double shell–burning
... < 0.08MSun before core temperature becomes hot enough for fusion. • Starlike objects not massive enough to start fusion are brown dwarfs. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... < 0.08MSun before core temperature becomes hot enough for fusion. • Starlike objects not massive enough to start fusion are brown dwarfs. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Debris disks and the search for life in the universe Gianni Cataldi
... leading to tff ≈ R3 /(GM) ≈ 1/(Gρ) with ρ the density. Plugging in the typical parameters of a dense core, one finds a tff of the order of 105 years. This is a quite short timescale compared to the time for the overall star formation process. ...
... leading to tff ≈ R3 /(GM) ≈ 1/(Gρ) with ρ the density. Plugging in the typical parameters of a dense core, one finds a tff of the order of 105 years. This is a quite short timescale compared to the time for the overall star formation process. ...
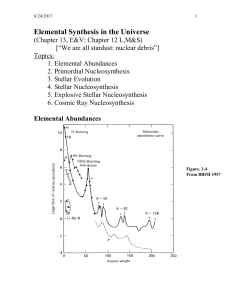
Elemental Synthesis in the Universe
... - instabilities and inhomogenities cause large clouds of H and He to coalesce and come together through force of gravity - heating can occur as matter comes closer, leading to ignition of nuclear reactions - leads to the formation of massive stars composed of H and He, with rather short lifetimes - ...
... - instabilities and inhomogenities cause large clouds of H and He to coalesce and come together through force of gravity - heating can occur as matter comes closer, leading to ignition of nuclear reactions - leads to the formation of massive stars composed of H and He, with rather short lifetimes - ...
An Estimate of the Age Distribution of Terrestrial Planets in the
... Planets such as the Earth cannot form unless elements heavier than helium are available. These heavy elements, or “metals,” were not produced in the Big Bang. They result from fusion inside stars and have been gradually building up over the lifetime of the Universe. Recent observations indicate that ...
... Planets such as the Earth cannot form unless elements heavier than helium are available. These heavy elements, or “metals,” were not produced in the Big Bang. They result from fusion inside stars and have been gradually building up over the lifetime of the Universe. Recent observations indicate that ...
Section 7 The Big Bang Theory
... Today, CMB radiation is very cold, only 2.725 K above absolute zero and this cooling of the photon means its frequency has reduced until the radiation shines primarily in the microwave portion of the electromagnetic spectrum and is invisible to the naked eye. However, it can be detected everywhere w ...
... Today, CMB radiation is very cold, only 2.725 K above absolute zero and this cooling of the photon means its frequency has reduced until the radiation shines primarily in the microwave portion of the electromagnetic spectrum and is invisible to the naked eye. However, it can be detected everywhere w ...
Bose-Einstein Condensation in a Gas of Sodium Atoms
... The lifetime of the condensate was about 1 s. This either by three-body lifetime is probably determined recombination [21] or by the heating rate of 300 nK/s, which was observed for a thermal cloud just above T, This heating rate is much higher than the estimated 8 nK/s for the off-resonant scatteri ...
... The lifetime of the condensate was about 1 s. This either by three-body lifetime is probably determined recombination [21] or by the heating rate of 300 nK/s, which was observed for a thermal cloud just above T, This heating rate is much higher than the estimated 8 nK/s for the off-resonant scatteri ...
CH13.AST1001.F16.EDS
... Protostar to Main Sequence • A protostar contracts and heats until the core temperature is sufficient for hydrogen fusion. • Contraction ends when energy released by hydrogen fusion balances energy radiated from the surface. • It takes 30 million years for a star like the Sun (less time for more ma ...
... Protostar to Main Sequence • A protostar contracts and heats until the core temperature is sufficient for hydrogen fusion. • Contraction ends when energy released by hydrogen fusion balances energy radiated from the surface. • It takes 30 million years for a star like the Sun (less time for more ma ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... moderate luminosity, possibly C-thick sources, in a secondary, relatively low-z phase of accretion (see “downsizing” or antihierarchical behaviour) ...
... moderate luminosity, possibly C-thick sources, in a secondary, relatively low-z phase of accretion (see “downsizing” or antihierarchical behaviour) ...
PPT presentation
... Mass loss rates increase precipitously stars die very soon after reaching dlogM/dlogL = -1 observations of mass loss rates and/or location of the Mira variables tells you which stars are now dying. Mass loss rates are sensitive to a combination of R, L, and M such that low metallicity stars, small ...
... Mass loss rates increase precipitously stars die very soon after reaching dlogM/dlogL = -1 observations of mass loss rates and/or location of the Mira variables tells you which stars are now dying. Mass loss rates are sensitive to a combination of R, L, and M such that low metallicity stars, small ...
Cosmic Hide and Seek: the Search for the Missing
... universe which says all the matter that exists was, at one time, compressed into a single point. The Big Bang distributed all the matter evenly in all directions. Then the matter started to clump together, attracted by gravity, to form the stars and galaxies that we see today. The expansion generate ...
... universe which says all the matter that exists was, at one time, compressed into a single point. The Big Bang distributed all the matter evenly in all directions. Then the matter started to clump together, attracted by gravity, to form the stars and galaxies that we see today. The expansion generate ...
Ch. 16 - Astro1010
... different, These stars are all more luminous than the Sun. Two new categories appear here – the red giants and the blue giants. Clearly, the brightest stars in the sky appear bright because of their enormous luminosities, not their proximity. ...
... different, These stars are all more luminous than the Sun. Two new categories appear here – the red giants and the blue giants. Clearly, the brightest stars in the sky appear bright because of their enormous luminosities, not their proximity. ...
$doc.title
... A long Chandra HETGS observa5on of ζ Ori: an exemplary study of X-‐ray line profiles as wind mass loss diagnos5cs for OB stars ...
... A long Chandra HETGS observa5on of ζ Ori: an exemplary study of X-‐ray line profiles as wind mass loss diagnos5cs for OB stars ...
Chapter 7 in the LSST Science Book
... interpretation of local data within a larger context: the stars that make galaxies are expected to form within dark matter halos that are themselves growing through gravitational collapse and mergers. In fact, we are very fortunate to live in a hierarchical Universe where the LV galaxies contain the ...
... interpretation of local data within a larger context: the stars that make galaxies are expected to form within dark matter halos that are themselves growing through gravitational collapse and mergers. In fact, we are very fortunate to live in a hierarchical Universe where the LV galaxies contain the ...
NAS biographical memoir of Martin Schwarzschild
... to burn its nuclear fuel through a sequence of phases: main sequence (like the sun) to red giant (like our neighbor Arcturus) to degenerate dwarf (like another neighbor, Sirius B). By now there have been innumerable quantitative tests of the theory. And it works! A normal star of mass similar to tha ...
... to burn its nuclear fuel through a sequence of phases: main sequence (like the sun) to red giant (like our neighbor Arcturus) to degenerate dwarf (like another neighbor, Sirius B). By now there have been innumerable quantitative tests of the theory. And it works! A normal star of mass similar to tha ...
Discovery of an unusual bright eclipsing binary with the longest
... MASTER OT J095310.04+335352.8 was initially bright, with an unfiltered magnitude of about 10.5 mag, on the MASTER-Net archive images from 2009-12-01.007 UT in MASTER-Kislovodsk, 2010-03-10.587 UT in MASTERTunka, and 2009-11-17.775 UT in the MASTER-Amur database. In November 2011−March 2012, however, ...
... MASTER OT J095310.04+335352.8 was initially bright, with an unfiltered magnitude of about 10.5 mag, on the MASTER-Net archive images from 2009-12-01.007 UT in MASTER-Kislovodsk, 2010-03-10.587 UT in MASTERTunka, and 2009-11-17.775 UT in the MASTER-Amur database. In November 2011−March 2012, however, ...
Calculating Parallax Lab
... Even when observed with the largest telescopes, stars are still just points of light. Although we may be able to tell a lot about a star through its light, these observations do not give us a reference scale to use to measure their distances. We need to rely on a method that you are actually already ...
... Even when observed with the largest telescopes, stars are still just points of light. Although we may be able to tell a lot about a star through its light, these observations do not give us a reference scale to use to measure their distances. We need to rely on a method that you are actually already ...
Chapter 13: Star Stuff 13.1 Star Birth How do stars form? Star
... Lower Limit on a Star's Mass • Fusion will not begin in a contracting cloud if some sort of force stops contraction before the core temperature rises above 107 K. • Thermal pressure cannot stop contraction because the star is constantly losing thermal energy from its surface through radiation. • ...
... Lower Limit on a Star's Mass • Fusion will not begin in a contracting cloud if some sort of force stops contraction before the core temperature rises above 107 K. • Thermal pressure cannot stop contraction because the star is constantly losing thermal energy from its surface through radiation. • ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.