The universe
... Planets around the sun and the surrounding planets revolve around the center of the galaxy (Milky Way). ...
... Planets around the sun and the surrounding planets revolve around the center of the galaxy (Milky Way). ...
Document
... Neutron stars emit little visible light Some neutron stars emit beams of radio waves as they spin – these stars are called pulsars because the seem to pulse as the beams rotate ...
... Neutron stars emit little visible light Some neutron stars emit beams of radio waves as they spin – these stars are called pulsars because the seem to pulse as the beams rotate ...
Stars: radius and mass
... then we can find the radius: L = 4R2T4 • Small stars will have low luminosities unless they are very hot. • Stars with low surface temperatures must be very large in order to have large luminosities. ...
... then we can find the radius: L = 4R2T4 • Small stars will have low luminosities unless they are very hot. • Stars with low surface temperatures must be very large in order to have large luminosities. ...
H-R Diagram - Faculty Website Listing
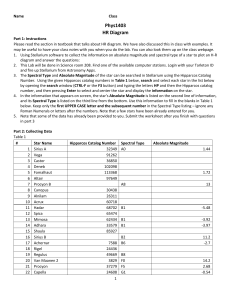
... Please read the section in textbook that talks about HR diagram. We have also discussed this in class with examples. It may be useful to have your class notes with you when you do the lab. You can also look them up on the class webpage. 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on abso ...
... Please read the section in textbook that talks about HR diagram. We have also discussed this in class with examples. It may be useful to have your class notes with you when you do the lab. You can also look them up on the class webpage. 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on abso ...
History of the Universe and Solar System
... first 2/3 of the Universe’s history. The expansion rate now seems to have increased for the last 1/3 of the Universe’s history. This is explained by “dark phantom energy”, which is hypothesized to be forming between galaxies and pushing them apart by repulsive gravitational force. Dark energy is cal ...
... first 2/3 of the Universe’s history. The expansion rate now seems to have increased for the last 1/3 of the Universe’s history. This is explained by “dark phantom energy”, which is hypothesized to be forming between galaxies and pushing them apart by repulsive gravitational force. Dark energy is cal ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... • Questions on motion of the stars? • Try out Sky View Café and/or Sky Chart III… ...
... • Questions on motion of the stars? • Try out Sky View Café and/or Sky Chart III… ...
Stars Unit 1-2: Stars
... in size, they vary even more in density! – Our sun has a density about 1.4 times greater than water. – Betelgeuse (don’t say it two more times!) is one-millionth the density of the sun. – Sirius is so dense, that one teaspoon of it would weigh more than a ton on earth! ...
... in size, they vary even more in density! – Our sun has a density about 1.4 times greater than water. – Betelgeuse (don’t say it two more times!) is one-millionth the density of the sun. – Sirius is so dense, that one teaspoon of it would weigh more than a ton on earth! ...
Stellar Evolution
... No, only out to a few hundred light years, i.e., in the neighborhood of our Sun, within our Milky Way. No, not in other galaxies, but throughout our Milky Way. Yes, but only nearby galaxies in our Local Group. Yes, out to about half the distance through the ...
... No, only out to a few hundred light years, i.e., in the neighborhood of our Sun, within our Milky Way. No, not in other galaxies, but throughout our Milky Way. Yes, but only nearby galaxies in our Local Group. Yes, out to about half the distance through the ...
Milky Way Galaxy
... – Nuclear bulge: center; highest density of stars older stars – Halo: around bulge & disk; thin gas; 90% of mass is here ...
... – Nuclear bulge: center; highest density of stars older stars – Halo: around bulge & disk; thin gas; 90% of mass is here ...
LIfe of a Star
... giants then white dwarfs More massive stars explode into a variety of objects ...
... giants then white dwarfs More massive stars explode into a variety of objects ...
the life cycle of stars
... • Energy is generated in the core and causes the star to shine. • The size of the star changes very little as long as its supply of hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium nuclei. ...
... • Energy is generated in the core and causes the star to shine. • The size of the star changes very little as long as its supply of hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium nuclei. ...
The Death of Stars
... Also, Type I seen in all kinds of galaxies, while Type II seen in spiral galaxies in star forming regions. Light curve shape and other differences as well. ...
... Also, Type I seen in all kinds of galaxies, while Type II seen in spiral galaxies in star forming regions. Light curve shape and other differences as well. ...
Astronomy Lecture Notes: Stellar Nomenclature I Introduction
... c. Apparent Magnitudes i. Apparent magnitude is a code for brightness ii. Established visually by Hipparcos around 140 B.C.E. iii. Now measured using solid state photometers iv. A backward scale with the brightest star represented by the lowest number v. The brightest star in the entire sky is Siriu ...
... c. Apparent Magnitudes i. Apparent magnitude is a code for brightness ii. Established visually by Hipparcos around 140 B.C.E. iii. Now measured using solid state photometers iv. A backward scale with the brightest star represented by the lowest number v. The brightest star in the entire sky is Siriu ...
Properties of Stars in general
... • Now, if we can find a binary system with a star of mass m in orbit around another star of unknown mass, we can deduce its mass too. • In this way, through observations of stellar binary systems we have been able to find the masses of stars of different types. • It turns out that the absolute brig ...
... • Now, if we can find a binary system with a star of mass m in orbit around another star of unknown mass, we can deduce its mass too. • In this way, through observations of stellar binary systems we have been able to find the masses of stars of different types. • It turns out that the absolute brig ...
life cycle of stars
... • Under collapse, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
... • Under collapse, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
Weekly Homework Questions #3, Sep. 14, 2010
... Instructor: Spangler Homework Assignment #3 September 14, 2010 Note: Corresponding quiz on ICON must be completed by 8AM, Monday, September 20 1. How can one measure the mass of a star other than the Sun? (a) measuring the color of the star and using a color-mass relationship (b) the apparent magnit ...
... Instructor: Spangler Homework Assignment #3 September 14, 2010 Note: Corresponding quiz on ICON must be completed by 8AM, Monday, September 20 1. How can one measure the mass of a star other than the Sun? (a) measuring the color of the star and using a color-mass relationship (b) the apparent magnit ...
DUPREE_SPLINTER
... Diagnostics of atmospheric motions Need to know where the diagnostic forms…. Contribution functions for a metal deficient giant star ...
... Diagnostics of atmospheric motions Need to know where the diagnostic forms…. Contribution functions for a metal deficient giant star ...
Stellar kinematics
Stellar kinematics is the study of the movement of stars without needing to understand how they acquired their motion. This differs from stellar dynamics, which takes into account gravitational effects. The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding part of the Milky Way.In astronomy, it is widely accepted that most stars are born within molecular clouds known as stellar nurseries. The stars formed within such a cloud compose open clusters containing dozens to thousands of members. These clusters dissociate over time. Stars that separate themselves from the cluster's core are designated as members of the cluster's stellar association. If the remnant later drifts through the Milky Way as a coherent assemblage, then it is termed a moving group.