
Chap 16: Galaxies
... stellar velocities near the center of a galaxy: Infer mass in the very center central black holes! Several million, up to more than a billion solar masses! Supermassive ...
... stellar velocities near the center of a galaxy: Infer mass in the very center central black holes! Several million, up to more than a billion solar masses! Supermassive ...
wing galaxies: a formation mechanism of the clumpy irregular galaxy
... is made for the data at PA = 0° through the clump B. The component trapped by the intruder is also seen in the model result. However, this component is not discriminated from the intrude in the observation. In the right panels, we show the velocity field of the intruder. The distance is measured fro ...
... is made for the data at PA = 0° through the clump B. The component trapped by the intruder is also seen in the model result. However, this component is not discriminated from the intrude in the observation. In the right panels, we show the velocity field of the intruder. The distance is measured fro ...
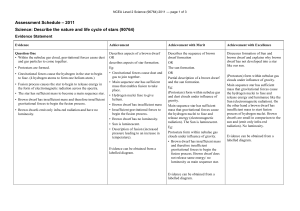
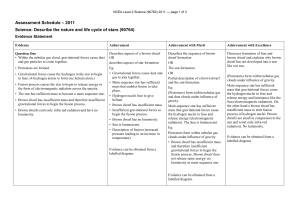
Assessment Schedule
... • Sirius A is more luminous due to the faster fuel burning rate and size. • Luminosity is the amount of light being given off by the star. • White dwarf is greater in mass than the main sequence star, but smaller in size. • White dwarf has no fuel to burn. Seen as result of radiation release. • Mass ...
... • Sirius A is more luminous due to the faster fuel burning rate and size. • Luminosity is the amount of light being given off by the star. • White dwarf is greater in mass than the main sequence star, but smaller in size. • White dwarf has no fuel to burn. Seen as result of radiation release. • Mass ...
Level 2 Science (90764) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... • Sirius A is more luminous due to the faster fuel burning rate and size. • Luminosity is the amount of light being given off by the star. • White dwarf is greater in mass than the main sequence star, but smaller in size. • White dwarf has no fuel to burn. Seen as result of radiation release. • Mass ...
... • Sirius A is more luminous due to the faster fuel burning rate and size. • Luminosity is the amount of light being given off by the star. • White dwarf is greater in mass than the main sequence star, but smaller in size. • White dwarf has no fuel to burn. Seen as result of radiation release. • Mass ...
Molecular cloud regulated star formation in galaxies
... According to Young & Scoville (1991), the fraction of gas in the molecular phase depends on Hubble type, with early-type spirals tending to be predominantly molecular and late types atomic. Optically barred spirals show a clear enhancement of CO emission along the bar. This suggests that the large-s ...
... According to Young & Scoville (1991), the fraction of gas in the molecular phase depends on Hubble type, with early-type spirals tending to be predominantly molecular and late types atomic. Optically barred spirals show a clear enhancement of CO emission along the bar. This suggests that the large-s ...
Accretion
... compact object assuming (1) steady state, (2) neglecting gas infall (no protostellar envelope in this case although gas inflow may occur as gas comes from the donor star in a binary system), (3) thin axisymmetric and (4) viscosity is the only source of heating in the disk - determines the disk temp ...
... compact object assuming (1) steady state, (2) neglecting gas infall (no protostellar envelope in this case although gas inflow may occur as gas comes from the donor star in a binary system), (3) thin axisymmetric and (4) viscosity is the only source of heating in the disk - determines the disk temp ...
Name:
... liquids, or high-density gases (such as found on the surface of a star) will produce a spectrum that contains all the ROY G. BIV colors and everything in between. CONTINUOUS SPECTRUM The CONTINUOUS spectrum is caused by gas particles (atoms and even molecules) moving at high speeds bumping into one ...
... liquids, or high-density gases (such as found on the surface of a star) will produce a spectrum that contains all the ROY G. BIV colors and everything in between. CONTINUOUS SPECTRUM The CONTINUOUS spectrum is caused by gas particles (atoms and even molecules) moving at high speeds bumping into one ...
L103 A NEW MILKY WAY DWARF SATELLITE IN CANES
... of the Milky Way. Together with the two dwarf irregulars (the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds), these make up all the known satellite galaxies of the Milky Way. The dSphs have such low surface brightness that they have often been found serendipitously. For example, while Sextans (Irwin et al. 1990 ...
... of the Milky Way. Together with the two dwarf irregulars (the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds), these make up all the known satellite galaxies of the Milky Way. The dSphs have such low surface brightness that they have often been found serendipitously. For example, while Sextans (Irwin et al. 1990 ...
Name: Three Views Spectrum Simulation This simulation uses the
... liquids, or high-density gases (such as found on the surface of a star) will produce a spectrum that contains all the ROY G. BIV colors and everything in between. CONTINUOUS SPECTRUM The CONTINUOUS spectrum is caused by gas particles (atoms and even molecules) moving at high speeds bumping into one ...
... liquids, or high-density gases (such as found on the surface of a star) will produce a spectrum that contains all the ROY G. BIV colors and everything in between. CONTINUOUS SPECTRUM The CONTINUOUS spectrum is caused by gas particles (atoms and even molecules) moving at high speeds bumping into one ...
Star formation and the interstellar medium in galaxy
... during their evolution. The gas is allowed to have temperatures between 10 and 106 K, although these high temperatures are never reached (we do not yet include supernovae that could produce them). We use a Jeans instability condition to localize star forming regions, and scale the collapse time for ...
... during their evolution. The gas is allowed to have temperatures between 10 and 106 K, although these high temperatures are never reached (we do not yet include supernovae that could produce them). We use a Jeans instability condition to localize star forming regions, and scale the collapse time for ...
Submillimeter Array 12CO (2-1) Imaging of the NGC
... Observations have revealed discrepancies regarding the CO-toH2 conversion factor XCO in NGC 6946. Donovan Meyer et al. (2012) derived an XCO similar to the Milky Way (MW) value (4.4 M☉pc−2 (K km s−1)−1; Sandstrom et al. 2013) by assuming that GMCs were in virial equilibrium. In contrast, analyses o ...
... Observations have revealed discrepancies regarding the CO-toH2 conversion factor XCO in NGC 6946. Donovan Meyer et al. (2012) derived an XCO similar to the Milky Way (MW) value (4.4 M☉pc−2 (K km s−1)−1; Sandstrom et al. 2013) by assuming that GMCs were in virial equilibrium. In contrast, analyses o ...
Evidence for 1000 km/s Molecular Outflows in the Local ULIRG
... Extreme star formation rates of & 103 M⊙ yr−1 have been derived for luminous infrared galaxies discovered by deep IR surveys (Downes & Solomon 1998; Younger et al. 2008; Riechers et al. 2009). In such radiation-pressure supported galactic disks with the maximum starburst (Thompson et al. 2005), larg ...
... Extreme star formation rates of & 103 M⊙ yr−1 have been derived for luminous infrared galaxies discovered by deep IR surveys (Downes & Solomon 1998; Younger et al. 2008; Riechers et al. 2009). In such radiation-pressure supported galactic disks with the maximum starburst (Thompson et al. 2005), larg ...
Toward $ ab\, initio $ extremely metal poor stars
... The precise nucleosynthetic yields in the ejecta of corecollapse supernovae are not known from first principles, primarily because a theoretically uncertain fraction of the supernova yield ends up trapped in the compact remnant (Heger & Woosley 2010). Three-dimensional simulations of the long-term e ...
... The precise nucleosynthetic yields in the ejecta of corecollapse supernovae are not known from first principles, primarily because a theoretically uncertain fraction of the supernova yield ends up trapped in the compact remnant (Heger & Woosley 2010). Three-dimensional simulations of the long-term e ...
The star Betelgeuse is about 500 light years away from us. If this star
... a. cannot be disproven as a scientific idea b. created the earth 4.5 billion years ago c. is the initial expansion of space d. was the emergence of the solar system from a black hole Our solar system is located in the a) Milky Way's galactic halo b) Milky Way's central nucleus c) Milky Way's galacti ...
... a. cannot be disproven as a scientific idea b. created the earth 4.5 billion years ago c. is the initial expansion of space d. was the emergence of the solar system from a black hole Our solar system is located in the a) Milky Way's galactic halo b) Milky Way's central nucleus c) Milky Way's galacti ...
01 - University of Warwick
... Why is 2003 EL61 spinning fast, shaped like a football, Here is an image of the satellite from the night of 30 June made out of ice-covered rock, and surrounded by tiny satel2005. 2003 EL 61 is the bright object in the center and the lites? satellite appears directly below about 0.5 arcseconds. To t ...
... Why is 2003 EL61 spinning fast, shaped like a football, Here is an image of the satellite from the night of 30 June made out of ice-covered rock, and surrounded by tiny satel2005. 2003 EL 61 is the bright object in the center and the lites? satellite appears directly below about 0.5 arcseconds. To t ...
B2 Star Formation and Nuclear Fusion
... timescale for expansion of a red giant in Case B mass transfer. Corresponds to pre-main-sequence lifetime τpre-ms of a protostar. Nuclear timescale τnuc Time for a star to exhaust its nuclear fuel. For main sequence stars, this is the H-burning or main-sequence ...
... timescale for expansion of a red giant in Case B mass transfer. Corresponds to pre-main-sequence lifetime τpre-ms of a protostar. Nuclear timescale τnuc Time for a star to exhaust its nuclear fuel. For main sequence stars, this is the H-burning or main-sequence ...
22 pm - Starmap
... As a starting point, face North, holding the map in your eyesight direction, with its North down. As you change the direction, rotate the map accordingly. The objects listed on the first page can be observed with naked eyes, in clear skies, with moderate light pollution. Close your eyes one minute a ...
... As a starting point, face North, holding the map in your eyesight direction, with its North down. As you change the direction, rotate the map accordingly. The objects listed on the first page can be observed with naked eyes, in clear skies, with moderate light pollution. Close your eyes one minute a ...
Chemical Universe. - University of Texas Astronomy
... Like the overall universe, stars are made mostly of hydrogen. A star forms when a vast cloud of gas and dust collapses. As it pulls in on itself, and its density increases, it gets hotter. When the temperature in the center of this collapsing star reaches about 10 million degrees Celsius (18 million ...
... Like the overall universe, stars are made mostly of hydrogen. A star forms when a vast cloud of gas and dust collapses. As it pulls in on itself, and its density increases, it gets hotter. When the temperature in the center of this collapsing star reaches about 10 million degrees Celsius (18 million ...
V - ESO
... This is generally assumed to be the reason why, though star formation proceeds on a typical scale comparable to the size of a giant molecular cloud (~80 pc, Efremov 1995, AJ 100, 2757), Milky Way massive clusters tend to be much smaller. Image taken from class by James Schombert, University of Oreg ...
... This is generally assumed to be the reason why, though star formation proceeds on a typical scale comparable to the size of a giant molecular cloud (~80 pc, Efremov 1995, AJ 100, 2757), Milky Way massive clusters tend to be much smaller. Image taken from class by James Schombert, University of Oreg ...
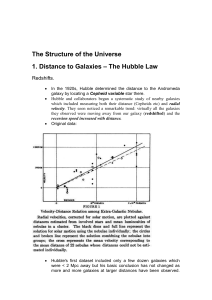
Chapter 17
... Galactic Galaxies move through space singly and in groups. Galaxies even collisions collide with each other in slow dances of stars that take millions of years to complete (Figure 17.5) Determining the Figuring out the distance between galaxies is one of the more difficult distance to tasks in astro ...
... Galactic Galaxies move through space singly and in groups. Galaxies even collisions collide with each other in slow dances of stars that take millions of years to complete (Figure 17.5) Determining the Figuring out the distance between galaxies is one of the more difficult distance to tasks in astro ...
PH607lec08
... Hubble and collaborators began a systematic study of nearby galaxies which included measuring both their distance (Cepheids etc) and radial velocity. They soon noticed a remarkable trend: virtually all the galaxies they observed were moving away from our galaxy (redshifted) and the recession speed i ...
... Hubble and collaborators began a systematic study of nearby galaxies which included measuring both their distance (Cepheids etc) and radial velocity. They soon noticed a remarkable trend: virtually all the galaxies they observed were moving away from our galaxy (redshifted) and the recession speed i ...
On the trend of [Mg/Fe] among giant elliptical galaxies
... versus < F e > relationship found for nuclei of elliptical galaxies (Faber et al. 1992; Worthey et al. 1992; Carollo et al. 1993; Davies et al. 1993), indicating that the Mg/Fe ratio should increase with galactic luminosity and mass. We transform the abundance of Fe, as predicted by classic wind mod ...
... versus < F e > relationship found for nuclei of elliptical galaxies (Faber et al. 1992; Worthey et al. 1992; Carollo et al. 1993; Davies et al. 1993), indicating that the Mg/Fe ratio should increase with galactic luminosity and mass. We transform the abundance of Fe, as predicted by classic wind mod ...
Dark Matter— More Than Meets The Eye
... maxi- or mini- black holes. Or massive cold gas clouds. All these phenomena are baryonic. There is some observational evidence for the existence of MACHOs. Because they can warp space enough to focus light from a distant star, MACHOs have played a critical role in a number of microlensing events in ...
... maxi- or mini- black holes. Or massive cold gas clouds. All these phenomena are baryonic. There is some observational evidence for the existence of MACHOs. Because they can warp space enough to focus light from a distant star, MACHOs have played a critical role in a number of microlensing events in ...
17 April 2013 When Galaxies Collide Professor Carolin Crawford
... Way in return, producing a slight warp across its disc. This is most apparent in the distribution of the hydrogen gas: one half of the disc rises a a little above, the other dips a little below the line of the Galactic plane traced by the stars. Although the Milky Way has only a very slight warp, su ...
... Way in return, producing a slight warp across its disc. This is most apparent in the distribution of the hydrogen gas: one half of the disc rises a a little above, the other dips a little below the line of the Galactic plane traced by the stars. Although the Milky Way has only a very slight warp, su ...


















![On the trend of [Mg/Fe] among giant elliptical galaxies](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/024377891_1-9ed25030908d9b00f4379170c2bcef77-300x300.png)

