Determining the inclination of the rotation axis of a sun-like Star
... rotation axis of a pulsating Sun-like star and the line of sight. A knowledge of i is important not just for obtaining improved stellar parameters, but also in order to determine the true masses of extrasolar planets detected from the radial velocity shifts of their central stars. By means of Monte ...
... rotation axis of a pulsating Sun-like star and the line of sight. A knowledge of i is important not just for obtaining improved stellar parameters, but also in order to determine the true masses of extrasolar planets detected from the radial velocity shifts of their central stars. By means of Monte ...
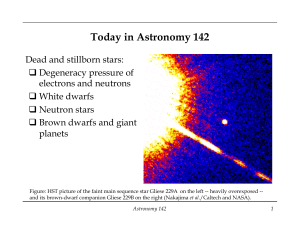
Today in Astronomy 142
... Beyond the Chandrasekhar mass: neutron stars ! The maximum mass calculation involves general relativity and an equation of state that includes the strong interaction. The maximum mass is about 2.2 M⊙; it could not possibly be > 3 M⊙. ! Neutron stars generally have very large magnetic fields (conser ...
... Beyond the Chandrasekhar mass: neutron stars ! The maximum mass calculation involves general relativity and an equation of state that includes the strong interaction. The maximum mass is about 2.2 M⊙; it could not possibly be > 3 M⊙. ! Neutron stars generally have very large magnetic fields (conser ...
AN ATTEMPT To prove the MOTION OF THE EARTH FROM
... with their Instruments and wayes of using them, we shall find that their performances thereby ...
... with their Instruments and wayes of using them, we shall find that their performances thereby ...
Star Classification and its Connection to Exoplanets.
... the pie, so the viewer can see the result: G classified (sun-like) stars have the majority of the exoplanets, at 38%. The second pie chart uses data from the percentage of stars that have planets, so at around 6.6% of a total of around 18%, G stars make up about 37%, again the dominant planet host. ...
... the pie, so the viewer can see the result: G classified (sun-like) stars have the majority of the exoplanets, at 38%. The second pie chart uses data from the percentage of stars that have planets, so at around 6.6% of a total of around 18%, G stars make up about 37%, again the dominant planet host. ...
Carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and lithium abundances of six
... Abstract. Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen abundances were derived from high-resolution spectra of 6 cool supergiants of the Small Magellanic Cloud. Oxygen-to-iron ratios (mean value [O/Fe] ≈–0.18 dex) are found to be similar to those found in young objects in the LMC and the Galaxy. This result is discu ...
... Abstract. Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen abundances were derived from high-resolution spectra of 6 cool supergiants of the Small Magellanic Cloud. Oxygen-to-iron ratios (mean value [O/Fe] ≈–0.18 dex) are found to be similar to those found in young objects in the LMC and the Galaxy. This result is discu ...
Astronomy 114 – Summary of Important Concepts #2 1 Stars: key
... where the subscripts i and f mean initial and final, respectively. Since mi = mf , we can solve this for vf , say: vf = vi ...
... where the subscripts i and f mean initial and final, respectively. Since mi = mf , we can solve this for vf , say: vf = vi ...
T
... The long-term precision of the instrument cannot be checked easily because it requires a long time base on one hand, and the knowledge of stable stellar sources on the other hand. Especially the latter point represents a new challenge since the intrinsic stability of the stars has never been studied ...
... The long-term precision of the instrument cannot be checked easily because it requires a long time base on one hand, and the knowledge of stable stellar sources on the other hand. Especially the latter point represents a new challenge since the intrinsic stability of the stars has never been studied ...
silicon and oxygen abundances in planet-host stars
... no such differences in their sample for alpha- and iron-peak elements. They observe no difference in the overall trends of [X/Fe] between planet hosts and their volume-limited sample of stars without any known planetary-mass companions. Based on their results, stars with planets appear to be indisti ...
... no such differences in their sample for alpha- and iron-peak elements. They observe no difference in the overall trends of [X/Fe] between planet hosts and their volume-limited sample of stars without any known planetary-mass companions. Based on their results, stars with planets appear to be indisti ...
Table of Contents
... how much belongs to the black hole? Stars have masses which range from 0.08 to ~120 Solar masses. The total mass computed in task 5 is much larger. Thus, regardless of what kind of star we are dealing with, it has a negligible mass mS compared to the mass of the black hole mBH (i.e., mBH >> mS ) . T ...
... how much belongs to the black hole? Stars have masses which range from 0.08 to ~120 Solar masses. The total mass computed in task 5 is much larger. Thus, regardless of what kind of star we are dealing with, it has a negligible mass mS compared to the mass of the black hole mBH (i.e., mBH >> mS ) . T ...
Studying the Stars
... Now that we can be more accurate in our measurements, stars can have more specific magnitudes like 1.5, 6.73, etc. and even negative numbers for those stars that are brighter than 1st order. ...
... Now that we can be more accurate in our measurements, stars can have more specific magnitudes like 1.5, 6.73, etc. and even negative numbers for those stars that are brighter than 1st order. ...
Deep SDSS optical spectroscopy of distant halo stars I. Atmospheric
... Figure 1 shows two examples of observed BOSS spectra, and our best-fitting models. At very low metallicity, the information on the stellar properties comes mainly from hydrogen (Balmer and Paschen) lines, Ca II lines (H and K in the blue, as well as the IR triplet). Our continuum correction scheme s ...
... Figure 1 shows two examples of observed BOSS spectra, and our best-fitting models. At very low metallicity, the information on the stellar properties comes mainly from hydrogen (Balmer and Paschen) lines, Ca II lines (H and K in the blue, as well as the IR triplet). Our continuum correction scheme s ...
Chapter 3 Cosmology 3.1 The Doppler effect
... that the expansion of the Universe is accelerating and has been for about the past 5000 million years. Before this discovery, most astronomers expected that the Universe was decelerating because very distant objects would be slowed down by the force of gravity from other galaxies. Many more observat ...
... that the expansion of the Universe is accelerating and has been for about the past 5000 million years. Before this discovery, most astronomers expected that the Universe was decelerating because very distant objects would be slowed down by the force of gravity from other galaxies. Many more observat ...
Isotopic composition of Hg and Pt in 5 slowly rotating HgMn stars *
... stars often relied on spectra of rather low resolution and low S/N ratio, so that only limited information could be derived from the centroid wavelength of unresolved isotopic blends. In this paper we present the results of a study of the isotopic compositions of Hg and Pt in 5 very slowly rotating ...
... stars often relied on spectra of rather low resolution and low S/N ratio, so that only limited information could be derived from the centroid wavelength of unresolved isotopic blends. In this paper we present the results of a study of the isotopic compositions of Hg and Pt in 5 very slowly rotating ...
exam 3 review lecture
... • Quasars are small, extremely luminous, extremely distant galactic nuclei • Luminosity and jets likely come from matter falling into big black hole (millions of solar masses) at the galaxies centers • Was our galaxy an AGN once? ...
... • Quasars are small, extremely luminous, extremely distant galactic nuclei • Luminosity and jets likely come from matter falling into big black hole (millions of solar masses) at the galaxies centers • Was our galaxy an AGN once? ...
... Studies of ice core show that concentrations of CO2 have not been so high for nearly half a million years. At the current rate of increase, they will have reached 800 ppm by the end of the 21st century! Beyond 550 ppm it would not be liveable! CO2 being emitted stays in the atmosphere for up to 200 ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Barium abundances in cool
... (1990) who compiled the results of 6 analyses. In both compilations the systematic differences from author-to-author are evident. For example, [Ba/Fe] of Leep & Wallerstein (1981) or Gilroy et al. (1988) is lower on average by 0.5 dex than the results of Magain (1989) or Peterson et al. (1990). Such ...
... (1990) who compiled the results of 6 analyses. In both compilations the systematic differences from author-to-author are evident. For example, [Ba/Fe] of Leep & Wallerstein (1981) or Gilroy et al. (1988) is lower on average by 0.5 dex than the results of Magain (1989) or Peterson et al. (1990). Such ...
Constellations Overview
... Some historians argue that many of the myths associated with the constellations were invented specifically to help farmers construct an accurate understanding of the sky. From ancient times farmers knew that for most crops, you plant in the spring and harvest in the autumn. ...
... Some historians argue that many of the myths associated with the constellations were invented specifically to help farmers construct an accurate understanding of the sky. From ancient times farmers knew that for most crops, you plant in the spring and harvest in the autumn. ...
Chapter 12
... Mass of a Star-Forming Cloud • A typical molecular cloud (T~ 30 K, n ~ 300 particles/cm3) must contain at least a few hundred solar masses for gravity to overcome pressure. • The cloud can prevent a pressure buildup by converting thermal energy into infrared and radio photons that escape the cloud. ...
... Mass of a Star-Forming Cloud • A typical molecular cloud (T~ 30 K, n ~ 300 particles/cm3) must contain at least a few hundred solar masses for gravity to overcome pressure. • The cloud can prevent a pressure buildup by converting thermal energy into infrared and radio photons that escape the cloud. ...
Is there a Supermassive Black Hole at the Center of the Milky Way?
... The rotation speed was about 1000 km s−1 at a radius of about 0.13 parsecs, requiring a central gravitational mass of 4 × 107 M⊙ . The corresponding enclosed mass density is 4 × 109 M⊙ pc−3 . Were one to place 4 × 107 stars inside a radius of 0.13 parsecs, the system would be dynamically unstable wi ...
... The rotation speed was about 1000 km s−1 at a radius of about 0.13 parsecs, requiring a central gravitational mass of 4 × 107 M⊙ . The corresponding enclosed mass density is 4 × 109 M⊙ pc−3 . Were one to place 4 × 107 stars inside a radius of 0.13 parsecs, the system would be dynamically unstable wi ...
Stellar kinematics
Stellar kinematics is the study of the movement of stars without needing to understand how they acquired their motion. This differs from stellar dynamics, which takes into account gravitational effects. The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding part of the Milky Way.In astronomy, it is widely accepted that most stars are born within molecular clouds known as stellar nurseries. The stars formed within such a cloud compose open clusters containing dozens to thousands of members. These clusters dissociate over time. Stars that separate themselves from the cluster's core are designated as members of the cluster's stellar association. If the remnant later drifts through the Milky Way as a coherent assemblage, then it is termed a moving group.