X-ray emission and the incidence of magnetic fields in the massive
... the echelle spectropolarimeter ESPaDOnS at CFHT. High resolution (R=65,000) measurements of Stokes I and V were obtained under good conditions, with an appreciable signal to noise ratio. The mean Stokes I and V profiles were extracted with the Least Square Deconvolution technique (LSD) of Donati et ...
... the echelle spectropolarimeter ESPaDOnS at CFHT. High resolution (R=65,000) measurements of Stokes I and V were obtained under good conditions, with an appreciable signal to noise ratio. The mean Stokes I and V profiles were extracted with the Least Square Deconvolution technique (LSD) of Donati et ...
A05715 ANY CALCULATOR Page 1 TURN OVER School of Physics
... Use Wien’s law to explain quantitatively in what way the spectrum of the light from the Sun, with a surface temperature of about 6000K, would differ from that of a B star. ...
... Use Wien’s law to explain quantitatively in what way the spectrum of the light from the Sun, with a surface temperature of about 6000K, would differ from that of a B star. ...
Study of energy transfer by electron cyclotron resonance in tokamak
... criterion [1], ݊ܶݐா 5. 10ଶଵ ݉ିଷ ܸ݇݁ ݏand to achieve these high temperatures, it is necessary to heat the plasma. The ohmic regime is a primary natural mechanism of heating. Unfortunately, this effect is proportional to the resistance of the plasma which tends to collapse when the temperature i ...
... criterion [1], ݊ܶݐா 5. 10ଶଵ ݉ିଷ ܸ݇݁ ݏand to achieve these high temperatures, it is necessary to heat the plasma. The ohmic regime is a primary natural mechanism of heating. Unfortunately, this effect is proportional to the resistance of the plasma which tends to collapse when the temperature i ...
The Exact Solution of Nonlinear Stress
... the convective flows vary considerably (due to the physical effects of stratification, partial ionization, radiation, and the like), changes in the uppermost layers are seen at the surface first, then those in the deeper layer, and finally those which occur at the position in the sun which marks the ...
... the convective flows vary considerably (due to the physical effects of stratification, partial ionization, radiation, and the like), changes in the uppermost layers are seen at the surface first, then those in the deeper layer, and finally those which occur at the position in the sun which marks the ...
Cosmic Rays and Plasma Astrophysics
... particle originated. The gyroradius of a 1012 eV proton in the interplanetary field of about 1 nT (i.e., 10–9 T) is about 20 AU (1 AU is the distance from the Sun to the Earth, which is 1.50108 km). Thus, particles below this energy will be strongly deflected by the magnetic field and their directi ...
... particle originated. The gyroradius of a 1012 eV proton in the interplanetary field of about 1 nT (i.e., 10–9 T) is about 20 AU (1 AU is the distance from the Sun to the Earth, which is 1.50108 km). Thus, particles below this energy will be strongly deflected by the magnetic field and their directi ...
model the Earth`s and Sun`s magnetic fields using a
... 3. Explain to students that a magnaprobe is a magnetic field detector. It can be used to trace a magnetic field in three-dimensions as well as show us the direction of magnetic poles in magnets. Tell them they will be using cow magnets and magnaprobes during the activity to investigate the magnetic ...
... 3. Explain to students that a magnaprobe is a magnetic field detector. It can be used to trace a magnetic field in three-dimensions as well as show us the direction of magnetic poles in magnets. Tell them they will be using cow magnets and magnaprobes during the activity to investigate the magnetic ...
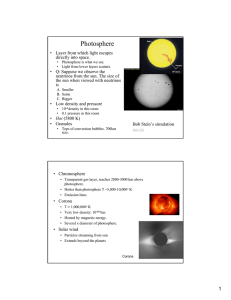
Photosphere
... Photosphere • Layer from which light escapes directly into space. • Photosphere is what we see. • Light from lower layers scatters. ...
... Photosphere • Layer from which light escapes directly into space. • Photosphere is what we see. • Light from lower layers scatters. ...
IMAP (Interstellar MApping Probe)
... electrons covering an extended energy range from ~few eV up to 100s of MeV/nucleon; b) the very energetic neutral atoms with temporal, spectral and spatial resolution; c) the energy spectra and timing of neutrons, X-rays and -rays from solar flares, d) the solar wind ions and electrons, and e) the ...
... electrons covering an extended energy range from ~few eV up to 100s of MeV/nucleon; b) the very energetic neutral atoms with temporal, spectral and spatial resolution; c) the energy spectra and timing of neutrons, X-rays and -rays from solar flares, d) the solar wind ions and electrons, and e) the ...
The Stellar Graveyard
... place. Since the electrons are packed so tightly together, they are always at the “same place” and therefore all the lower energy states of the electron gas are filled. The left over electrons (and there are lots of them) have no choice but to occupy a higher energy state. This causes their velocity ...
... place. Since the electrons are packed so tightly together, they are always at the “same place” and therefore all the lower energy states of the electron gas are filled. The left over electrons (and there are lots of them) have no choice but to occupy a higher energy state. This causes their velocity ...
EARTH & SPACE SCIENCE
... glows a reddish color during eclipses. The chromosphere lies just above the photosphere. The chromosphere’s temperature ranges from 4,000°C to 50,000 °C. The gases of the chromosphere move away from the photosphere, forming narrow jets of hot gas that shoot outward and then fade away within a few mi ...
... glows a reddish color during eclipses. The chromosphere lies just above the photosphere. The chromosphere’s temperature ranges from 4,000°C to 50,000 °C. The gases of the chromosphere move away from the photosphere, forming narrow jets of hot gas that shoot outward and then fade away within a few mi ...
AAS_WFXT_Solar_System_11Jan2010
... study. Most objects have been detected with only a few photons. • There is an important list of solar system objects that have yet to be detected in the x-ray : Mercury, the ice giants Uranus/Neptune, the Main Belt comets,KBOs, and the heliopause. • Large Scale WFXT Imaging will allow for direct, co ...
... study. Most objects have been detected with only a few photons. • There is an important list of solar system objects that have yet to be detected in the x-ray : Mercury, the ice giants Uranus/Neptune, the Main Belt comets,KBOs, and the heliopause. • Large Scale WFXT Imaging will allow for direct, co ...
STAR UNIT FLASH BACKS
... away from earth, how many years will it take for its light to reach earth? a.) 1 b.) 100,000,000,000 ...
... away from earth, how many years will it take for its light to reach earth? a.) 1 b.) 100,000,000,000 ...
What is the Solar Wind
... What is the Solar Wind?! Hello, sensei. Today I have a question about the wind blowing from the Sun. Can it be seen from a space station? The solar wind blowing near the earth contains only about 10 particles per a sugar cube in volume. It is a very thin gas, almost a vacuum, not emitting light str ...
... What is the Solar Wind?! Hello, sensei. Today I have a question about the wind blowing from the Sun. Can it be seen from a space station? The solar wind blowing near the earth contains only about 10 particles per a sugar cube in volume. It is a very thin gas, almost a vacuum, not emitting light str ...
What is the Solar Wind?!
... What is the Solar Wind?! Hello, sensei. Today I have a question about the wind blowing from the Sun. Can it be seen from a space station? The solar wind blowing near the earth contains only about 10 particles per a sugar cube in volume. It is a very thin gas, almost a vacuum, not emitting light str ...
... What is the Solar Wind?! Hello, sensei. Today I have a question about the wind blowing from the Sun. Can it be seen from a space station? The solar wind blowing near the earth contains only about 10 particles per a sugar cube in volume. It is a very thin gas, almost a vacuum, not emitting light str ...
Enhanced temperature regions in the polar zones of the Sun
... the receiver is sufficient for 0.1 sfu resolution. In the temperature scale this corresponds to better than 100 K, and it is limited by short term changes in the atmospheric attenuation. Solar maps are measured by scanning the solar disk in right ascension and by changing the declination in small st ...
... the receiver is sufficient for 0.1 sfu resolution. In the temperature scale this corresponds to better than 100 K, and it is limited by short term changes in the atmospheric attenuation. Solar maps are measured by scanning the solar disk in right ascension and by changing the declination in small st ...
ALLAN SACHA BRUN Head of the Laboratory on Dynamics
... - Zahn, J.-P., Brun, A.S., Mathis, S. 2007, ``On magnetic instabilities and dynamo action in stellar radiation zones’’, A&A, 474, 145 - Miesch, M.S., Brun, A.S., Derosa, M. , Toomre, J. 2008, “Structure and evolution of giant cells in global models of solar convection’’, ApJ, 673, 557 - Brun, A.S. & ...
... - Zahn, J.-P., Brun, A.S., Mathis, S. 2007, ``On magnetic instabilities and dynamo action in stellar radiation zones’’, A&A, 474, 145 - Miesch, M.S., Brun, A.S., Derosa, M. , Toomre, J. 2008, “Structure and evolution of giant cells in global models of solar convection’’, ApJ, 673, 557 - Brun, A.S. & ...
5-th_state_matter - The 5th state of matter
... This paper calls to mind that all these celestial bodies which do not seem to obey thermodynamics, gravity and many other physical laws - have a filament form. Now, this paper shows that they are not in the fourth but in a fifth state of matter. No complicated, forced, “ad hoc” models like magnetic ...
... This paper calls to mind that all these celestial bodies which do not seem to obey thermodynamics, gravity and many other physical laws - have a filament form. Now, this paper shows that they are not in the fourth but in a fifth state of matter. No complicated, forced, “ad hoc” models like magnetic ...
00 T Tauri Stars Have Extensive Coronae?
... UV and X-ray Observations of T Tauri Stars Observations of T Tauri stars in the satellite UV spectral range with the International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) provided us with new information on the emission line chromospheric region. As an example Figure 1 shows the UV spectra (1200 A S A S 3200 A) ...
... UV and X-ray Observations of T Tauri Stars Observations of T Tauri stars in the satellite UV spectral range with the International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) provided us with new information on the emission line chromospheric region. As an example Figure 1 shows the UV spectra (1200 A S A S 3200 A) ...
PPT
... Important progress has been made both in laboratory experiments and solar and space observations making it possible to collaborate in study of magnetic reconnection/self-orhanization – Transition from collisional to collisionless regime documented – Generalized Sweet Parker model was tested in an ax ...
... Important progress has been made both in laboratory experiments and solar and space observations making it possible to collaborate in study of magnetic reconnection/self-orhanization – Transition from collisional to collisionless regime documented – Generalized Sweet Parker model was tested in an ax ...
Scientific astrology
... • ~ 10-5 gr/cm3 = 10-2 kg/m3 a ~ 10-8 m/s2 • t ~ 108 s dVsurf ~ m/s Corresponds to the observed variation of Vsurf ...
... • ~ 10-5 gr/cm3 = 10-2 kg/m3 a ~ 10-8 m/s2 • t ~ 108 s dVsurf ~ m/s Corresponds to the observed variation of Vsurf ...
Question Title
... Justification: Other (much less common) options are: a)Some planetoids will collide with such high energies that they do not break into pieces. Instead they meld to form one planetoid. b)Other planetoids will break into smaller pieces. In this case, the smaller pieces will likely be pulled in by the ...
... Justification: Other (much less common) options are: a)Some planetoids will collide with such high energies that they do not break into pieces. Instead they meld to form one planetoid. b)Other planetoids will break into smaller pieces. In this case, the smaller pieces will likely be pulled in by the ...
- The 5th state of matter
... This paper calls to mind that all these celestial bodies which do not seem to obey thermodynamics, gravity and many other physical laws - have a filament form. Now, this paper shows that they are not in the fourth but in a fifth state of matter. No complicated, forced, “ad hoc” models like magnetic ...
... This paper calls to mind that all these celestial bodies which do not seem to obey thermodynamics, gravity and many other physical laws - have a filament form. Now, this paper shows that they are not in the fourth but in a fifth state of matter. No complicated, forced, “ad hoc” models like magnetic ...
Physical Sciences Astronomy: The Formation of The Solar System
... Justification: Other (much less common) options are: ...
... Justification: Other (much less common) options are: ...
o - Salem State University
... 53. Differential rotation of the sun a. causes the heating in the chromosphere and corona that makes them hotter than the photosphere. b. is caused by the magnetic dynamo inside the sun. c. implies that the equatorial regions of the sun rotate more rapidly than the polar regions. d. causes the sunsp ...
... 53. Differential rotation of the sun a. causes the heating in the chromosphere and corona that makes them hotter than the photosphere. b. is caused by the magnetic dynamo inside the sun. c. implies that the equatorial regions of the sun rotate more rapidly than the polar regions. d. causes the sunsp ...
Determination of a Correlation of Sunspot Number and 20.1 MHz
... Some of these questions involve the sun’s magnetic field, sunspots, solar flares, and solar radio bursts. We know that due to differential rotation the magnetic fields get tangled and twisted resulting in sunspots. It is theorized that solar radio bursts are a result of solar flares accelerating cha ...
... Some of these questions involve the sun’s magnetic field, sunspots, solar flares, and solar radio bursts. We know that due to differential rotation the magnetic fields get tangled and twisted resulting in sunspots. It is theorized that solar radio bursts are a result of solar flares accelerating cha ...
Corona

A corona (Latin, 'crown') is an aura of plasma that surrounds the sun and other celestial bodies. The Sun's corona extends millions of kilometres into space and is most easily seen during a total solar eclipse, but it is also observable with a coronagraph. The word ""corona"" is a Latin word meaning ""crown"", from the Ancient Greek κορώνη (korōnē, “garland, wreath”).The high temperature of the Sun's corona gives it unusual spectral features, which led some in the 19th century to suggest that it contained a previously unknown element, ""coronium"". Instead, these spectral features have since been explained by highly ionized iron (Fe-XIV). Bengt Edlén, following the work of Grotrian (1939), first identified the coronal lines in 1940 (observed since 1869) as transitions from low-lying metastable levels of the ground configuration of highly ionised metals (the green Fe-XIV line at 5303 Å, but also the red line Fe-X at 6374 Å). These high stages of ionisation indicate a plasma temperature in excess of 1,000,000 kelvin, much hotter than the surface of the sun.Light from the corona comes from three primary sources, which are called by different names although all of them share the same volume of space. The K-corona (K for kontinuierlich, ""continuous"" in German) is created by sunlight scattering off free electrons; Doppler broadening of the reflected photospheric absorption lines completely obscures them, giving the spectral appearance of a continuum with no absorption lines. The F-corona (F for Fraunhofer) is created by sunlight bouncing off dust particles, and is observable because its light contains the Fraunhofer absorption lines that are seen in raw sunlight; the F-corona extends to very high elongation angles from the Sun, where it is called the zodiacal light. The E-corona (E for emission) is due to spectral emission lines produced by ions that are present in the coronal plasma; it may be observed in broad or forbidden or hot spectral emission lines and is the main source of information about the corona's composition.