
Document
... between yearly epochs at the 5 level with the CFHT Legacy Survey optical catalog. • Rule out sources with optical hosts with the colors and morphology of a star or quasar. • Follow up galaxy hosts that do not have an hard X-ray detection with optical spectroscopy to look for signs of an AGN. • Trig ...
... between yearly epochs at the 5 level with the CFHT Legacy Survey optical catalog. • Rule out sources with optical hosts with the colors and morphology of a star or quasar. • Follow up galaxy hosts that do not have an hard X-ray detection with optical spectroscopy to look for signs of an AGN. • Trig ...
Asteroseismology and stellar rotation - IAG-Usp
... --> Core rotates faster than envelope (surface 2 km/s) Vaissala frequency ...
... --> Core rotates faster than envelope (surface 2 km/s) Vaissala frequency ...
1998 - Universitäts-Sternwarte München
... found to be metal-poor objects – as opposed to the understanding when they were first analyzed in the 1950s. Interestingly, these stars also reveal a very different kinematic behaviour in that they do not take share in the rotation of the Galactic disk, i.e. they constitute a different stellar popul ...
... found to be metal-poor objects – as opposed to the understanding when they were first analyzed in the 1950s. Interestingly, these stars also reveal a very different kinematic behaviour in that they do not take share in the rotation of the Galactic disk, i.e. they constitute a different stellar popul ...
Radiative feedback from protoplanets in self
... irradiation, τ is the optical depth estimate, given by τ = κ(T)ρs (cf. Galvagni et al. 2012). The length scale s is given by s = (M/ρ)1/3 , where M = 10MJ , and varies from a few au to tens of au for the range of densities found in the simulation. The opacity law is κ(T) = 0.01(T/10 K), as in the an ...
... irradiation, τ is the optical depth estimate, given by τ = κ(T)ρs (cf. Galvagni et al. 2012). The length scale s is given by s = (M/ρ)1/3 , where M = 10MJ , and varies from a few au to tens of au for the range of densities found in the simulation. The opacity law is κ(T) = 0.01(T/10 K), as in the an ...
Estimating the Age of Supernova Remnants - Chandra X
... most of the gas in the remnant is not from the star. As the ejected material expands outwards, it encounters and intermingles with the interstellar medium and propels it outward, building up the outer shock wave. The volume through which the remnant has expanded and the density of the interstellar m ...
... most of the gas in the remnant is not from the star. As the ejected material expands outwards, it encounters and intermingles with the interstellar medium and propels it outward, building up the outer shock wave. The volume through which the remnant has expanded and the density of the interstellar m ...
Spectral classification of O–M stars on the basis of UBV photometry
... For construction of reliable absorption curves the open cluster members should be excluded from the analyzed sample of stars because random errors of determination distances to the cluster members can exceed a linear size of the cluster by one or two orders. As a consequence E(B − V ) and (V0 − MV ) ...
... For construction of reliable absorption curves the open cluster members should be excluded from the analyzed sample of stars because random errors of determination distances to the cluster members can exceed a linear size of the cluster by one or two orders. As a consequence E(B − V ) and (V0 − MV ) ...
The effects of red supergiant mass loss on
... lower than the escape velocity from the stellar photosphere, v esc ∼ 100 km s−1 . He assessed the possibility that radiation pressure on the circumstellar ions (and atoms) could drive the wind until the local escape velocity would have dropped below the wind speed, but the values for the achieved ac ...
... lower than the escape velocity from the stellar photosphere, v esc ∼ 100 km s−1 . He assessed the possibility that radiation pressure on the circumstellar ions (and atoms) could drive the wind until the local escape velocity would have dropped below the wind speed, but the values for the achieved ac ...
The Layout of the Night Sky - Peterborough Astronomical Society
... southern horizon in these maps may not be visible because they are below the horizon. Print each of the four circular maps and take them outside with you. To read these circular star charts, here’s what to do… • Find a location that’s isolated from street and house lights. Stray light will make it h ...
... southern horizon in these maps may not be visible because they are below the horizon. Print each of the four circular maps and take them outside with you. To read these circular star charts, here’s what to do… • Find a location that’s isolated from street and house lights. Stray light will make it h ...
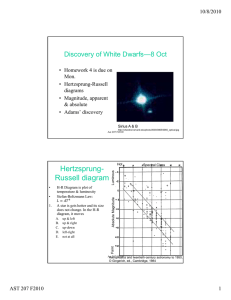
Discovery of White Dwarfs—8 Oct
... Main-sequence or dwarf stars Giants Horizontal-branch stars White dwarfs are too faint for these observations. A star lives a long time as a dwarf. It is on the main sequence. When it runs out of fuel, it becomes a giant and subsequently “traces out the giant branch.” ...
... Main-sequence or dwarf stars Giants Horizontal-branch stars White dwarfs are too faint for these observations. A star lives a long time as a dwarf. It is on the main sequence. When it runs out of fuel, it becomes a giant and subsequently “traces out the giant branch.” ...
Chapter 5 - Leiden Observatory
... Nelemans et al., 2001c] for fast stellar and binary evolution computations. Stars are evolved from the zero-age main sequence (ZAMS) until remnant formation and beyond. Stars are parametrised by mass, radius, luminosity, core mass, etc. as functions of time and initial mass. Mass loss from winds, wh ...
... Nelemans et al., 2001c] for fast stellar and binary evolution computations. Stars are evolved from the zero-age main sequence (ZAMS) until remnant formation and beyond. Stars are parametrised by mass, radius, luminosity, core mass, etc. as functions of time and initial mass. Mass loss from winds, wh ...
Chapter 12
... by which the star shifts is extremely small. It was not until the 1830s that the first parallax was measured by the German astronomer Friedrich Bessel at Königsberg Observatory (now in Kaliningrad). Even now, the method fails for most stars farther away than about 100 parsecs because the Earth’s atm ...
... by which the star shifts is extremely small. It was not until the 1830s that the first parallax was measured by the German astronomer Friedrich Bessel at Königsberg Observatory (now in Kaliningrad). Even now, the method fails for most stars farther away than about 100 parsecs because the Earth’s atm ...
Infrared colours, distance determination and absolute magnitudes of
... quincunx (to facilitate sky subtraction - see Section 2.1). The individual images were made up of 200-s (100 s x 2 coadds) and 180-s (30 s x 6 coadds) exposures in J and K respectively. Dark frames were obtained at regular intervals throughout the night. Since the dark current is non-linear with exp ...
... quincunx (to facilitate sky subtraction - see Section 2.1). The individual images were made up of 200-s (100 s x 2 coadds) and 180-s (30 s x 6 coadds) exposures in J and K respectively. Dark frames were obtained at regular intervals throughout the night. Since the dark current is non-linear with exp ...
arXiv:1604.01613v2 [astro-ph.SR] 23 Aug 2016
... In order to identify main-sequence FGK stars with UVexcesses in the southern hemisphere sky, we used data from the RAVE survey2 data release 4 (Kordopatis et al. 2013). RAVE is a magnitude limited survey of randomly selected southern hemisphere stars spanning 9< I <12. It has collected spectra for o ...
... In order to identify main-sequence FGK stars with UVexcesses in the southern hemisphere sky, we used data from the RAVE survey2 data release 4 (Kordopatis et al. 2013). RAVE is a magnitude limited survey of randomly selected southern hemisphere stars spanning 9< I <12. It has collected spectra for o ...
A Budget and Accounting of Metals at z~ 0: Results from the COS
... for high-ionization gas and in Werk et al. (2013) for lowionization gas. Tumlinson et al. (2011) reported that the mass of oxygen traced by the highly ionized O VI in the CGM of star-forming galaxies is comparable to the mass of oxygen in their ISM. COS-Halos has specifically addressed the metal con ...
... for high-ionization gas and in Werk et al. (2013) for lowionization gas. Tumlinson et al. (2011) reported that the mass of oxygen traced by the highly ionized O VI in the CGM of star-forming galaxies is comparable to the mass of oxygen in their ISM. COS-Halos has specifically addressed the metal con ...
22. Dark Matter and the Fate of the Universe
... front of a star where they… • gravitationally lens the star’s light • the star gets much brighter for a few days to weeks • we can measure the MACHO’s mass ...
... front of a star where they… • gravitationally lens the star’s light • the star gets much brighter for a few days to weeks • we can measure the MACHO’s mass ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.

















![arXiv:1604.01613v2 [astro-ph.SR] 23 Aug 2016](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015708841_1-69411a0a7e7ee9a8690efbc066a22153-300x300.png)


