Lecture 24 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... How bright (L in watts)? Luminosity at the source is determined from apparent brightness and distance (d). Apparent magnitude (old way). We can see about 1,000 stars in Northern Hemisphere with naked eye. Hipparchus rated them from 1 to 6. A '1' is 2.52 x brighter than a '2', etc. Range in brightnes ...
... How bright (L in watts)? Luminosity at the source is determined from apparent brightness and distance (d). Apparent magnitude (old way). We can see about 1,000 stars in Northern Hemisphere with naked eye. Hipparchus rated them from 1 to 6. A '1' is 2.52 x brighter than a '2', etc. Range in brightnes ...
ON STARS, THEIR EVOLUTION AND THEIR STABILITY
... I do not see how a star which has once got into this compressed state is ever going to get out of it... It would seem that the star will be in an awkward predicament when its supply of subatomic energy fails. The paradox posed by Eddington was reformulated in clearer physical terms by R. H. Fowler. ...
... I do not see how a star which has once got into this compressed state is ever going to get out of it... It would seem that the star will be in an awkward predicament when its supply of subatomic energy fails. The paradox posed by Eddington was reformulated in clearer physical terms by R. H. Fowler. ...
Watch - ggg999.org
... By using information from all of the modes, we can model the inside of the Sun! Good news! There are more than a million modes Bad news! There are more than a million modes ...
... By using information from all of the modes, we can model the inside of the Sun! Good news! There are more than a million modes Bad news! There are more than a million modes ...
What is your wager?
... Did you know? The moon is responsible for the changing sea levels that occurs regularly around the world - often referred to as the tides. ...
... Did you know? The moon is responsible for the changing sea levels that occurs regularly around the world - often referred to as the tides. ...
Neutrino Masses, Dark Matter and the Mysterious Early Quasars
... form Gyr to the observed times of te ~ 0.85 Gyr after zreion ~ 11 or treion ~ 0.365 Gyr ...
... form Gyr to the observed times of te ~ 0.85 Gyr after zreion ~ 11 or treion ~ 0.365 Gyr ...
The Curtis-Shapley debate – two different views of
... with a diameter of 17 kiloparsecs with the Sun apparently close to its centre. Shapley’s view of the Universe He believed that out galaxy was the whole universe, that it had a diameter 300 000 light years (100 kiloparsecs) and that the Sun was about 20 kiloparsecs from its centre. He argued that the ...
... with a diameter of 17 kiloparsecs with the Sun apparently close to its centre. Shapley’s view of the Universe He believed that out galaxy was the whole universe, that it had a diameter 300 000 light years (100 kiloparsecs) and that the Sun was about 20 kiloparsecs from its centre. He argued that the ...
Stellar Remnants - Sierra College Astronomy Home Page
... Earth’s), and a teaspoon of white dwarf material would weigh 2 tons. ...
... Earth’s), and a teaspoon of white dwarf material would weigh 2 tons. ...
Outer Space 2 - World of Teaching
... Stellar formation in Papillon Nebula in Large Magellanic Cloud ...
... Stellar formation in Papillon Nebula in Large Magellanic Cloud ...
ph507lecnote07
... This energy can provide the fuel which allows the endothermic fusion reactions to create very high mass elements such as Uranium. The supernovae are responsible for all the elements with masses larger than iron found on Earth. ...
... This energy can provide the fuel which allows the endothermic fusion reactions to create very high mass elements such as Uranium. The supernovae are responsible for all the elements with masses larger than iron found on Earth. ...
Structure of Neutron Stars
... Kv – observed semi-amplitude of line of sight velocity of the normal star (in km/s), P – orbital period (in days), e – orbital eccentricity, i – orbital inclination (the angle between the prbital plane and line of sight). ...
... Kv – observed semi-amplitude of line of sight velocity of the normal star (in km/s), P – orbital period (in days), e – orbital eccentricity, i – orbital inclination (the angle between the prbital plane and line of sight). ...
Astronomy Exam #4
... 26. An O star is known to be eight times the temperature of the Sun and fivr times its radius. What is its luminosity? You may answer either in Watts or in units of solar luminosity. Note: the radius of the Sun is 696,000 km and the temperature of the Sun is 5,800 K. ...
... 26. An O star is known to be eight times the temperature of the Sun and fivr times its radius. What is its luminosity? You may answer either in Watts or in units of solar luminosity. Note: the radius of the Sun is 696,000 km and the temperature of the Sun is 5,800 K. ...
Globular Clusters Dynamic Lives The
... are not physically colliding in this celestial pinball game, just deflecting each other gravitationally. This energy exchange eventually leads to thermal equilibrium. In a typical cluster this takes about a hundred million years, during which an individual star may cross the cluster a hundred times. ...
... are not physically colliding in this celestial pinball game, just deflecting each other gravitationally. This energy exchange eventually leads to thermal equilibrium. In a typical cluster this takes about a hundred million years, during which an individual star may cross the cluster a hundred times. ...
Stellar Atmospheres
... spectrum of the light generated here is dominated by Hwavelength. Temperature of Chromosphere is up to 20,000K. Transition Region: In the Sun, a region between the Chromosphere and Corona. Corona: In the Sun, a type of plasma atmosphere that extends millions of kilometers into space. High temperat ...
... spectrum of the light generated here is dominated by Hwavelength. Temperature of Chromosphere is up to 20,000K. Transition Region: In the Sun, a region between the Chromosphere and Corona. Corona: In the Sun, a type of plasma atmosphere that extends millions of kilometers into space. High temperat ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 16 Notes: Post
... After a short period the luminosity stabilizes, and since Lnuc < L, the star responds by having its envelope contract. That contraction leaves the luminosity unchanged, but moves the star to higher effective temperature. The motion is roughly horizontal in the HR diagram, so this is known as the hor ...
... After a short period the luminosity stabilizes, and since Lnuc < L, the star responds by having its envelope contract. That contraction leaves the luminosity unchanged, but moves the star to higher effective temperature. The motion is roughly horizontal in the HR diagram, so this is known as the hor ...
Part II: Ideas in Conflict.
... Trapping of Light by a Black Hole • (a) The paths and color of light rays departing from a main-sequence, giant, or supergiant star are affected very little by the star’s gravitational ...
... Trapping of Light by a Black Hole • (a) The paths and color of light rays departing from a main-sequence, giant, or supergiant star are affected very little by the star’s gravitational ...
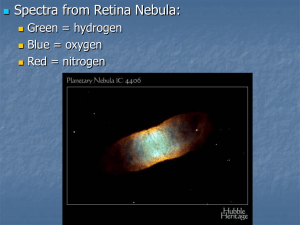
Spectra
... of an object’s motion toward or away from us The amount of blue or red shift tells us an object’s speed toward or away from us: ...
... of an object’s motion toward or away from us The amount of blue or red shift tells us an object’s speed toward or away from us: ...
File
... containing some 200 billion stars (though composed primarily of dark matter), and is approximately 13 billion years old (based on the age of the oldest stars). The Sun is located near the outer edge, and is orbiting the galactic core at 220 km per second. Milky Way in the Night Sky ...
... containing some 200 billion stars (though composed primarily of dark matter), and is approximately 13 billion years old (based on the age of the oldest stars). The Sun is located near the outer edge, and is orbiting the galactic core at 220 km per second. Milky Way in the Night Sky ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.