슬라이드 1
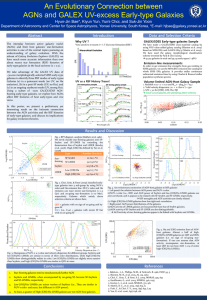
... Fig. 4. An evolutionary connection of AGN-host galaxies to RSF galaxies • Left panel: the relation between AGN power and NUV-r color. (1)NUV-r color (i.e., RSF) and AGN power of Seyfert and low-[OII]/Hα LINER galaxies are anti-correlated, and it appears to be related with SF-Seyfert and SF-LINER, re ...
... Fig. 4. An evolutionary connection of AGN-host galaxies to RSF galaxies • Left panel: the relation between AGN power and NUV-r color. (1)NUV-r color (i.e., RSF) and AGN power of Seyfert and low-[OII]/Hα LINER galaxies are anti-correlated, and it appears to be related with SF-Seyfert and SF-LINER, re ...
Str\" omgren uvby photometry of the peculiar globular cluster NGC
... [Mg/Fe]∼-1 dex) and enhanced in K ([K/Fe] ∼ +1.5 dex). These two populations produce a pronounced Mg-K anti-correlation in NGC 2419. In this respect NGC 2419 appears unique among Galactic GCs (Carretta et al. 2013), even though Mucciarelli et al. (2015) recently found a similar, but less extreme pop ...
... [Mg/Fe]∼-1 dex) and enhanced in K ([K/Fe] ∼ +1.5 dex). These two populations produce a pronounced Mg-K anti-correlation in NGC 2419. In this respect NGC 2419 appears unique among Galactic GCs (Carretta et al. 2013), even though Mucciarelli et al. (2015) recently found a similar, but less extreme pop ...
ExoOrg_NAI
... Executive Summary Planetary Systems form by collapse of dense interstellar cloud cores (Frontispiece). Some stages in this evolution can be directly observed when stellar nurseries are imaged (Figure ES.1), while other stages remain cloaked behind an impenetrable veil of dust and gas. Yet to underst ...
... Executive Summary Planetary Systems form by collapse of dense interstellar cloud cores (Frontispiece). Some stages in this evolution can be directly observed when stellar nurseries are imaged (Figure ES.1), while other stages remain cloaked behind an impenetrable veil of dust and gas. Yet to underst ...
GRB prompt emission
... Hosts! • Hosts of long GRBs are star-forming galaxies • GRBs trace the stellar distribution (in distance from galaxy center) • GRBs occur in dense environments (star forming regions?) ...
... Hosts! • Hosts of long GRBs are star-forming galaxies • GRBs trace the stellar distribution (in distance from galaxy center) • GRBs occur in dense environments (star forming regions?) ...
Planetary detection limits taking into account stellar noise
... In this paper, we study different observational strategies to average out as much as possible the effect of stellar noise on RV measurements. The main goal is to find a strategy capable of detecting very small mass planets in habitable regions. To be able to search for such long-period planets, observ ...
... In this paper, we study different observational strategies to average out as much as possible the effect of stellar noise on RV measurements. The main goal is to find a strategy capable of detecting very small mass planets in habitable regions. To be able to search for such long-period planets, observ ...
SN 2011dh and the progenitors of Type IIb supernovae Mattias Ergon
... Core-collapse supernovae (SNe) are the observed events following the collapse of the core of evolved massive stars. The gravitational energy released creates a powerful shock that disrupts the star and ejects the heated material into the surrounding circumstellar medium. The observed properties depe ...
... Core-collapse supernovae (SNe) are the observed events following the collapse of the core of evolved massive stars. The gravitational energy released creates a powerful shock that disrupts the star and ejects the heated material into the surrounding circumstellar medium. The observed properties depe ...
SKA and VLBI synergies
... be also observed in the halos of large galaxies and in the arms of spiral galaxies, where they manifest themselves as ultraluminous X-ray sources [7]. Stellar-mass black holes accreting at Eddington or super-Eddington rates could explain the X-ray emission of ultraluminous X-ray sources up to LX = 5 ...
... be also observed in the halos of large galaxies and in the arms of spiral galaxies, where they manifest themselves as ultraluminous X-ray sources [7]. Stellar-mass black holes accreting at Eddington or super-Eddington rates could explain the X-ray emission of ultraluminous X-ray sources up to LX = 5 ...
On the interpretation of stellar disc observations in terms of diameters
... this layer contribute only a small fraction of the observed intensity and observed flux. If the star were observed in different spectral features with successively increasing strength at about the same wavelength, an observer who cannot spatially resolve the disc and tries to interpret lunar-occulta ...
... this layer contribute only a small fraction of the observed intensity and observed flux. If the star were observed in different spectral features with successively increasing strength at about the same wavelength, an observer who cannot spatially resolve the disc and tries to interpret lunar-occulta ...
Kinematic signature of an intermediate
... Meylan 1993), and assuming a black-hole mass correlation with velocity dispersion, make NGC 6388 a good candidate for detecting an intermediate-mass black hole. Besides the kinematic properties, the photometric characteristics are also quite interesting. Noyola & Gebhardt (2006, hereafter NG06) foun ...
... Meylan 1993), and assuming a black-hole mass correlation with velocity dispersion, make NGC 6388 a good candidate for detecting an intermediate-mass black hole. Besides the kinematic properties, the photometric characteristics are also quite interesting. Noyola & Gebhardt (2006, hereafter NG06) foun ...
JUL 12 ARCHNES LIBRARIES
... weren't. They lay far beyond the reaches of the Milky Way, blazing from the distant past, when the universe was only a few billion years old. But while these sources were far enough away to look like pinpricks on the sky, their light was very different from starlight: it came not from a single orb b ...
... weren't. They lay far beyond the reaches of the Milky Way, blazing from the distant past, when the universe was only a few billion years old. But while these sources were far enough away to look like pinpricks on the sky, their light was very different from starlight: it came not from a single orb b ...
astro-ph/9808039 PDF
... to make the FUV fluxes too high by a factor of ∼ 2. The corrected rocket calibration is consistent with that for an earlier flight using the same detector (Smith et al. 1992). Many of the arguments of Paper I relied on the Hα/FUV flux ratio. Coincidentally, the FUV calibration error was nearly cance ...
... to make the FUV fluxes too high by a factor of ∼ 2. The corrected rocket calibration is consistent with that for an earlier flight using the same detector (Smith et al. 1992). Many of the arguments of Paper I relied on the Hα/FUV flux ratio. Coincidentally, the FUV calibration error was nearly cance ...
The extended structure of the dwarf irregular galaxies Sextans A and
... dwarfs may represent the test case of evolution without interactions and can provide constraints on the initial conditions at the epoch of formation. These considerations were the driving case for a large Hubble Space Telescope (HST) programme (Gallart 2008) that performs extremely deep observation ...
... dwarfs may represent the test case of evolution without interactions and can provide constraints on the initial conditions at the epoch of formation. These considerations were the driving case for a large Hubble Space Telescope (HST) programme (Gallart 2008) that performs extremely deep observation ...
Astronomy Astrophysics - Niels Bohr Institutet
... effort has been devoted to the fundamental issue of determining reliable isochrone ages for as many stars as possible, and we believe that a rather more realistic assessment of the errors of such ages has been obtained. Finally, we have computed individual Galactic orbits for all stars with adequate ...
... effort has been devoted to the fundamental issue of determining reliable isochrone ages for as many stars as possible, and we believe that a rather more realistic assessment of the errors of such ages has been obtained. Finally, we have computed individual Galactic orbits for all stars with adequate ...
Dynamics of galaxies and clusters in refracted gravity
... 4.1 Application to a model disk galaxy 4.2 Rotation curves of NGC1560 and NGC6946 4.3 Intracluster gas temperature of A1991 and A1795 ...
... 4.1 Application to a model disk galaxy 4.2 Rotation curves of NGC1560 and NGC6946 4.3 Intracluster gas temperature of A1991 and A1795 ...
EXCITATION OF RADIAL P-MODES IN THE SUN AND STARS ROBERT STEIN
... compressibility. Excitation decreases at high frequencies because convection lacks high frequency motions. Finally, we apply our formula to the excitation of stellar p-mode oscillations using simulations of nine stars near the main sequence and a cool sub-giant (Section 6). We find that the total ex ...
... compressibility. Excitation decreases at high frequencies because convection lacks high frequency motions. Finally, we apply our formula to the excitation of stellar p-mode oscillations using simulations of nine stars near the main sequence and a cool sub-giant (Section 6). We find that the total ex ...
The occurrence of nitrogen-enhanced metal
... of NEMP stars. We therefore performed a literature search to obtain a more complete overview of the situation. Characterising a star as NEMP requires measurements of both the C and N abundances, which are only available for a limited number of halo stars. In Fig. 1 we show the distribution of [N/Fe] ...
... of NEMP stars. We therefore performed a literature search to obtain a more complete overview of the situation. Characterising a star as NEMP requires measurements of both the C and N abundances, which are only available for a limited number of halo stars. In Fig. 1 we show the distribution of [N/Fe] ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.