In order to avoid being in the same state some of the electrons need to move faster ...
Numerical simulations of convection in A
... velocities are of the order of a few km s −1. In the lower atmpsphere they are due to overturning convective motions (overshoot). In the upper atmosphere they are due to pressure waves generated by instationary convective motions. A non–magnetic atmosphere should be mixed on a time scale of a few ho ...
... velocities are of the order of a few km s −1. In the lower atmpsphere they are due to overturning convective motions (overshoot). In the upper atmosphere they are due to pressure waves generated by instationary convective motions. A non–magnetic atmosphere should be mixed on a time scale of a few ho ...
chapter18StarDeath
... — Use orbital properties of companion — Measure velocity and distance of orbiting gas It’s a black hole if it’s not a star and its mass exceeds the neutron star limit (~3 MSun) ...
... — Use orbital properties of companion — Measure velocity and distance of orbiting gas It’s a black hole if it’s not a star and its mass exceeds the neutron star limit (~3 MSun) ...
The cosmic origin of fluorine and sulphur
... Practically only the two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium, were formed during the Big Bang when our Universe was born. All other elements have been formed, and keep being formed, in different processes in different types of stars. is means that all atoms, except hydrogen and helium, that build ...
... Practically only the two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium, were formed during the Big Bang when our Universe was born. All other elements have been formed, and keep being formed, in different processes in different types of stars. is means that all atoms, except hydrogen and helium, that build ...
Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard What is a white dwarf
... – A black hole is a massive object whose radius is so small that the escape velocity exceeds the speed of light ...
... – A black hole is a massive object whose radius is so small that the escape velocity exceeds the speed of light ...
www.astro.org.uk www.facebook.com/Stra ordAstro www.twi er.com
... The improvement in the measurement of the distance to the Large Magellanic Cloud also gives be4er distances for many Cepheid variable stars . These bright pulsa:ng stars are used as standard candles to measure distances out to more remote galaxies and to determine the expansion rate of the Universe ...
... The improvement in the measurement of the distance to the Large Magellanic Cloud also gives be4er distances for many Cepheid variable stars . These bright pulsa:ng stars are used as standard candles to measure distances out to more remote galaxies and to determine the expansion rate of the Universe ...
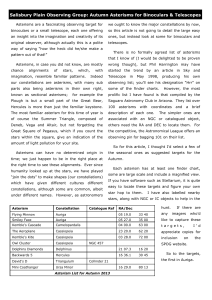
Autumn Asterisms for binoculars 2013
... (the Giraffe) is not one of the brightest constellations, but the Cascade is one of its showpiece objects, with the open cluster NGC 1502 to its end. It is an easy object in binoculars and a favourite of mine. You can find it by taking a line from Capella in ...
... (the Giraffe) is not one of the brightest constellations, but the Cascade is one of its showpiece objects, with the open cluster NGC 1502 to its end. It is an easy object in binoculars and a favourite of mine. You can find it by taking a line from Capella in ...
Chapter 10 Neutron Stars and General Relativity
... things must happen • A binary must form with two stars massive enough to become supernovae and produce neutron stars, and the neutron stars thus formed must remain bound to each other through the two supernova explosions. • The neutron star binary must result from gravitational capture of one neutro ...
... things must happen • A binary must form with two stars massive enough to become supernovae and produce neutron stars, and the neutron stars thus formed must remain bound to each other through the two supernova explosions. • The neutron star binary must result from gravitational capture of one neutro ...
P7 Further Physics : Observing the Universe
... The Textbook presents the content of the specification in four topics: • Observatories and telescopes highlights the use of the full electromagnetic spectrum to understand the cosmic landscape, and then describes refractors and reflectors and how they work. • Mapping the heavens discusses observatio ...
... The Textbook presents the content of the specification in four topics: • Observatories and telescopes highlights the use of the full electromagnetic spectrum to understand the cosmic landscape, and then describes refractors and reflectors and how they work. • Mapping the heavens discusses observatio ...
FREE Sample Here
... 2) Briefly explain what we mean by the statement "The farther away we look in distance, the further back we look in time." Answer: It means that when we look at a distant object, we see it as it was some time in the past, rather than as it is now. This is because the light we see has taken time to t ...
... 2) Briefly explain what we mean by the statement "The farther away we look in distance, the further back we look in time." Answer: It means that when we look at a distant object, we see it as it was some time in the past, rather than as it is now. This is because the light we see has taken time to t ...
Physical structure of the local interstellar medium
... various ions provides the opportunity not only to measure the velocity structure along the line of sight, but to also measure the temperature, turbulent velocity, ionization, abundances, and depletions. Because the kinematic structure along a line of sight that is <100 pc is relatively simple, with ...
... various ions provides the opportunity not only to measure the velocity structure along the line of sight, but to also measure the temperature, turbulent velocity, ionization, abundances, and depletions. Because the kinematic structure along a line of sight that is <100 pc is relatively simple, with ...
3.7 Isotope Effect - Institute for Astronomy | ETH
... The solar isotope ratios, e.g. 12C/13C = 80, corresponds to the chemical composition of our galaxy 4.6 × 109 years ago at the birthplace of the Sun. A comparison with today’s isotope ratios in the interstellar medium provides important clues on the production rate of heavier elements in stars and al ...
... The solar isotope ratios, e.g. 12C/13C = 80, corresponds to the chemical composition of our galaxy 4.6 × 109 years ago at the birthplace of the Sun. A comparison with today’s isotope ratios in the interstellar medium provides important clues on the production rate of heavier elements in stars and al ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Why do we use light years? We need numbers that make sense to us in relationship to objects; we scale up and use meters and kilometers for large numbers. Distances between stars and galaxies Different wavelengths of Electromagnetic spectrum are used to gain information about distances and pro ...
... Why do we use light years? We need numbers that make sense to us in relationship to objects; we scale up and use meters and kilometers for large numbers. Distances between stars and galaxies Different wavelengths of Electromagnetic spectrum are used to gain information about distances and pro ...
Galaxy Powerpoint Notes
... Galaxy collisions The Big Band Theory states that the Universe began a long time ago, with galaxies and early stars forming just after. It also states that the Universe is still expanding today, meaning that the galaxies that we see today are travelling at high speeds. Eventually, sooner or later, t ...
... Galaxy collisions The Big Band Theory states that the Universe began a long time ago, with galaxies and early stars forming just after. It also states that the Universe is still expanding today, meaning that the galaxies that we see today are travelling at high speeds. Eventually, sooner or later, t ...
Binarity in carbon-enhanced metal-poor stars
... theoretically expected from massive AGB stars with hot dredge-up, terminating the AGB process before the star had time to develop s-process elements (Herwig 2004), or some rotating AGB companions (Herwig, Langer & Lugaro 2003; Siess, Goriely & Langer 2004). However, this result is dependent on the p ...
... theoretically expected from massive AGB stars with hot dredge-up, terminating the AGB process before the star had time to develop s-process elements (Herwig 2004), or some rotating AGB companions (Herwig, Langer & Lugaro 2003; Siess, Goriely & Langer 2004). However, this result is dependent on the p ...
PODEX – PhOtometric Data EXtractor
... The reduction process is started by clicking the START Reduction button. First, the bias image is subtracted from the raw image and the residual image is divided by the flat field image (optional). After these corrections the image is divided by integration time to normalise the intensity to ADU per ...
... The reduction process is started by clicking the START Reduction button. First, the bias image is subtracted from the raw image and the residual image is divided by the flat field image (optional). After these corrections the image is divided by integration time to normalise the intensity to ADU per ...
The Next Great Exoplanet Hunt Please share
... around a Sun-like star. For this reason, a meaningful transit survey must include tens of thousands of stars, or more. Because faint stars far outnumber bright ones in any given region of the sky, a practical strategy is to monitor a rich field of relatively faint stars. This is precisely what the K ...
... around a Sun-like star. For this reason, a meaningful transit survey must include tens of thousands of stars, or more. Because faint stars far outnumber bright ones in any given region of the sky, a practical strategy is to monitor a rich field of relatively faint stars. This is precisely what the K ...
Observations of binary systems with pulsating components
... lines owing to Doppler effect caused by orbital motion. • Depending on components’ relative brightness, the observed spectrum will show the displacement of lines of one or both components (if a star is too faint, its lines will not be visible). • If displacement of both components’ lines is visible, ...
... lines owing to Doppler effect caused by orbital motion. • Depending on components’ relative brightness, the observed spectrum will show the displacement of lines of one or both components (if a star is too faint, its lines will not be visible). • If displacement of both components’ lines is visible, ...
Determining Distances to Other Galaxies
... Vr stays roughly constant with R as far as luminous matter can be detected Masses from 1011 to 2x1012 Msun 50% to 80% of mass is Dark matter. DM does not have to be confined to the disk – distributed spherically ...
... Vr stays roughly constant with R as far as luminous matter can be detected Masses from 1011 to 2x1012 Msun 50% to 80% of mass is Dark matter. DM does not have to be confined to the disk – distributed spherically ...
Stellar kinematics
Stellar kinematics is the study of the movement of stars without needing to understand how they acquired their motion. This differs from stellar dynamics, which takes into account gravitational effects. The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding part of the Milky Way.In astronomy, it is widely accepted that most stars are born within molecular clouds known as stellar nurseries. The stars formed within such a cloud compose open clusters containing dozens to thousands of members. These clusters dissociate over time. Stars that separate themselves from the cluster's core are designated as members of the cluster's stellar association. If the remnant later drifts through the Milky Way as a coherent assemblage, then it is termed a moving group.