
Symbiotic Relationships
... Competition – occurs when organisms of the same or different species attempt to use an ecological resource in the same place at the same time ...
... Competition – occurs when organisms of the same or different species attempt to use an ecological resource in the same place at the same time ...
Mutualism Commensalism
... explain the specific benefit received by one of the organisms involved in this relationship. ...
... explain the specific benefit received by one of the organisms involved in this relationship. ...
Objectives 5 – Parasitism
... By the end of this unit you should be able to; 1. Define the term ‘parasite’ and be able to give named examples of parasites (e.g. protists, platyhelminths, nematodes, arthropods, bacteria and viruses), and their hosts. 2. Understand and be able to define the terms: ecological niche, a fundamental n ...
... By the end of this unit you should be able to; 1. Define the term ‘parasite’ and be able to give named examples of parasites (e.g. protists, platyhelminths, nematodes, arthropods, bacteria and viruses), and their hosts. 2. Understand and be able to define the terms: ecological niche, a fundamental n ...
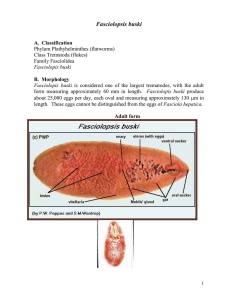
Fasciolopsis buski
... samples or vomitus; however, Fasciolopis buski eggs cannot be distinguished from the eggs of Fasciola hepatica. Although the eggs cannot be differentiated, one can determine the type of infection by the organs affected. F. hepatica infects the liver, while F. buski infects the small intestine. Occas ...
... samples or vomitus; however, Fasciolopis buski eggs cannot be distinguished from the eggs of Fasciola hepatica. Although the eggs cannot be differentiated, one can determine the type of infection by the organs affected. F. hepatica infects the liver, while F. buski infects the small intestine. Occas ...
Community Interactions: Competition, Predation and Symbiosis Part
... 10) The zebra population decreases and the lion population decreases because of it. After a while, will the zebra population start to increase or decrease because of the decrease in lion population? Explain why: ...
... 10) The zebra population decreases and the lion population decreases because of it. After a while, will the zebra population start to increase or decrease because of the decrease in lion population? Explain why: ...
4-2 ch5
... Exploitation competition – when one group uses a resource faster than another, indirectly limits a resource Ex. Plant removes nutrients/water from soil faster than its neighbor Protection from Predation What are some defense mechanisms used by prey to prevent being eaten? Armor Camouflag ...
... Exploitation competition – when one group uses a resource faster than another, indirectly limits a resource Ex. Plant removes nutrients/water from soil faster than its neighbor Protection from Predation What are some defense mechanisms used by prey to prevent being eaten? Armor Camouflag ...
Relationships within Ecosystem Worksheet/Writing Assignment
... 9. Cattle egrets and cow birds feed on the insects flushed out of the grass by grazing bison, cattle and other herbivores. _______________________________________ 10. One species benefits from the interaction but the other is unaffected. ______________________________________ 11. When populations of ...
... 9. Cattle egrets and cow birds feed on the insects flushed out of the grass by grazing bison, cattle and other herbivores. _______________________________________ 10. One species benefits from the interaction but the other is unaffected. ______________________________________ 11. When populations of ...
VIII. Phylum Acanthocephala [“Thorny-headed worms”] (Chapter 32) 2011
... Evolutionary question: How can this parasite have such a wide distribution if their hosts live in freshwater habitats that are isolated from one another by salt water? ...
... Evolutionary question: How can this parasite have such a wide distribution if their hosts live in freshwater habitats that are isolated from one another by salt water? ...
PARASITISM Definition. Parasitism is an association of two
... The cow bird of the new world and the Cuckoo of the old world do not building nests of their own. They lay their eggs in the nest of the Other species of birds and leave. The unwilling Foster parents incubate the eggs and care for the young ones as their own. The young of parasitic birds are stronge ...
... The cow bird of the new world and the Cuckoo of the old world do not building nests of their own. They lay their eggs in the nest of the Other species of birds and leave. The unwilling Foster parents incubate the eggs and care for the young ones as their own. The young of parasitic birds are stronge ...
1.3_Interactions in Ecosystems 856KB May 22 2015 12:21:25 PM
... one species benefits from a relationship and the other organism is neither harmed nor does it benefit in any way. ...
... one species benefits from a relationship and the other organism is neither harmed nor does it benefit in any way. ...
SYMBIOSIS
... close association with the other, the host, which is harmed. • The harm and benefit in parasitic interactions concern the biological fitness of the organisms involved. Parasites reduce host fitness in many ways. Parasites increase their fitness by exploiting hosts for food, habitat and dispersal. ...
... close association with the other, the host, which is harmed. • The harm and benefit in parasitic interactions concern the biological fitness of the organisms involved. Parasites reduce host fitness in many ways. Parasites increase their fitness by exploiting hosts for food, habitat and dispersal. ...
Lecture 8
... A. Symbiosis 1. Definition 2. Types (parasitism, mutualism, commensalism) B. How common are parasites? C. Parasitism vs. predation 1. Higher reproductive rates 2. Don’t usually kill host 3. Specialized to few hosts 4. Can live inside or on host D. Parasite defenses 1. Immune 2. Biochemical 3. Mutual ...
... A. Symbiosis 1. Definition 2. Types (parasitism, mutualism, commensalism) B. How common are parasites? C. Parasitism vs. predation 1. Higher reproductive rates 2. Don’t usually kill host 3. Specialized to few hosts 4. Can live inside or on host D. Parasite defenses 1. Immune 2. Biochemical 3. Mutual ...
symbiotic relatioships
... • Some animals' physical features make them a very undesirable meal. Porcupines make it very difficult for predators with their extremely sharp quills. ...
... • Some animals' physical features make them a very undesirable meal. Porcupines make it very difficult for predators with their extremely sharp quills. ...
Examples of competition
... not receive much light in winter and are shaded by taller plants and therefore die (intra-specific). Cactus plants compete for water. They are not found very close together because of their roots that can radiate far from the plant to obtain as much rain during rainfall season (intra-specific). ...
... not receive much light in winter and are shaded by taller plants and therefore die (intra-specific). Cactus plants compete for water. They are not found very close together because of their roots that can radiate far from the plant to obtain as much rain during rainfall season (intra-specific). ...
Parasitoids (insects whose larvae are the actual “predator”)
... Parasitoids (insects whose larvae are the actual “predator”) Parasitoids differ from parasites in that they almost always kill their hosts. The adult parasitoid only needs the host as food for its offspring Parasites are obligately dependent on their hosts – so better adapted parasites get what they ...
... Parasitoids (insects whose larvae are the actual “predator”) Parasitoids differ from parasites in that they almost always kill their hosts. The adult parasitoid only needs the host as food for its offspring Parasites are obligately dependent on their hosts – so better adapted parasites get what they ...
Lecture 32
... A form of the parasite passes out of the infected sheep/cow in its feces Cionella, a snail, picks up the parasite while feeding on sheep/cow poop The parasite metamorphoses ending up in the snail’s “lungs” and is released along with the mucous in the snails’ slime trails Ants pick up the par ...
... A form of the parasite passes out of the infected sheep/cow in its feces Cionella, a snail, picks up the parasite while feeding on sheep/cow poop The parasite metamorphoses ending up in the snail’s “lungs” and is released along with the mucous in the snails’ slime trails Ants pick up the par ...
Commensalism
... A cactus wren builds its nest in a cholla cactus to protect its young from predators such as raven. There is no harm to the cactus. Commensalism : We will begin by looking at commensalistic relationships, as there are some very interesting examples of this form of symbiosis where we have been diving ...
... A cactus wren builds its nest in a cholla cactus to protect its young from predators such as raven. There is no harm to the cactus. Commensalism : We will begin by looking at commensalistic relationships, as there are some very interesting examples of this form of symbiosis where we have been diving ...
Microbial Interactions
... Cooperation • Like commensalism, a positive (not obligate) symbiosis which involves syntrophic (one organism lives off the byproducts of another) relationships • Benefits both organisms in relationship • Differs from mutualism because cooperative relationship is not obligatory ...
... Cooperation • Like commensalism, a positive (not obligate) symbiosis which involves syntrophic (one organism lives off the byproducts of another) relationships • Benefits both organisms in relationship • Differs from mutualism because cooperative relationship is not obligatory ...
PowerPoint
... Cooperation • Like commensalism, a positive (not obligate) symbiosis which involves syntrophic (one organism lives off the byproducts of another) relationships • Benefits both organisms in relationship • Differs from mutualism because cooperative relationship is not obligatory ...
... Cooperation • Like commensalism, a positive (not obligate) symbiosis which involves syntrophic (one organism lives off the byproducts of another) relationships • Benefits both organisms in relationship • Differs from mutualism because cooperative relationship is not obligatory ...
Parasitoid

A parasitoid is an organism that spends a significant portion of its life history attached to or within a single host organism in a relationship that is in essence parasitic; unlike a true parasite, however, it ultimately sterilises or kills, and sometimes consumes, the host. Thus parasitoids are similar to typical parasites except in the more dire prognosis for the host.







![VIII. Phylum Acanthocephala [“Thorny-headed worms”] (Chapter 32) 2011](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000047953_1-fc89e37ea1bee6f8d75fabf163e10133-300x300.png)














