Charting The Universe - University of Windsor
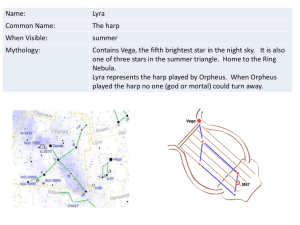
... • Ancient Calendars: for religious festivals and agriculture. (Geocentric model) • There are 88 constellations. (Most are seen in Windsor at some part of the year.) • Still useful for depicting regions of the sky. • Note: the stars are not close to each other…they just appear to be! ...
... • Ancient Calendars: for religious festivals and agriculture. (Geocentric model) • There are 88 constellations. (Most are seen in Windsor at some part of the year.) • Still useful for depicting regions of the sky. • Note: the stars are not close to each other…they just appear to be! ...
Carolina Kehrig
... (Crowther & Hadfield 2006), ≥ 100 WRs is required to explain the Q(HeII)obs , but such very large WR population is not compatible with: (> 8 times) Total stellar mass of the NW cluster WR/O stars ratio at the metallicity of IZw18 (e.g. Maeder & Meynet 2012) Stellar evolutionary models for single mas ...
... (Crowther & Hadfield 2006), ≥ 100 WRs is required to explain the Q(HeII)obs , but such very large WR population is not compatible with: (> 8 times) Total stellar mass of the NW cluster WR/O stars ratio at the metallicity of IZw18 (e.g. Maeder & Meynet 2012) Stellar evolutionary models for single mas ...
Lecture 16: Iron Core Collapse, Neutron Stars, and Nucleosynthesis
... made during the explosion. Some of these, like 56Ni, are radioactive and will play a role in powering the light curve ...
... made during the explosion. Some of these, like 56Ni, are radioactive and will play a role in powering the light curve ...
Supplemental Resources - Morehead Planetarium and Science
... 7c. Identify at least one red star, one blue star, and one yellow star (other than the Sun). Explain the meaning of these colors. Look up into the sky and you’ll see the stars twinkling in different colors. Some are dull and red, while others are white and others look bright blue. So how do you get ...
... 7c. Identify at least one red star, one blue star, and one yellow star (other than the Sun). Explain the meaning of these colors. Look up into the sky and you’ll see the stars twinkling in different colors. Some are dull and red, while others are white and others look bright blue. So how do you get ...
The End of the Dark Ages
... Shull & Ferrara (2000) have estimated the fraction of ionizing photons emitted by OB associations that escapes the H I disk of a disk galaxy into the halo and intergalactic medium (IGM) by solving the timedependent radiation transfer problem of stellar radiation through evolving superbubbles within ...
... Shull & Ferrara (2000) have estimated the fraction of ionizing photons emitted by OB associations that escapes the H I disk of a disk galaxy into the halo and intergalactic medium (IGM) by solving the timedependent radiation transfer problem of stellar radiation through evolving superbubbles within ...
1. Base your answer to the following question
... Base your answers to questions 47 through 50 on the graph below, which shows two conditions responsible for the formation and composition of some planets in our solar system. The distances of Earth and Neptune from the Sun, in astronomical units (AU), are shown beneath the horizontal axis. (1 AU = 1 ...
... Base your answers to questions 47 through 50 on the graph below, which shows two conditions responsible for the formation and composition of some planets in our solar system. The distances of Earth and Neptune from the Sun, in astronomical units (AU), are shown beneath the horizontal axis. (1 AU = 1 ...
The North Star
... is used as a navigational star. The North Star is was mostly used for slaves back in the 1650s. We should care about the north star because it points the way to the north pole. ...
... is used as a navigational star. The North Star is was mostly used for slaves back in the 1650s. We should care about the north star because it points the way to the north pole. ...
Friday, January 27, 2017 First exam a week from today. Review
... structure with 100 times the area of the Earth was orbiting the star. Some suggested an alien structure. Bunk (no heat signal), but still not well explained with serious science. ...
... structure with 100 times the area of the Earth was orbiting the star. Some suggested an alien structure. Bunk (no heat signal), but still not well explained with serious science. ...
Chapter 17 Star Stuff
... • Protostar looks starlike after the surrounding gas is blown away, but its thermal energy comes from gravitational contraction, not fusion • Contraction must continue until the core becomes hot enough for nuclear fusion • Contraction stops when the energy released by core fusion balances energy rad ...
... • Protostar looks starlike after the surrounding gas is blown away, but its thermal energy comes from gravitational contraction, not fusion • Contraction must continue until the core becomes hot enough for nuclear fusion • Contraction stops when the energy released by core fusion balances energy rad ...
The 100-billion-body problem A full-scale computer simulation of the
... The stars left behind give up some of their kinetic energy in this transaction, but the cluster as a whole also loses mass, so that the stars are less tightly bound together. The ultimate fate of the cluster may be the very opposite of condensation: evaporation, as all of the stars disperse. The Mil ...
... The stars left behind give up some of their kinetic energy in this transaction, but the cluster as a whole also loses mass, so that the stars are less tightly bound together. The ultimate fate of the cluster may be the very opposite of condensation: evaporation, as all of the stars disperse. The Mil ...
the chromospheres of classical cepheids. 111. a search for transition
... extent which ranges from several tenths of a stellar radius to several stellar radii in various stars. This is much larger than the solar chromosphere, but not as extended as the chromospheres of late-type giants. In Paper I we presented the strengths of lines in the farultraviolet region. The inten ...
... extent which ranges from several tenths of a stellar radius to several stellar radii in various stars. This is much larger than the solar chromosphere, but not as extended as the chromospheres of late-type giants. In Paper I we presented the strengths of lines in the farultraviolet region. The inten ...
Dark Matter in the Universe
... a star or nearby a star; brightening of the star candidates for MACHOS black holes neutron stars black dwarfs ...
... a star or nearby a star; brightening of the star candidates for MACHOS black holes neutron stars black dwarfs ...
A Chandra Observation of the Massive Star-Forming
... from an evaporating gaseous globule (EGG) for the first time A significant population of X-ray emitting low mass stars (~700) detected, increasing the cluster known members by a factor of 40 ...
... from an evaporating gaseous globule (EGG) for the first time A significant population of X-ray emitting low mass stars (~700) detected, increasing the cluster known members by a factor of 40 ...
A-105 Homework 1
... 14. (2 pts.) Everything that has mass has a Schwarzschild radius. If that mass is somehow compressed inside a volume of that radius, it’ll become a black hole. What is the Schwarzschild radius of Jupiter (mass 2 10 27 kg)? What is your Schwarzschild radius (1 lb = 0.454 kg)? (You may use 75 kg a ...
... 14. (2 pts.) Everything that has mass has a Schwarzschild radius. If that mass is somehow compressed inside a volume of that radius, it’ll become a black hole. What is the Schwarzschild radius of Jupiter (mass 2 10 27 kg)? What is your Schwarzschild radius (1 lb = 0.454 kg)? (You may use 75 kg a ...
HR Diagram
... 4. How many of the stars in table 10.1 are hotter than the Sun (spectral classes O,B,A,F)? If double star both must be considered. # = __________ How many of the stars in table 10.2 are hotter than the Sun (spectral classes O,B,A,F)? If double star both must be considered. # = __________ ...
... 4. How many of the stars in table 10.1 are hotter than the Sun (spectral classes O,B,A,F)? If double star both must be considered. # = __________ How many of the stars in table 10.2 are hotter than the Sun (spectral classes O,B,A,F)? If double star both must be considered. # = __________ ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.