Lecture19
... arcminutes. The expansion velocity is measured from the Doppler shift to be 1450 km/s. Estimate the age of the nebula. How bright would the supernova that gave rise to the Crab nebula have been? ...
... arcminutes. The expansion velocity is measured from the Doppler shift to be 1450 km/s. Estimate the age of the nebula. How bright would the supernova that gave rise to the Crab nebula have been? ...
The Celestial Sphere
... correct—some stars are much further away than others—but the visual image presents a handy way of thinking about the sky. ...
... correct—some stars are much further away than others—but the visual image presents a handy way of thinking about the sky. ...
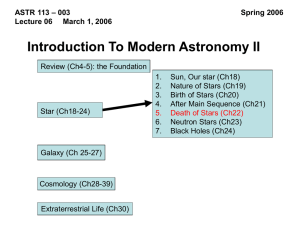
Stellar Evolution: the Death of Stars
... • A high-mass star dies in a violent cataclysm in which its core collapses and most of its matter is ejected into space at high speeds • The luminosity of the star increases suddenly by a factor of around 108 during this explosion, producing a supernova • The matter ejected from the supernova, movin ...
... • A high-mass star dies in a violent cataclysm in which its core collapses and most of its matter is ejected into space at high speeds • The luminosity of the star increases suddenly by a factor of around 108 during this explosion, producing a supernova • The matter ejected from the supernova, movin ...
Contents ISP 205 Section 2 Study Guide for Test 3 28 March 2007
... o Giants burn hydrogen in a shell, helium, or other elements White dwarfs are earth-sized, dead stars. Main sequence is a mass sequence o O stars are massive o M stars have least mass Hot massive stars live a short life and cool stars live a long time o Lifetime=mass/luminosity o Comparison: If sun ...
... o Giants burn hydrogen in a shell, helium, or other elements White dwarfs are earth-sized, dead stars. Main sequence is a mass sequence o O stars are massive o M stars have least mass Hot massive stars live a short life and cool stars live a long time o Lifetime=mass/luminosity o Comparison: If sun ...
Measuring the Properties of Stars - Sierra College Astronomy Home
... Spectroscopic Parallax Knowing a star’s luminosity class and temperature (spectral class) gives its absolute magnitude. Knowing a star’s absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude gives its distance. The distances to stars too far away for parallax measurements can be determined using this proc ...
... Spectroscopic Parallax Knowing a star’s luminosity class and temperature (spectral class) gives its absolute magnitude. Knowing a star’s absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude gives its distance. The distances to stars too far away for parallax measurements can be determined using this proc ...
ALUMINIUM-26 IN THE EARLY SOLAR SYSTEM : A PROBABILITY
... formation [21]. It is comparable to the probability estimate calculated by [7, 8] for injection by a single SN. These works however vastly surestimated the fraction of disks (or cores) present within 1 pc of a SN. In fact, when massive stars are ready to explode as SNe, they are surrounded by HII re ...
... formation [21]. It is comparable to the probability estimate calculated by [7, 8] for injection by a single SN. These works however vastly surestimated the fraction of disks (or cores) present within 1 pc of a SN. In fact, when massive stars are ready to explode as SNe, they are surrounded by HII re ...
File
... If the surface of the neutron star is hotter than about a million K, the surface would be liquid form, while if it's cooler than that, it would be solid. Below that is a solid crust, about a kilometer thick. This crust is very hard and very smooth. Gravity would probably prevent any irregularities l ...
... If the surface of the neutron star is hotter than about a million K, the surface would be liquid form, while if it's cooler than that, it would be solid. Below that is a solid crust, about a kilometer thick. This crust is very hard and very smooth. Gravity would probably prevent any irregularities l ...
PDF Version
... variation, which is the amount of time before the star’s brightness curve repeats itself, varies with the star’s intrinsic brightness. The star’s apparent brightness, which is the brightness that we can see ourselves, is equal to the intrinsic brightness divided by the square of the distance from us ...
... variation, which is the amount of time before the star’s brightness curve repeats itself, varies with the star’s intrinsic brightness. The star’s apparent brightness, which is the brightness that we can see ourselves, is equal to the intrinsic brightness divided by the square of the distance from us ...
Absorption efficiencies of antenna complexes in photosynthetic
... efficiencies under seven different stellar radiation spectra at the top of atmosphere (TOA) of the planets [1]. Both the pigments and the LHC have three main absorption bands: Soret, the Qx and the Qy in order of the wavelength (see the Figure). We have found that the efficiencies of the pigments ar ...
... efficiencies under seven different stellar radiation spectra at the top of atmosphere (TOA) of the planets [1]. Both the pigments and the LHC have three main absorption bands: Soret, the Qx and the Qy in order of the wavelength (see the Figure). We have found that the efficiencies of the pigments ar ...
PHYS 390 Lecture 29 - White dwarfs and neutron stars 29
... temperature (determined half a century later) of a very hot 27,000 K in spite of a luminosity just 0.03 that of our Sun. These observations can be taken together to paint a picture of an altogether different type of star than the Sun: • luminosity + temperature give a radius of 0.008 solar radii, ab ...
... temperature (determined half a century later) of a very hot 27,000 K in spite of a luminosity just 0.03 that of our Sun. These observations can be taken together to paint a picture of an altogether different type of star than the Sun: • luminosity + temperature give a radius of 0.008 solar radii, ab ...
Document
... luminosity, and then compute its radius. Note, however, that the radius measured this way is not very accurate, owing to the uncertainty in the distance. • Is it possible to measure the radius of a distant star accurately? Also, are there other properties we can measure? Yes, use binary stars! ...
... luminosity, and then compute its radius. Note, however, that the radius measured this way is not very accurate, owing to the uncertainty in the distance. • Is it possible to measure the radius of a distant star accurately? Also, are there other properties we can measure? Yes, use binary stars! ...
THE METER STICK MODEL OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM
... would have been a better unit of measurement.) 5. Ask the students to predict how long it would take to run or walk 63,360 inches. 6. Explain that since an inch is so small compared to the total distance being measured, it is hard to imagine how far 63,360 inches is. For this reason, it is difficult ...
... would have been a better unit of measurement.) 5. Ask the students to predict how long it would take to run or walk 63,360 inches. 6. Explain that since an inch is so small compared to the total distance being measured, it is hard to imagine how far 63,360 inches is. For this reason, it is difficult ...
stellar remenants
... it doesn’t accumulate too much mass. • If the mass is over the Chandrasekhar –Limit, it will explode. ...
... it doesn’t accumulate too much mass. • If the mass is over the Chandrasekhar –Limit, it will explode. ...
Galactic Star Formation Science with Integral Field
... – Very sensitive VLT + SINFONI observations – 170+ Emission lines detected – Many very high excitation lines of H2 and [Fe II] – Bow-shock apex shows extremely high temperature T~6000K - revealing that the H2 molecule persists in these very high temperature regions Giannini et al. “Near-infrared, IF ...
... – Very sensitive VLT + SINFONI observations – 170+ Emission lines detected – Many very high excitation lines of H2 and [Fe II] – Bow-shock apex shows extremely high temperature T~6000K - revealing that the H2 molecule persists in these very high temperature regions Giannini et al. “Near-infrared, IF ...
Assignment 7 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... ____ 25. A white dwarf, compared to a main sequence star with the same mass, would always be: a. larger in diameter b. smaller in diameter c. the same size in diameter d. younger in age e. less massive ____ 26. A team of astronomers discovers one of the most massive stars ever found. If this star i ...
... ____ 25. A white dwarf, compared to a main sequence star with the same mass, would always be: a. larger in diameter b. smaller in diameter c. the same size in diameter d. younger in age e. less massive ____ 26. A team of astronomers discovers one of the most massive stars ever found. If this star i ...
Lecture Eleven (Powerpoint format)
... Elliptical galaxies are distinguished by their Reddish light indicative of older stars Absence of current star formation Smooth centrally-condensed distribution of light, and absence of other ...
... Elliptical galaxies are distinguished by their Reddish light indicative of older stars Absence of current star formation Smooth centrally-condensed distribution of light, and absence of other ...
Stellar kinematics
Stellar kinematics is the study of the movement of stars without needing to understand how they acquired their motion. This differs from stellar dynamics, which takes into account gravitational effects. The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding part of the Milky Way.In astronomy, it is widely accepted that most stars are born within molecular clouds known as stellar nurseries. The stars formed within such a cloud compose open clusters containing dozens to thousands of members. These clusters dissociate over time. Stars that separate themselves from the cluster's core are designated as members of the cluster's stellar association. If the remnant later drifts through the Milky Way as a coherent assemblage, then it is termed a moving group.