Mass models of the Milky Way
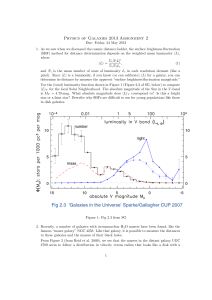
... virial mass Mvir – which is the mass contained within the virial radius rvir – and the concentration c = r−2 /rvir , where r−2 is the radius at which the logarithmic slope of the density profile d log ρ/ d log r = −2 (for an NFW profile, r−2 = rh ). The virial radius rvir is defined as the radius of ...
... virial mass Mvir – which is the mass contained within the virial radius rvir – and the concentration c = r−2 /rvir , where r−2 is the radius at which the logarithmic slope of the density profile d log ρ/ d log r = −2 (for an NFW profile, r−2 = rh ). The virial radius rvir is defined as the radius of ...
Sharp Images of Galaxy Groups: Chandra and XMM Uncover New
... • Proposed by Condon et al. (1993) for UGC 12914/12915: radio bridge explained in terms of gas and magnetic fields from postcollision galaxies • Could NGC 741/742 constitute such a pair? Relative narrowness of bridge due to greater concentration of gas in ellipticals into dense cores (in comparison ...
... • Proposed by Condon et al. (1993) for UGC 12914/12915: radio bridge explained in terms of gas and magnetic fields from postcollision galaxies • Could NGC 741/742 constitute such a pair? Relative narrowness of bridge due to greater concentration of gas in ellipticals into dense cores (in comparison ...
chapter16StarBirth
... • Without CO molecules to provide cooling, the clouds that formed the first stars had to be considerably warmer than today’s molecular clouds • The first stars must therefore have been more massive than most of today’s stars, for gravity to overcome pressure ...
... • Without CO molecules to provide cooling, the clouds that formed the first stars had to be considerably warmer than today’s molecular clouds • The first stars must therefore have been more massive than most of today’s stars, for gravity to overcome pressure ...
ABSTRACT Stellar feedback, star formation and
... large star cluster that takes multiple free-fall times to form. As a result, the cloud can survive a finite level of stellar feedback before ultimately being dispersed by its internal processes. Based on their results from observations of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), Kawamura et al. (2009) pres ...
... large star cluster that takes multiple free-fall times to form. As a result, the cloud can survive a finite level of stellar feedback before ultimately being dispersed by its internal processes. Based on their results from observations of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), Kawamura et al. (2009) pres ...
The Interstellar Medium in High Redshift Galaxies Comes of Age
... Studying the astrochemistry of the early Universe is crucial for understanding the properties of molecular gas in galaxy formation and for providing fundamental constraints on galaxy evolution. To date, a fairly small number of species, other than CO, have been detected at z > 2 (e.g. HCN, HNC, CN, ...
... Studying the astrochemistry of the early Universe is crucial for understanding the properties of molecular gas in galaxy formation and for providing fundamental constraints on galaxy evolution. To date, a fairly small number of species, other than CO, have been detected at z > 2 (e.g. HCN, HNC, CN, ...
Molecular cloud - University of Western Ontario
... - significant power generated on largest scales even with driving on smaller scales, due to stratification effect - dissipation time is related to cloud size, not internal driving scale: provides a way out of “luminosity problem” if this result holds for the large cloud complexes. • Two-dimensional ...
... - significant power generated on largest scales even with driving on smaller scales, due to stratification effect - dissipation time is related to cloud size, not internal driving scale: provides a way out of “luminosity problem” if this result holds for the large cloud complexes. • Two-dimensional ...
H2CO and CO in S140
... We report observations of the region including the S140 H arc and the molecular/dust cloud L1204 with the Onsala 25-m telescope in the 6 cm (111-110) transition of H2CO. This spectral line is seen here in absorption against the cosmic microwave background, and is a tracer for the presence of relati ...
... We report observations of the region including the S140 H arc and the molecular/dust cloud L1204 with the Onsala 25-m telescope in the 6 cm (111-110) transition of H2CO. This spectral line is seen here in absorption against the cosmic microwave background, and is a tracer for the presence of relati ...
Observations with Herschel: High-mass star formation and the
... influencing the star formation rate and galactic evolution. In a cyclic process, gas and dust clouds collapse gravitationally to form stars which in the end of their lives eject gas and dust back to the ISM. The gas is, however, at this point enriched with small amounts of elements heavier than heliu ...
... influencing the star formation rate and galactic evolution. In a cyclic process, gas and dust clouds collapse gravitationally to form stars which in the end of their lives eject gas and dust back to the ISM. The gas is, however, at this point enriched with small amounts of elements heavier than heliu ...
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy - University of Texas Astronomy
... How were the atoms in your body made? The hydrogen atoms (or the protons and electrons they are made of) were made in the big bang. Many of the helium atoms in the Universe were also made in the big bang. The other atoms were made inside of stars or during explosions of stars. When the Sun becomes ...
... How were the atoms in your body made? The hydrogen atoms (or the protons and electrons they are made of) were made in the big bang. Many of the helium atoms in the Universe were also made in the big bang. The other atoms were made inside of stars or during explosions of stars. When the Sun becomes ...
Sterrenstelsels en Cosmologie Docent: M. Franx, kamer 425
... Currently, these classifications have become less important. We now have distances to most galaxies, and multi-wavelength information. We characterize galaxies by their stellar mass, age, star formation rate, metallicity, and halo mass (or environment). Homework Questions: 6) Why are galaxy classifi ...
... Currently, these classifications have become less important. We now have distances to most galaxies, and multi-wavelength information. We characterize galaxies by their stellar mass, age, star formation rate, metallicity, and halo mass (or environment). Homework Questions: 6) Why are galaxy classifi ...
solar.gmu.edu
... 4. How can material ejected from quasars appear to travel faster than light? 5. What could power the incredible energy output from active galaxies? 6. Why do many active galaxies emit ultrafast jets of material? 7. What are gamma-ray bursters? How did astronomers discover how far away they are? ...
... 4. How can material ejected from quasars appear to travel faster than light? 5. What could power the incredible energy output from active galaxies? 6. Why do many active galaxies emit ultrafast jets of material? 7. What are gamma-ray bursters? How did astronomers discover how far away they are? ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... (b) The effect of ‘differential rotation’. This term refers to the variation of the angular velocity with dΩ/dR radius. The region ABCD now changes in shape as well as in orientation. The diagonal AC has shrunk and the diagonal BD has expanded. This means that differential rotation causes a Doppler ...
... (b) The effect of ‘differential rotation’. This term refers to the variation of the angular velocity with dΩ/dR radius. The region ABCD now changes in shape as well as in orientation. The diagonal AC has shrunk and the diagonal BD has expanded. This means that differential rotation causes a Doppler ...
2.1 Introduction
... associated with the Carina nebula at a distance of 3.2 kpc. It is immediately obvious from these images that: (a) stars have a range of colours, and (b) some stars are intrinsically brighter than others. More generally, we can make a list of what we may consider to be the most important physical pro ...
... associated with the Carina nebula at a distance of 3.2 kpc. It is immediately obvious from these images that: (a) stars have a range of colours, and (b) some stars are intrinsically brighter than others. More generally, we can make a list of what we may consider to be the most important physical pro ...
normal and active - FirstLight Astro
... 2. Which type of galaxy can be spherical to flat? 3. Which type can be loosely wound to tightly wound? 4. Which type is filled with older stars and little gas? 5. Which type has stars moving in seemingly random directions? 6. Which two have active star formation? ...
... 2. Which type of galaxy can be spherical to flat? 3. Which type can be loosely wound to tightly wound? 4. Which type is filled with older stars and little gas? 5. Which type has stars moving in seemingly random directions? 6. Which two have active star formation? ...
A Massive Galaxy in its Core Formation Phase Three Billion Years
... Space Telescope Science Institute, 3700 San Martin Drive, Baltimore, MD 21218, USA ...
... Space Telescope Science Institute, 3700 San Martin Drive, Baltimore, MD 21218, USA ...
file - University of California San Diego
... The forest, Burbidge notes, may represent light not from the quasar itself but from diffuse gas clouds that lie along our line of sight to the quasar and absorb some of its spectrum. "These gas clouds may be in a primordial region, perhaps evolving into a cluster of galaxies around the quasar," Burb ...
... The forest, Burbidge notes, may represent light not from the quasar itself but from diffuse gas clouds that lie along our line of sight to the quasar and absorb some of its spectrum. "These gas clouds may be in a primordial region, perhaps evolving into a cluster of galaxies around the quasar," Burb ...
Galaxies - Indiana University Astronomy
... Using the same website as above, click on “spectrum” for the two galaxies whose distances you measured. The optical spectrum of the galaxy is shown at the top of the spectrum page. Shown are many different spectral features, including absorption lines and emission lines, superimposed on continuum em ...
... Using the same website as above, click on “spectrum” for the two galaxies whose distances you measured. The optical spectrum of the galaxy is shown at the top of the spectrum page. Shown are many different spectral features, including absorption lines and emission lines, superimposed on continuum em ...
imaging spectroscopy of the centers of nearby agn
... It therefore seems likely that nuclear starbursts are episodic in nature. Given that the star formation occurs on scales of < 50 pc, it is inevitable that it and the AGN will have some mutual influence on each other. Our data hint at a possible relationship between the characteristic age of the star ...
... It therefore seems likely that nuclear starbursts are episodic in nature. Given that the star formation occurs on scales of < 50 pc, it is inevitable that it and the AGN will have some mutual influence on each other. Our data hint at a possible relationship between the characteristic age of the star ...
Problem Set 2
... For the Milky Way, LD ≈ 1.5 × 1010 L in the V band and hR ≈ 4 mathrmkpc. Show that the disk’s surface brightness at the Sun’s position, 8 kpc from the Galactic Center, is ∼ 20 L pc−2 . The mass density in the disk is 40 − 60 M pc−2 , so M/LV ∼ 2 − 3 (in solar units). Why is this larger than M/LV ...
... For the Milky Way, LD ≈ 1.5 × 1010 L in the V band and hR ≈ 4 mathrmkpc. Show that the disk’s surface brightness at the Sun’s position, 8 kpc from the Galactic Center, is ∼ 20 L pc−2 . The mass density in the disk is 40 − 60 M pc−2 , so M/LV ∼ 2 − 3 (in solar units). Why is this larger than M/LV ...
Quiz 2 Lecture 12
... a. Ring galaxies can be produced by head-on collisions between galaxies. b. The ratio of the number of elliptical to spiral galaxies remains constant over time. c. The Magellanic Clouds may eventually be "cannibalized" by our Galaxy. d. The shape of a galaxy can be influenced by collision with anoth ...
... a. Ring galaxies can be produced by head-on collisions between galaxies. b. The ratio of the number of elliptical to spiral galaxies remains constant over time. c. The Magellanic Clouds may eventually be "cannibalized" by our Galaxy. d. The shape of a galaxy can be influenced by collision with anoth ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... 1.7x1020kg (0.0023MMoon) within a factor of 2. Towards the star itself, the total CO column is 2.5(+2.5,-‐1.2)x1015 cm-‐2 ; results from UV absorption line measurements range between 0.6-‐2.1x1015 c ...
... 1.7x1020kg (0.0023MMoon) within a factor of 2. Towards the star itself, the total CO column is 2.5(+2.5,-‐1.2)x1015 cm-‐2 ; results from UV absorption line measurements range between 0.6-‐2.1x1015 c ...
Slide 1
... No and no. While often difficult to detect in visible wavelengths, these are not hidden from resourceful astronomers. We can detect gas and dust at whatever temperature you might devise. Black dwarfs (cooled white dwarfs), black holes? No and no. Black dwarf wannabes have not had enough time to cool ...
... No and no. While often difficult to detect in visible wavelengths, these are not hidden from resourceful astronomers. We can detect gas and dust at whatever temperature you might devise. Black dwarfs (cooled white dwarfs), black holes? No and no. Black dwarf wannabes have not had enough time to cool ...
12/08/14-- Student ID ______ TA Name
... that the Milky Way was just one of many galaxies, showed us something quite different. Almost over night we discovered that a. a huge volume of dark matter and dark energy surrounds the Milky Way. b. our solar system was just one of many planetary systems in the Orion Arm of the Galaxy. c. our solar ...
... that the Milky Way was just one of many galaxies, showed us something quite different. Almost over night we discovered that a. a huge volume of dark matter and dark energy surrounds the Milky Way. b. our solar system was just one of many planetary systems in the Orion Arm of the Galaxy. c. our solar ...